* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macromolecules Vocabulary and Concepts
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
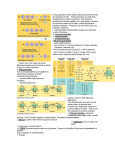
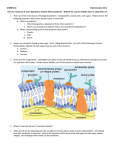
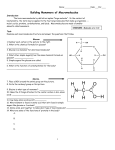
Chapter 5: Macromolecules Key Vocabulary and Concepts to Review Four Organic Macromolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids Polymers carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids form polymers made of monomers Describe the two types of reactions listed below, and explain how they are involved in forming or breaking down polymers. o Dehydration Synthesis o Hydrolysis Reaction Carbohydrates Uses o Energy, structure, and support Monosaccharide – simple sugars o Glucose, Fructose, Galactose Disaccharide o Sucrose (Glucose + Fructose) o Maltose (Glucose + Glucose) Polysaccharide (Polymers of Glucose) o Ring form of glucose comes in two forms: alpha and beta glucose o Starch: polymer of alpha glucose, energy storage in plants, digested by animals o Glycogen: polymer of alpha glucose, energy storage in animals o Cellulose: polymer of beta glucose, structural component of plants, not digested by animals Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose are all polymers of glucose o Identify differences and similarities between starch, glycogen, and cellulose. Focus on structure, function, and where each is found. Glycosidic linkages join monosaccharides that make up disaccharides and polysaccharides. They are formed through Dehydration Synthesis. Lipids Hydrophobic Do NOT form polymers Types o Fats and Oils (Triglycerides) Fats are solid at room temperature, oils are liquid at room temperature Energy storage Glycerol + 3 fatty acids Ester Linkage joins fatty acids to the glycerol molecule ? What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? o Phospholipid Glycerol, 2 fatty acids, 1 phosphate Amphipathic Cell membranes ? How does the degree of saturation of fatty acids in a cell membrane affect the fluidity of the membrane? o Steroids o Waxes o Vitamins – some vitamins are not water soluble (A, D, E, and K) Protein Many Uses: structural support, protection, transport, catalysis (enzymes), defense, regulation (hormones), movement. Polymer of amino acids Polypeptide o Peptide Bonds join amino acids. Amino Acids are linked together through a dehydration synthesis reaction. Amino Acids o Central asymmetric carbon, hydrogen, carboxyl group, amino group, functional group o Functional groups can be Hydrophobic (Nonpolar), Hydrophilic (Polar), or Ionic (Electrically Charged). Structure o Primary o Secondary o Tertiary o Quaternary Protein Folding Denaturing ? Discuss how the phrase “structure determines function” applies to proteins. Nucleic Acids Polymer o Phosphodiester bonds Five bases (monomers): adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine, uracil DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid RNA = ribonucleic acid