macromolecules
... • Polysaccharides (“complex carbs”) – consists of many monosaccharides (usually more ...
... • Polysaccharides (“complex carbs”) – consists of many monosaccharides (usually more ...
Nutrients note
... C) Polysaccharides (complex carbohydrates) - contain tens, hundreds even thousands of monosaccharides strung together as long chains - insoluble and very large, therefore when eaten, reactions in the digestive system break everything down to glucose molecules - there are three important polysacchari ...
... C) Polysaccharides (complex carbohydrates) - contain tens, hundreds even thousands of monosaccharides strung together as long chains - insoluble and very large, therefore when eaten, reactions in the digestive system break everything down to glucose molecules - there are three important polysacchari ...
Abstract The possible role of glycosphingolipids as adhesion
... when the different lactosylceramide species were incorporated into liposomes, but only in the presence of cholesterol, suggesting that this selectivity may be present also in vivo . Importantly, lactosylceramide with sphingosine and hydroxy fatty acids does not bind in this assay. Furthermore, a lac ...
... when the different lactosylceramide species were incorporated into liposomes, but only in the presence of cholesterol, suggesting that this selectivity may be present also in vivo . Importantly, lactosylceramide with sphingosine and hydroxy fatty acids does not bind in this assay. Furthermore, a lac ...
Complex Lipids Sections 13.4-13.8
... similar to fats Membrane components of cells throughout the body Alcohol in it is glycerol ...
... similar to fats Membrane components of cells throughout the body Alcohol in it is glycerol ...
Ch.24Pt.6_000
... Exercise and Carbohydrate & Lipid metabolism Humans burn more fat than carbs (2:1) in resting state. Beginning exercise: sudden need for energy. Glycogen much faster to release glucose-6-phosphate for fuel. 1st few minutes = 80% fuel from glycogen. Fats 1st broken down to F.A.s, then attach to prot ...
... Exercise and Carbohydrate & Lipid metabolism Humans burn more fat than carbs (2:1) in resting state. Beginning exercise: sudden need for energy. Glycogen much faster to release glucose-6-phosphate for fuel. 1st few minutes = 80% fuel from glycogen. Fats 1st broken down to F.A.s, then attach to prot ...
Lactic Acid and Energy from Fats and Proteins
... Process where lactic acid is converted to pyruvate Lactate is transported (by blood) to the liver and converted back to glucose It is then converted into glycogen so that it can be used for energy ...
... Process where lactic acid is converted to pyruvate Lactate is transported (by blood) to the liver and converted back to glucose It is then converted into glycogen so that it can be used for energy ...
Covalent Reactions Atoms SHARE electrons
... • Phospholipids- like fats but has phosphate group instead of third fatty acid • Steroids- has a backbone of 4 fused carbon rings (Cholesterol is a type of steroid) ...
... • Phospholipids- like fats but has phosphate group instead of third fatty acid • Steroids- has a backbone of 4 fused carbon rings (Cholesterol is a type of steroid) ...
Slide 1
... sequential loss of acetyl groups from carbon chain of fatty acid) – Energy yield depends on length of carbon chain (ex. 16C palmitic acid results in 129 ATPs, ~3.5x more than glucose) – Ketoacidosis: results if oxaloacetate in short supply; acetyl-CoA converted into ketones, which are weak acids; ca ...
... sequential loss of acetyl groups from carbon chain of fatty acid) – Energy yield depends on length of carbon chain (ex. 16C palmitic acid results in 129 ATPs, ~3.5x more than glucose) – Ketoacidosis: results if oxaloacetate in short supply; acetyl-CoA converted into ketones, which are weak acids; ca ...
Lecture 3 (BY 14)
... Glycogen • Sugar storage form in _______ • Large stores in ______ and _______ cells • When blood sugar decreases, liver cells degrade glycogen, release glucose ...
... Glycogen • Sugar storage form in _______ • Large stores in ______ and _______ cells • When blood sugar decreases, liver cells degrade glycogen, release glucose ...
Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... – Small, simple molecules – Amino acid, fatty acid, nucleotide, monosaccharide ...
... – Small, simple molecules – Amino acid, fatty acid, nucleotide, monosaccharide ...
Macromolecules in Organisms
... oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are ...
... oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are ...
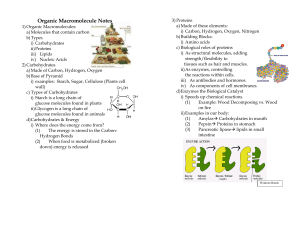
Organic Macromolecule Notes
... a) Made of these elements: i) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen b) Building Blocks: i) Amino acids c) Biological roles of proteins i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies ...
... a) Made of these elements: i) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen b) Building Blocks: i) Amino acids c) Biological roles of proteins i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies ...
BioN08 Metabolism of lipids Summer 2015
... • When energy is needed, lipases within fat cells are activated by hormones (insulin and glucagon). • The stored TAGs are hydrolyzed to fatty acids, and the free fatty acids and glycerol are released into • the bloodstream. • The fatty acids travel in association with albumins to cells where they ar ...
... • When energy is needed, lipases within fat cells are activated by hormones (insulin and glucagon). • The stored TAGs are hydrolyzed to fatty acids, and the free fatty acids and glycerol are released into • the bloodstream. • The fatty acids travel in association with albumins to cells where they ar ...
BCBT100 Biochemistry of Food Study Guide
... I think it will be very helpful if you can understand more than the vocabulary. The best way to prepare is to look at each bullet and then read up on that topic from the ...
... I think it will be very helpful if you can understand more than the vocabulary. The best way to prepare is to look at each bullet and then read up on that topic from the ...
Tymoczko, Biochemistry: A Short Course 3e, Launchpad
... 6. Advanced glycation end products are a. products of reactions between reducing sugars and free amino groups. b. two or more sugars joined together in a covalent bond. c. products of a reaction between sucrose and proteins. d. solely composed of long carbohydrate polymers on free amino groups. 7. H ...
... 6. Advanced glycation end products are a. products of reactions between reducing sugars and free amino groups. b. two or more sugars joined together in a covalent bond. c. products of a reaction between sucrose and proteins. d. solely composed of long carbohydrate polymers on free amino groups. 7. H ...
Macromolecule Expert Sheets
... 3. Draw and label the levels of organization of the protein structure. 4. What types of atoms are found in proteins? 5. Draw the general structure for an amino acid and label its functional groups. 6. Which part of an amino acid determines its specific properties? 7. When 2 amino acids are joined to ...
... 3. Draw and label the levels of organization of the protein structure. 4. What types of atoms are found in proteins? 5. Draw the general structure for an amino acid and label its functional groups. 6. Which part of an amino acid determines its specific properties? 7. When 2 amino acids are joined to ...
chapter 5 the structure & function of macromolecules
... double bonds between the carbons in the chain. (Liquids at room temp due to “kinks” in the fatty acid which prevents it from solidifying) Fat Molecules are storage for energy. ...
... double bonds between the carbons in the chain. (Liquids at room temp due to “kinks” in the fatty acid which prevents it from solidifying) Fat Molecules are storage for energy. ...
Lipids2
... to achieve this. Odd-numbered fatty acids yields propionylCoA, which is converted to succinylCoA to enter the TCA. ...
... to achieve this. Odd-numbered fatty acids yields propionylCoA, which is converted to succinylCoA to enter the TCA. ...
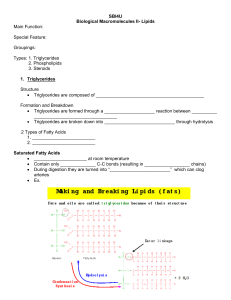
student note
... Contain only ______________ C-C bonds (resulting in __________________ chains) During digestion they are turned into “________________________” which can clog arteries Ex. ...
... Contain only ______________ C-C bonds (resulting in __________________ chains) During digestion they are turned into “________________________” which can clog arteries Ex. ...
MACROMOLECULE SUMMARY SHEET
... 1. How are monosaccharides and polysaccharides related? 2. Compare (what’s the same) and contrast (what’s different) about starch and glycogen? ...
... 1. How are monosaccharides and polysaccharides related? 2. Compare (what’s the same) and contrast (what’s different) about starch and glycogen? ...
BIOS 1300 SI WORKSHEET 2 (Chapter 2) SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries
... d. omega – 3 fatty acid e. diglyceride 17.How does boiling a protein affect its structural and functional properties? 18.On average, lipids provide roughly twice as much energy as carbohydrates do, gram for gram, when broken down in the body. T/F ...
... d. omega – 3 fatty acid e. diglyceride 17.How does boiling a protein affect its structural and functional properties? 18.On average, lipids provide roughly twice as much energy as carbohydrates do, gram for gram, when broken down in the body. T/F ...