* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Building Monomers of Macromolecules
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
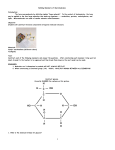
Name:_________________________Date:___Per:____ Building Monomers of Macromolecules Introduction: The term macromolecule by definition implies "large molecule". In the context of biochemistry, the term may be applied to the four large molecules that make up organisms --nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Macromolecules are made of smaller subunits called monomers. REMEMBER: Molecules are 3-D! Task: Examine each macromolecule structure and answer the questions that follow. Glucose 1. Number each carbon in the picture to the right. 2. What is the chemical formula for glucose? __________________ 3. Glucose is a monomer for what macromolecule? ___________________________ 4. What other simple sugar(s) has the same chemical formula as glucose? ________________ 5. Simple sugars like glucose are called ____________________________________. 6. What is the function of carbohydrates for the body? ___________________________ Glycine. 7. Place a BOX around the amino group on this picture. 8. Circle the carboxyl group on this picture. 9. Glycine is what type of monomer? _____________________ 10. Name the 4 things attached to the center carbon in ALL amino acids. ______________________, __________________, _______________________, ______________________ 11. How many amino acids exist?__________ 12. What element is found in amino acid that isn’t found in simple sugars like glucose or fructose? __________________ 13. Amino acids join together to make what type of macromolecule? _________________ 14. What are some of the functions of proteins in the body? A. B. C. D. 1 Glycerol 15. Place a CIRCLE around a hydroxyl group. 16. Glycerol is one of two molecules that make up a monomer known as _T_ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ _S_. 17. Besides glycerol, what 3 other molecules make up a triglyceride? __________________________ 18. Glycerol and other organic compounds with an –ol ending are called ___________________. 19. Triglycerides are the monomers for what type of macromolecule? ____________________ 20. What are some of the functions of lipids? Fatty acid 21. Place a BOX around the hydrocarbon chain in these pictures. 22. Circle the carboxyl group in both pictures. 23. Fatty acids are made of long chains of _______________ atoms with attached ______________ atoms. 24. What 3 elements make up fatty acids? _________________ 25. How are saturated and unsaturated fatty acid chains structurally different? _______________________________ _________________________________________________ 26. How are saturated and unsaturated fats physically different? _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ 2