* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Today is Monday Aug 31, 2015
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
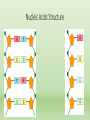
Biology Today is Friday Sept 4, 2015 Drill: What foods do you eat that contain lipids? Outcome: Compare the structure and function of all 4 macromolecules. What foods do you eat that contain lipids? REMEMBER!!!! Organic Molecules = Macromolecules • Organic= made of carbon • Also Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen • Monomers: Smallest unit (puzzle pieces) • Polymers: Many monomers put together (the completed puzzle) Organic Molecules = Macromolecules 1. Carbohydrates: main source of energy 2. Protein: build and repair body tissue (muscles) 3. Lipids: Long term energy storage. 4. Nucleic Acids: genetic information Protein Function • One of the four organic molecules (or macromolecules) • Function is to control the rate of chemical reactions and regulate cell processes • Example: Enzymes • Lactase helps break down lactose (the sugar found in milk) • Function is to transport substances in and out of cells. • Examples: Proteins channels Proteins Structure • Contains Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen • Amino acid and carboxyl groups do not change • “R” group changes Protein Building Blocks • The building block (monomer) is amino acids • There are 20 different types of amino acids • Change based on the “R” Group Nucleic Acid Function • One of the four organic molecules (or macromolecules) • Function is to carrier genetic information • Example: DNA • Function is to create (synthesize) proteins • Example: RNA Nucleic Acids Structure Review • You will be completing a organizer to study for your quiz • You must be able to: • Name each macromolecule and their monomer (building block) • Explain the function • Explain the structure Exit Ticket A scientist removed the cell membranes from bacteria cells in a culture. She analyzed the cell membranes for specific molecules. Which of these was probably the most common type of molecule present in the bacteria cell membranes? A. lipid B. amino acid C. nucleic acid D. carbohydrate