Hardening of the arteries
... What is atherosclerosis? Hardening of the arteries, also called atherosclerosis, is a common disorder. It occurs when fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up in the walls of arteries and form hard structures called plaques. Over time, these plaques can block the arteries and cause symptoms ...
... What is atherosclerosis? Hardening of the arteries, also called atherosclerosis, is a common disorder. It occurs when fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up in the walls of arteries and form hard structures called plaques. Over time, these plaques can block the arteries and cause symptoms ...
Lipids General function
... a- Insolubility in water and solubility in organic solvents like chloroform-,etc b- some relation to fatty acids esters, either actual or potential phospholipids have very little solubility in water total body lipid in man is ...
... a- Insolubility in water and solubility in organic solvents like chloroform-,etc b- some relation to fatty acids esters, either actual or potential phospholipids have very little solubility in water total body lipid in man is ...
Organic Macromolecules
... Organic Macromolecules Graphic Organizer Read Chapter 3 in your book and fill out this graphic organizer. You will use this when you do your Macromolecule Flapbook. Organic Molecule Simple Carbohydrate ...
... Organic Macromolecules Graphic Organizer Read Chapter 3 in your book and fill out this graphic organizer. You will use this when you do your Macromolecule Flapbook. Organic Molecule Simple Carbohydrate ...
Metabolism Metabolism refers to all the chemical reactions within an
... The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that oxidize acetyl residues (as acetyl-CoA) and reduce coenzymes that upon reoxidation are linked to the formation of ATP. The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the aerobic oxidation of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein b ...
... The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that oxidize acetyl residues (as acetyl-CoA) and reduce coenzymes that upon reoxidation are linked to the formation of ATP. The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the aerobic oxidation of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein b ...
Remember: Condensation makes bonds: Hydrolysis breaks bonds.
... 2. List three carbon-containing groups or molecules that are not organic. There are many organic molecules in living things. The same (or very similar) molecules are used in many different living things for the same purpose. 3. Saccharides are sugars and carbohydrates. Sugars (monosaccharides and di ...
... 2. List three carbon-containing groups or molecules that are not organic. There are many organic molecules in living things. The same (or very similar) molecules are used in many different living things for the same purpose. 3. Saccharides are sugars and carbohydrates. Sugars (monosaccharides and di ...
annotated slides Power Point
... • Some of the acetyl-CoA produced by fatty acid oxidation in liver mitochondria is converted to acetone, acetoacetate and b-hydroxybutyrate • These are called "ketone bodies" • Source of fuel for brain, heart and muscle • Major energy source for brain during starvation • They are transportable forms ...
... • Some of the acetyl-CoA produced by fatty acid oxidation in liver mitochondria is converted to acetone, acetoacetate and b-hydroxybutyrate • These are called "ketone bodies" • Source of fuel for brain, heart and muscle • Major energy source for brain during starvation • They are transportable forms ...
Thiomucase Profile
... before a contest. Most feel that the orals are not effective. Finally there is a suppository form of this medication. They are inserted twice daily for about a week before a contest. Often all of these methods are used at the same time. Most bodybuilders who used these items reported some degree of ...
... before a contest. Most feel that the orals are not effective. Finally there is a suppository form of this medication. They are inserted twice daily for about a week before a contest. Often all of these methods are used at the same time. Most bodybuilders who used these items reported some degree of ...
Macromolecules Vocabulary and Concepts
... o Ring form of glucose comes in two forms: alpha and beta glucose o Starch: polymer of alpha glucose, energy storage in plants, digested by animals o Glycogen: polymer of alpha glucose, energy storage in animals o Cellulose: polymer of beta glucose, structural component of plants, not digested by an ...
... o Ring form of glucose comes in two forms: alpha and beta glucose o Starch: polymer of alpha glucose, energy storage in plants, digested by animals o Glycogen: polymer of alpha glucose, energy storage in animals o Cellulose: polymer of beta glucose, structural component of plants, not digested by an ...
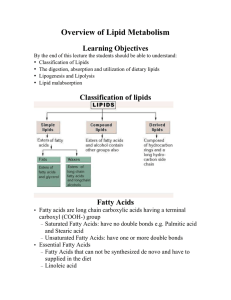
Overview of Lipid Metabolism
... Lipid transport from intestinal mucosa • Once inside the intestinal mucosal cells, the absorbed lipids are resynthesized into TG and CE ( cholesterol esters ) • Intestinal cells synthesize apolipoprotein B-48 and package TG and CE into Chylomicrons • Chylomicrons are secreted first into the lymphat ...
... Lipid transport from intestinal mucosa • Once inside the intestinal mucosal cells, the absorbed lipids are resynthesized into TG and CE ( cholesterol esters ) • Intestinal cells synthesize apolipoprotein B-48 and package TG and CE into Chylomicrons • Chylomicrons are secreted first into the lymphat ...
Regulation of fatty acid synthesis and degradation by the AMP
... falling ATP, which together signal a fall in cellular energy status. Although it probably has many targets, two key targets are acetylCoA carboxylase-1 and -2 (ACCI and ACCZ), both of which are inactivated by AMPK. A C C l catalyzes the key regulated step in fatty acid synthesis in liver and other t ...
... falling ATP, which together signal a fall in cellular energy status. Although it probably has many targets, two key targets are acetylCoA carboxylase-1 and -2 (ACCI and ACCZ), both of which are inactivated by AMPK. A C C l catalyzes the key regulated step in fatty acid synthesis in liver and other t ...
Glycolysis II
... Acetyl CoA splits off and rest of chain is bound to another CoA. … until fatty acid is at its end. Special cases are unsaturated fatty acids and fatty acids with odd numbers of C atoms. Fatty acid oxidation takes also place in peroxisomes, but no ATP generation. Acetyl-CoA back to cytosol (synthesis ...
... Acetyl CoA splits off and rest of chain is bound to another CoA. … until fatty acid is at its end. Special cases are unsaturated fatty acids and fatty acids with odd numbers of C atoms. Fatty acid oxidation takes also place in peroxisomes, but no ATP generation. Acetyl-CoA back to cytosol (synthesis ...
LIPIDS
... • Saturated fatty acid-a fatty acid where all the carbon to carbon bonds are single bonds • Unsaturated fatty acid- there is at least on carbon to carbon double bond • Higher ratio of carbon and hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms • causes them to have more carbon to hydrogen bonds which store more ener ...
... • Saturated fatty acid-a fatty acid where all the carbon to carbon bonds are single bonds • Unsaturated fatty acid- there is at least on carbon to carbon double bond • Higher ratio of carbon and hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms • causes them to have more carbon to hydrogen bonds which store more ener ...
Study guide for Midterm 3.
... fatty acyl–CoA from the cytosol to the mitochondrion in preparation for β oxidation (see Fig. 17-6). One result of that shuttle was separation of the mitochondrial and cytosolic pools of CoA. Does the acetyl group shuttle also accomplish this? Explain. 3. Consider a preparation that contains all the ...
... fatty acyl–CoA from the cytosol to the mitochondrion in preparation for β oxidation (see Fig. 17-6). One result of that shuttle was separation of the mitochondrial and cytosolic pools of CoA. Does the acetyl group shuttle also accomplish this? Explain. 3. Consider a preparation that contains all the ...
What is Ketosis
... OOC-CH2-C-CH3 O CO2 NADH + H+ NAD+ CH3-C-CH3 OOC-CH2-CH-CH3 O Acetone OH -hydroxybutyrate ...
... OOC-CH2-C-CH3 O CO2 NADH + H+ NAD+ CH3-C-CH3 OOC-CH2-CH-CH3 O Acetone OH -hydroxybutyrate ...
Cell structure and Bioenergetics
... Lipid containing a ring system with a hydroxyl or ketone groups Cholesterol : cellular membrane, modulates membrane fluidity Precursor for synthesis of steroid hormones, skin-derived vitamin D, and bile acids – Cholesterol: 27 Carbons – Bile acids: 24 carbons – Androgens: 19 carbons – Progestero ...
... Lipid containing a ring system with a hydroxyl or ketone groups Cholesterol : cellular membrane, modulates membrane fluidity Precursor for synthesis of steroid hormones, skin-derived vitamin D, and bile acids – Cholesterol: 27 Carbons – Bile acids: 24 carbons – Androgens: 19 carbons – Progestero ...
Energy Production II - University of Massachusetts Amherst
... Not used much by most tissues except after a meal, reserved for the brain and "special" situations At rest: 250 mg glucose/min = 20 min of glucose in blood at any one time. ...
... Not used much by most tissues except after a meal, reserved for the brain and "special" situations At rest: 250 mg glucose/min = 20 min of glucose in blood at any one time. ...
Ch03Water,pH,Biological Molecules
... c. Cellulose, functions to provide structure to plants; indigestible to mammals (fiber on food label) d. Chitin, functions in external skeleton of arthropods B. Lipids 1. Common characteristics of lipids: composed of C, H, and O, but insoluble in water. 2. Major function: Energy storage and insulati ...
... c. Cellulose, functions to provide structure to plants; indigestible to mammals (fiber on food label) d. Chitin, functions in external skeleton of arthropods B. Lipids 1. Common characteristics of lipids: composed of C, H, and O, but insoluble in water. 2. Major function: Energy storage and insulati ...
Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... – Small, simple molecules – Amino acid, fatty acid, nucleotide, monosaccharide ...
... – Small, simple molecules – Amino acid, fatty acid, nucleotide, monosaccharide ...
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... -starch = glucose polymer in plants used for energy storage ( ...
... -starch = glucose polymer in plants used for energy storage ( ...
Molecular Modeling Activity Lipids (Saturated and Unsaturated Fats
... Lipids are a diverse group of chemical compounds that are related by their insolubility in water. Lipids include phospholipids, sterols, and triglycerides. ❏ Phospholipids are important parts of cell membranes. Sterols such as cholesterol form vital biological compounds including hormones. ❏ Triglyc ...
... Lipids are a diverse group of chemical compounds that are related by their insolubility in water. Lipids include phospholipids, sterols, and triglycerides. ❏ Phospholipids are important parts of cell membranes. Sterols such as cholesterol form vital biological compounds including hormones. ❏ Triglyc ...
2008b(12): Detail the protective and regulatory roles of the liver
... o catabolic hormones: glucagons, cortisol, adrenaline o anabolic hormones: insulin, GH - anabolic functions o CHO: glycogenesis ↑glucose trapping (hepatocytes) 2° ↑glucokinase activity o fats: fatty acid formation • once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolized to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fat ...
... o catabolic hormones: glucagons, cortisol, adrenaline o anabolic hormones: insulin, GH - anabolic functions o CHO: glycogenesis ↑glucose trapping (hepatocytes) 2° ↑glucokinase activity o fats: fatty acid formation • once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolized to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fat ...
4 TYPES OF LIPIDS Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Waxes, Steroids
... Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature (such as plant oils). ...
... Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature (such as plant oils). ...