Chapter 8 Summary
... Cells rely on the energy contained in the chemical bonds of ATP. Some ATP is generated by substrate phosphorylation, a process that adds a phosphate group (P i) directly to ADP. However, most ATP is synthesized by oxidative phosphorylation, which involves a series of chemical reactions that make up ...
... Cells rely on the energy contained in the chemical bonds of ATP. Some ATP is generated by substrate phosphorylation, a process that adds a phosphate group (P i) directly to ADP. However, most ATP is synthesized by oxidative phosphorylation, which involves a series of chemical reactions that make up ...
Biochemistry Test Review KEY
... 14. What effect does pH levels have on a certain enzyme? Slows or speeds up rate of reaction, as well as the modifies the enzyme’s shape 15. Describe the active site of an enzyme. It is a small port in an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction 16. Enzymes are what type ...
... 14. What effect does pH levels have on a certain enzyme? Slows or speeds up rate of reaction, as well as the modifies the enzyme’s shape 15. Describe the active site of an enzyme. It is a small port in an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction 16. Enzymes are what type ...
Cellular Respiration Scenarios – Teacher Answers
... would die. If this were a muscle cell, they could revert to anaerobic respiration for a short time to recycle their NAD+ and make ATP via glycolysis. Gradually, the muscle will stiffen and it will succumb too. 2) You are the designer of what you believe is the “wonder” weight loss drug. The drug mak ...
... would die. If this were a muscle cell, they could revert to anaerobic respiration for a short time to recycle their NAD+ and make ATP via glycolysis. Gradually, the muscle will stiffen and it will succumb too. 2) You are the designer of what you believe is the “wonder” weight loss drug. The drug mak ...
BIOL 1322 - Victoria College
... What are the benefits and risks of taking protein and amino acid supplements? ...
... What are the benefits and risks of taking protein and amino acid supplements? ...
Food and Feeding
... butter, oils, nuts, milk and general fatty foods. Contain the elements Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen but not in any given ratio unlike Carbohydrates. A unit of fat (called a triglyceride) is made up of one molecule of Glycerol with three fatty acids chemically attached. ...
... butter, oils, nuts, milk and general fatty foods. Contain the elements Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen but not in any given ratio unlike Carbohydrates. A unit of fat (called a triglyceride) is made up of one molecule of Glycerol with three fatty acids chemically attached. ...
File
... Lipids are a diverse group of macromolecules with one property in common: they do not dissolve in water (nonpolar). ...
... Lipids are a diverse group of macromolecules with one property in common: they do not dissolve in water (nonpolar). ...
optional activity key File
... Saturated fats are saturated with respect to hydrogen. They tend to exist as solids at room temperature because they can pack more densely Unsaturated fats are not saturated with respect to hydrogen because they contain a double bond between carbons. They tend to exist as liquids at room temperature ...
... Saturated fats are saturated with respect to hydrogen. They tend to exist as solids at room temperature because they can pack more densely Unsaturated fats are not saturated with respect to hydrogen because they contain a double bond between carbons. They tend to exist as liquids at room temperature ...
Cell Metabolism - Florida International University
... one form to another but is never created or destroyed. All body activities depend on the availability of chemical energy. Most of the chemical energy in the cell is provided by Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) 1) Oxidation Process of combining oxygen with another chemical to release energy by remo ...
... one form to another but is never created or destroyed. All body activities depend on the availability of chemical energy. Most of the chemical energy in the cell is provided by Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) 1) Oxidation Process of combining oxygen with another chemical to release energy by remo ...
Catabolic Pathways and Glycolysis
... Catabolic Pathways and Glycolysis • The ability to do that work depends on catabolic process that harvest the potential energy found in organic molecules. The 2 catabolic processes that occur in organisms are fermentation (breakdown without O2)and cellular respiration (breakdown with O2). ...
... Catabolic Pathways and Glycolysis • The ability to do that work depends on catabolic process that harvest the potential energy found in organic molecules. The 2 catabolic processes that occur in organisms are fermentation (breakdown without O2)and cellular respiration (breakdown with O2). ...
Project 2 - University of South Florida
... •The simulations were carried out for the three substrates, glucose,lactate and palmitic acid. The complete utilzation of 1 mol of glucose results in the formation of 38 ATP with the concomitant utilization of 6 mol of oxygen. The utilization of 1 mol of lactate forms 17.5 ATP with the utilization ...
... •The simulations were carried out for the three substrates, glucose,lactate and palmitic acid. The complete utilzation of 1 mol of glucose results in the formation of 38 ATP with the concomitant utilization of 6 mol of oxygen. The utilization of 1 mol of lactate forms 17.5 ATP with the utilization ...
AP Chemistry Test Review
... 46) know the signs for ∆S, ∆G, and ∆H and when each of the values are zero 47) spontaneous reactions have −∆G or + E°cell 48) ∆G° = zero for pure elements in their standard state 49) LEO- ANO; CPR-GER…how to balance redox reactions and find ox. agents or red. agents 50) calculate E°cell and be able ...
... 46) know the signs for ∆S, ∆G, and ∆H and when each of the values are zero 47) spontaneous reactions have −∆G or + E°cell 48) ∆G° = zero for pure elements in their standard state 49) LEO- ANO; CPR-GER…how to balance redox reactions and find ox. agents or red. agents 50) calculate E°cell and be able ...
role of respiration in glycolysis, co2 and h20 production
... from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the oxidation of one molecule and the reduction of another. ...
... from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the oxidation of one molecule and the reduction of another. ...
Overview of Inherited Metabolic Disorders
... appropriate body tissues in sufficient but non-toxic amounts maintain appropriate biosynthetic mechanisms to convert dietary nutrients into required metabolites maintain metabolic homeostatic mechanisms to ensure that critical nutrients are available as necessary ensure optimum levels of nutri ...
... appropriate body tissues in sufficient but non-toxic amounts maintain appropriate biosynthetic mechanisms to convert dietary nutrients into required metabolites maintain metabolic homeostatic mechanisms to ensure that critical nutrients are available as necessary ensure optimum levels of nutri ...
photosynthesis and cellular resp jeopardy 9th bio
... forming this and releasing coenzyme A in the first step of the Krebs Cycle. C 400 ...
... forming this and releasing coenzyme A in the first step of the Krebs Cycle. C 400 ...
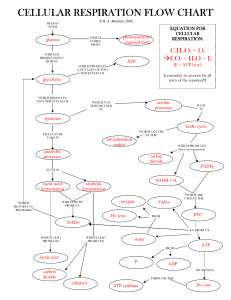
cellular respiration flow chart cellular respiration flow
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION FLOW CHART © R. A. Mathiak 2009 ...
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION FLOW CHART © R. A. Mathiak 2009 ...
C483 Study Guide for Exam 2 Fall 2015 Basic Information Exam 3
... o Cofactors needed for transformation o Arrow mechanisms if mechanism is given in notes Pentose phosphate pathway: know stages, purposes, 4 modes, which type of enzyme needed for a given transformation, transketalase mechanism Electron transport chain/oxidative phosphorylation o Order of main comple ...
... o Cofactors needed for transformation o Arrow mechanisms if mechanism is given in notes Pentose phosphate pathway: know stages, purposes, 4 modes, which type of enzyme needed for a given transformation, transketalase mechanism Electron transport chain/oxidative phosphorylation o Order of main comple ...
Organic Compounds Overview - Kenwood Academy High School
... • Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H) and Oxygen (O) in a 1:2:1 ratio • Standard chemical formula (for monosaccharides): CxH2xOx • Ex) Glucose=C6H12O6 ...
... • Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H) and Oxygen (O) in a 1:2:1 ratio • Standard chemical formula (for monosaccharides): CxH2xOx • Ex) Glucose=C6H12O6 ...
Topic 3 – The Chemistry of Life
... new strands formed on each of the two single strands nucleotides added to form new strands complementary base pairing A to T and G to C DNA polymerase forms the new complementary strands replication is semi-conservative each of the DNA molecules formed has one old and one new strand ...
... new strands formed on each of the two single strands nucleotides added to form new strands complementary base pairing A to T and G to C DNA polymerase forms the new complementary strands replication is semi-conservative each of the DNA molecules formed has one old and one new strand ...
Sport`s Nutrition Slides
... minutes, glucose is broken down anaerobically through glycolysis. You can produce energy very fast this way, but not for long. Glucose is broken down to pyruvate, so when not enough oxygen is available, lactic acid forms. Lactic acid changes the pH in the muscle, which results in the burning sensati ...
... minutes, glucose is broken down anaerobically through glycolysis. You can produce energy very fast this way, but not for long. Glucose is broken down to pyruvate, so when not enough oxygen is available, lactic acid forms. Lactic acid changes the pH in the muscle, which results in the burning sensati ...
Macromoleucles Notes
... A three carbon alcohol o 3 ____________ _____________ Long hydrocarbon chains Non polar o The combining of these two molecules makes a __________________________. Made up of: ___________________. Monomer (basic unit): ______________ ___________ Polymer (chain of units): _____________ o S ...
... A three carbon alcohol o 3 ____________ _____________ Long hydrocarbon chains Non polar o The combining of these two molecules makes a __________________________. Made up of: ___________________. Monomer (basic unit): ______________ ___________ Polymer (chain of units): _____________ o S ...
View as PDF - Helen Money Nutrition
... When the body undergoes increased synthesis basal metabolic rate increases; energy is used in mending the injury. Very low calorie diets aimed at weight loss during this period are not advised as this will slow the recovery process. The nutritional value of diet is also important, each of the macron ...
... When the body undergoes increased synthesis basal metabolic rate increases; energy is used in mending the injury. Very low calorie diets aimed at weight loss during this period are not advised as this will slow the recovery process. The nutritional value of diet is also important, each of the macron ...
Fermentation and Biosynthetic Pathways File
... intermediates produced during glycolysis, Krebs cycle and from lipids or amino acids. Bacteria may assemble it into the more complex polysaccharides. Biosynthesis of Lipids Lipids vary in chemical composition, cells synthesize fats by joining glycerol and fatty acids. The glycerol portion of the fat ...
... intermediates produced during glycolysis, Krebs cycle and from lipids or amino acids. Bacteria may assemble it into the more complex polysaccharides. Biosynthesis of Lipids Lipids vary in chemical composition, cells synthesize fats by joining glycerol and fatty acids. The glycerol portion of the fat ...
Do Now - Montville.net
... down into different elements. ii. Elements: pure substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by physical or chemical means. ...
... down into different elements. ii. Elements: pure substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by physical or chemical means. ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.