* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2 Test Review
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
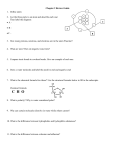
1. Reactant 2. Product 3. Acid 4. Base 5. pH 6. Organic Compound 7. Monomer 8. Polymer 9. Carbohydrate 10. Lipid 11. Protein 12. Amino Acid 13. Enzyme 14. Catalyst 15. Active Site 16. Substrate 17. Denature 18. Nucleic Acids 19. Nucleotide a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. p. q. r. s. Unit 2 Vocabulary Assignment Organic molecule made of nucleotides; used for information storage Molecules that are ‘used’ in a chemical reaction; on the left side of the equation Fats and oils; used for long term energy storage Organic compound that is the building block of organisms; made of amino acids Number (from 0-14) measuring the amount of hydrogen ions in a solution Molecules made during chemical reactions; on the right side of the equation A chemical that releases hydrogen ions in a solution Chemicals centered around carbon, not including carbon dioxide A chain of small units, which forms a large compound Monomer of Nucleic Acids; has different bases named with letters When a protein’s shape has been disturbed, causing it to no longer function A special type of protein that catalyzes chemical reactions Small molecules that link to form very large ones The monomer that makes up proteins A chemical that releases hydroxide (-OH) ions in a solution Any chemical that speeds up chemical reactions without being used up The chemical that an enzyme modifies Part of the enzyme that the substrate bonds to; specially shaped Large sugars, used for quick energy Unit 2 Test Review – Biochemistry 1. What are the three main bond types? Describe them 2. What is the pH scale? Draw it 3. Which end is acid? Which is base? What is neutral? 4. What are the characteristics of water that make it important to life? 5. What does it mean that water is polar? 6. Explain the bonding within and between water molecules. 7. What is the difference in organic and inorganic molecules? 8. What are the 4 organic molecules and the monomer (subunit) of each? 9. What is the purpose of each of the macromolecules? 10. What is the difference in a monosaccharide, disaccharide, and polysaccharide? 11. What are some examples of each of the 4 macromolecules? 12. Define catalyst 13. What are 2 things that can change the rate of enzyme reaction? 14. What is the difference in the active site and the substrate? 15. What does the “lock and key” feature of enzymes indicate?