* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Macromolecules Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
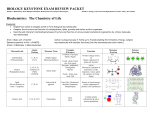
Honors Macromolecules Study Guide 1. Write a sentence for each vocabulary word on P.55(text book) 2. Name the most common atom found in living things. Name three other common atoms found in living things. 3. Name and describe draw the type of reaction that links monomers together. Name and describe and draw the reaction that breaks polymers back to monomers. 4. List the four main types of macromolecules. ***How are they different from each other? ***How are they similar to each other? 5. List the monomer and polymer names for the 4 macromolecules we’re learning. Study and know them. Example---Carbohydrates: Monomer: Monosaccharide Polymer: Polysaccharide 6. State the main function(s) of each of the 4 macromolecules we’re learning. Study and know them. Example: Carbohydrates: Main source of energy, structural support 7. Explain the connection between energy from the sun, the carbon cycle, carbohydrates (glucose), autotrophs, and heterotrophs. (This is a hard one but I know you can make the connections) Hint: The sun gives energy to the autotrophs which capture the energy in……… 8. Which macromolecule do you think has the most important function? Justify your answer. 9. a. At home, look at the labels of 3 common foods you eat. b. What macromolecules are in them? c. Any building blocks you get to many or too few of? d. Describe what your body does with these macromolecules. e. Many people say “you are what you eat.” Why is this a true statement from a biology standpoint? 10. Draw the monomer for a nucleic acid and label its three parts. How is it different from other monomers? 11. Define enzyme. What type of macromolecule is an enzyme? 12. Explain why enzymes are so important. What would happen if there were no enzymes? 13. Describe activation energy. Draw a graph that shows how enzymes affect activation energy. (p.36,37) GO TO( www.PHSchool.com Web code is cbp-1024) 14. Explain how enzymes identify their substrates. 15. Describe the two main conditions needed for enzyme activity to take place.