* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heine - MrZitarelli
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
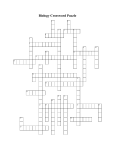
Chapter 2 Review Guide - 1. Define atom: - 2. List the three parts to an atom and describe each one: Then label the diagram: A– B– + + + C + A C – - B 3. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in the atom Fluorine? 4. What are ions? How do negative ions form? 5. Compare ionic bonds to covalent bonds. Give an example of each one. 6. Draw a water molecule and label the positive end and negative end: 7. What is the chemical formula for ribose? Use the structural formula below to fill in the subscripts. Chemical formula C H O 8. What is polarity? Why is water considered polar? 9. Why can certain molecules dissolve in water while others cannot? 10. What is the difference between hydrophobic and hydrophilic substances? 11. What is the difference between cohesion and adhesion? 12. What is the scale used to measure acids and bases? Where are the acids found on this scale? Where are the bases found on this scale? Give three examples of each one. 13. Give 2 examples of disaccharides. What 2 monosaccharides make up those particular disaccharides? 14. What is activation energy? What do catalysts do to activation energy? 15. What is an enzyme? 16. Which one of the four carbon based molecules are enzymes? What are their monomers called? 17. Can any enzyme work with any substrate? Explain why or why not. 18. Completely fill in the chart below for the Carbon Based Molecules. Name and General Characteristics Monomer 19. Identify the type of carbon-based molecule for each of the following structural formulas. ____________________ ________________________ ______________________ ______________________ Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to fill in the spaces in the puzzle with the correct words. Across Down 1. element or compound that enters into a chemical reaction 2. negatively charged subatomic particle 4. process that changes one set of chemicals into another 5. bond formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another 7. positively charged subatomic particle 6. monomer of nucleic acid 8. substance formed by the chemical combination of elements 9. monomer of protein 11. positively or negatively charged atom 3. compound that forms hydroxide ions in solution 10. compound that forms hydrogen ions in solution 12. carbon compound that stores and transmits genetic information 13. atom of an element that differs in the number of neutrons compared with other atoms of the same element 14. the center of an atom 15. basic unit of matter 16. bond formed when electrons are shared between atoms 17. macromolecule formed when monomers join together Test-Taking Tip: Anticipate the Answer When you take a test, read the question slowly. Don’t look at the answer choices. Try to think of a possible answer for the question. Once you’ve thought of an answer, look at your choices. Do you see a match? Read the following question. Do not read the answer choices. Think of a possible answer. What property of water molecules causes surface tension? A. adhesion B. cohesion C. heat capacity D. solubility Step 1 What is the question asking? The question is asking you to identify the property that produces surface tension. Step 2 Think about what you know about the question. You may remember that water is a polar molecule, and water molecules are connected together by hydrogen bonds. The words adhesion and cohesion were discussed in the lesson on water. You may remember that surface tension is related to cohesion. Step 3 Think about how you would answer the question. Then read the answer choices. The answer B matches what you know. It is the correct answer. Self-Test Practice what you have learned by answering the questions. Read the question and think of an answer. Then read the answer choices and circle the answer that is the best match. 1. The positively charged particle in an atom is called a A. neutron. B. ion. C. proton. D. electron. 2. Two or more different atoms are combined in definite proportions in any A. symbol. B. isotope. C. element. D. compound. 3. Proteins are polymers formed from A. lipids. B. amino acids. C. carbohydrates. D. nucleic acids. 4. Nucleotides consist of a phosphate group, a nitrogenous base, and a A. fatty acid. B. 5-carbon sugar. C. 6-carbon sugar. D. lipid. 5. In a chemical reaction, a reactant binds to an enzyme at a region known as the A. catalyst. B. product. C. substrate. D. active site. 6. Which of the following molecules is made up of a glycerol molecule combined with fatty acids? A. lipid B. sugar C. starch D. nucleic acid Short-Response Question Answer the following question in two or three sentences. 8. Changing the temperature or pH can change the shape of an enzyme. How might changes in temperature or pH affect the function of an enzyme?