* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macromoleucles Notes
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
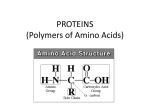
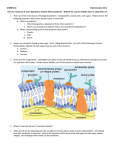
Comp. 2 – Macromolecules Organic compounds ____________________ _____________________ - usually bonded to oxygen, hydrogen, and other carbon atoms. Most of the matter in your body is _______________!! These are compounds that usually come from organisms Macromolecules Cells and their organelles are made up of smaller building blocks called ______________________________. There are 4 basic types of macromolecules. They are: o ________________ o ____________________ o __________________________ o ________________ ______________ Monomers and polymers o Macromolecules are actually made up of even smaller subunits. Each subunit of a macromolecule is called a ________________ o The macromolecules themselves are called ___________________, because they are made up of many of these subunits. o Monomer: ______________ basic unit or subunit o Polymer: a chain of ____________ basic units Carbohydrates Made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a _____________ __________________. Key source of ______________ ( __________________) - found in fruits and vegetables. _________________________________ - single sugars. o The building blocks of carbs o Ends in __________ o Examples: glucose, fructose, maltose Monomer (basic unit): simple sugars or _________________________________ o Ex: glucose Polymer (chain of units): complex carbohydrates or __________________________ o Ex: starch, cellulose, chitin, glycogen Disaccharides and polysaccharides o Disaccharides - _________ sugars Glucose + fructose = sucrose o Polysaccharides A macromolecule made of ______________ _____________ Storehouse for _______________ Excess energy is stored as: ________________ - in plants _________________ - in animals _________________ - found in plant cell walls Indicator tests o Simple sugars ____________________ __________________: blue solution turns orange/green/brown o Complex carbs _______________ _______________/ ____________________: turns from orange-red-brown to blackpurple Let’s draw a glucose molecule! Lipids Are ____________________ _____________, ______________, phospholipids, _______________ (cholesterol) and waxes Fats are lipids that store ________________ for long term, make up the cell membrane (phospholipids), provide cell __________________, and provide insulation Lipids are made by combining two types of molecules o __________________ A three carbon alcohol o 3 ____________ _____________ Long hydrocarbon chains Non polar o The combining of these two molecules makes a __________________________. Made up of: ___________________. Monomer (basic unit): ______________ ___________ Polymer (chain of units): _____________ o Specific examples: triglycerides, phospholipids Saturated = __________________ bond Unsaturated = ________________ bond Indicator test o _______________ _____________ test Smear substance onto paper bag. If see-thru, it contains lipids. Proteins Build and repair muscle and tissues __________________ - proteins that ______________________ chemical reactions by lowering the ______________ ___________________. Most enzymes end in _________________. Made of chains of _______________ ______________ There are 20 known amino acids. These are found in all biological species _______________________ - protein found in skin ____________________________ - blood clots, and muscles. Structure: o Made up of: ___________________. o Monomer (basic unit): ____________ _____________ (20 different kinds!) o Polymer (chain of units): __________________ More specifically __________________________. (amino acids linked by _______________________ bonds) o _________________ _____________________ - makes center of amino acid o __________________ ________________ o ____________________ _________________ - this is an acid A single hydrogen ___________________ ___________________ There are 20 R groups Therefore there are 20 different amino acids in all living things Lets draw an amino acid o o Proteins have complex structures. The ________________ of a protein determines its ____________________! The levels of protein structure are: o __________________ ____________________: polypeptide chain o _______________________ ___________________: polypeptides in coils or sheets o ____________________ ______________________: coils or sheets form a tangle o ________________________ ____________________: more than one tangle combine to make a very complex protein! Enzymes: o Enzyme + Substrate = _____________________________. o Substrate is the ___________________ an enzyme ___________________ ________. It specifically _______________________ the enzyme. o The ______________________ _______________ is where the enzyme and the substrate __________ together and ________________. This activates the __________________. o Enzymes are _________________ for what they will catalyze. o Enzymes end is ______________ They must fit together like a ____________________________. o Draw an enzyme substrate complex: Energy is needed to start a chemical reaction o ___________________ __________________ - the energy needed to start a chemical reaction o Chemical push ________________ help biochemical reactions occur o Allows reactions to occur quickly and at ___________ temperatures o Increases the ________________ of chemical react ions o Most are _________________ o Act as _____________________ - reduce the amount of activation energy required o Helps maintain homeostasis. Three things that affect enzyme action. o Amount of enzyme __________________________ o ____________________________ o ____________ Indicator test: o _____________________ ______________________: turns from _____________________________________ if protein is present Nucleic Acids Function: Stores and carries ______________________ information Structure o Made up of _________________________. o Monomers (basic unit): _______________________ o Polymers (chain of units): ____________ or ___________ Made of ___________________ Nucleotides contain a sugar, phosphate and a ______________________________________. _____________ - double stranded and makes up chromosomes _____________ - single stranded, used in making proteins ATP Stands for ______________________________________________. ______________ currency for the cells Cells need a constant supply of ATP to function Organisms need energy for life processes o ______________ - the ability to move or change matter o Energy is stored and released by _______________ ____________________ o Reactants and Products o Chemical Reaction Absorb and release energy o Example: Freezing water releases energy Melting ice absorbs energy ATP = ______________________________ ATP has _______ phosphates, a sugar (________________), and ________________________. Energy is ____________________________ when the ________ phosphate bond ___________________________. o This leaves __________________ and a ___________________________. ADP – ATP cycle ADP joins together with a ________________________________________ gained through energy from _________. This makes ________________. Then ATP ____________________ energy for __________ by breaking the ________ phosphate which makes ____________and a ___________________________.