FALSE degradation also needs to be considered. A change in
... a. Why would gluconeogenesis from alanine require increased transport of malate across the mitochondrial membrane, whereas gluconeogenesis from lactate would not. The conversion of lactate to pyruvate in the cytosol generates an NADH molecule from NAD.. If alanine is transaminated in the mitochondri ...
... a. Why would gluconeogenesis from alanine require increased transport of malate across the mitochondrial membrane, whereas gluconeogenesis from lactate would not. The conversion of lactate to pyruvate in the cytosol generates an NADH molecule from NAD.. If alanine is transaminated in the mitochondri ...
Organic Compounds Overview - Kenwood Academy High School
... Contractile (muscles) Enzymes Defensive (immune system) Signal (coordinate body functions) Receptor (on cell membranes) Transport (hemoglobin carries oxygen) ...
... Contractile (muscles) Enzymes Defensive (immune system) Signal (coordinate body functions) Receptor (on cell membranes) Transport (hemoglobin carries oxygen) ...
Chapter 5 – Quiz #2-A Take Home Quiz
... 9. Which of the following is/are a precursor of bile, vitamin D, and some sex hormones? a. phospholipids b. triglycerides c. cholesterol d. alpha-linolenic acid True or False: Place a T or an F to the left of the number of the question. 10. LDL is a type of lipoprotein that carries digested fat from ...
... 9. Which of the following is/are a precursor of bile, vitamin D, and some sex hormones? a. phospholipids b. triglycerides c. cholesterol d. alpha-linolenic acid True or False: Place a T or an F to the left of the number of the question. 10. LDL is a type of lipoprotein that carries digested fat from ...
Metabolism08
... When completely broken down, each glucose molecule yields carbon dioxide, water, and ATP 30-32 ATP are formed by the complete break down of glucose ...
... When completely broken down, each glucose molecule yields carbon dioxide, water, and ATP 30-32 ATP are formed by the complete break down of glucose ...
Saturated fatty acid
... 36 carbons, whereas the alcohols have an even number from 24 to 36 carbons. ► A component in beeswax is the ester formed from a 30-C alcohol (triacontanol) and a 16-C acid (palmitic acid). ...
... 36 carbons, whereas the alcohols have an even number from 24 to 36 carbons. ► A component in beeswax is the ester formed from a 30-C alcohol (triacontanol) and a 16-C acid (palmitic acid). ...
File - Principles of Biology 103
... 15. Amino acids are small organic compounds that are the basic subunits of: C. Proteins 16. Metabolism refers to the enzyme-mediated chemical reactions by which cells: A. Acquire and use energy as they build and break down organic molecules 17. What is the main structural component of plants: C. Ce ...
... 15. Amino acids are small organic compounds that are the basic subunits of: C. Proteins 16. Metabolism refers to the enzyme-mediated chemical reactions by which cells: A. Acquire and use energy as they build and break down organic molecules 17. What is the main structural component of plants: C. Ce ...
Dominant Dietary Fatty Acids
... Peroxisome – 20 C fatty acids that don’t enter mitochondrial oxidation…18 C can enter it o In times of need, structural (long) can be β-oxidized (shortened down) and shunted to break down to get energy (?) Mechanism of fat synthesis o Conversion to fat Excess carbohydrate after glycogen filled E ...
... Peroxisome – 20 C fatty acids that don’t enter mitochondrial oxidation…18 C can enter it o In times of need, structural (long) can be β-oxidized (shortened down) and shunted to break down to get energy (?) Mechanism of fat synthesis o Conversion to fat Excess carbohydrate after glycogen filled E ...
Classes of Biomolecules Lipids Biological Functions of Lipids
... substances soluble in organic solvents but not in water • Differential is their state at room temperature ...
... substances soluble in organic solvents but not in water • Differential is their state at room temperature ...
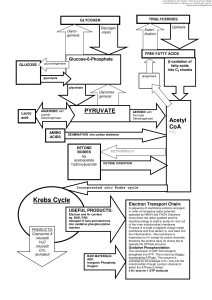
The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle)
... The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that oxidize acetyl residues (as acetyl-CoA) and reduce coenzymes that upon reoxidation are linked to the formation of ATP. The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the aerobic oxidation of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein b ...
... The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that oxidize acetyl residues (as acetyl-CoA) and reduce coenzymes that upon reoxidation are linked to the formation of ATP. The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the aerobic oxidation of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein b ...
NATURE`S BIOLOGICAL BUILDING BLOCKS
... Composed of subunits (molecules) called amino acids joined together by a peptide bond. Proteins may be structural (as in muscle tissue and connective tissue) or enzymatic. They may also function as hormones. ...
... Composed of subunits (molecules) called amino acids joined together by a peptide bond. Proteins may be structural (as in muscle tissue and connective tissue) or enzymatic. They may also function as hormones. ...
MacromoleculeReview
... 24. Using a structural formula diagram, show how a peptide bond is formed between two amino acids. ...
... 24. Using a structural formula diagram, show how a peptide bond is formed between two amino acids. ...
Name - MsOttoliniBiology
... in the immune system) Speeding up Reactions (enzymes) Movement (ex: muscle proteins) Transport (ex: hemoglobin transporting oxygen in red blood cells) ...
... in the immune system) Speeding up Reactions (enzymes) Movement (ex: muscle proteins) Transport (ex: hemoglobin transporting oxygen in red blood cells) ...
Introduction to 9th Grade Biology
... • Unsaturated fats : – liquid at room temp – one or more double bonds between carbons in the fatty acids allows for “kinks” in the tails – most plant fats ...
... • Unsaturated fats : – liquid at room temp – one or more double bonds between carbons in the fatty acids allows for “kinks” in the tails – most plant fats ...
Food Utilization
... • Recommended daily allowances (RDA) – safe estimate of daily intake for standard needs • Essential nutrients can not be synthesized – minerals, vitamins, 8 amino acids and 1-3 fatty acids ...
... • Recommended daily allowances (RDA) – safe estimate of daily intake for standard needs • Essential nutrients can not be synthesized – minerals, vitamins, 8 amino acids and 1-3 fatty acids ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 11. The internal reference electrode in a combination electrode is _____________. 12. The torsion angle between Cα and C is denoted as__________________. 13. Pyruvate is converted to acetyl-coA by _____________ enzyme complex. 14. The charge on a charged amino acid becomes neutral at _______________ ...
... 11. The internal reference electrode in a combination electrode is _____________. 12. The torsion angle between Cα and C is denoted as__________________. 13. Pyruvate is converted to acetyl-coA by _____________ enzyme complex. 14. The charge on a charged amino acid becomes neutral at _______________ ...
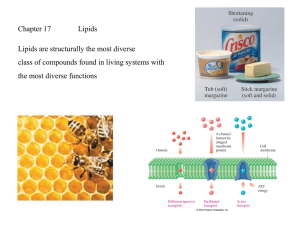
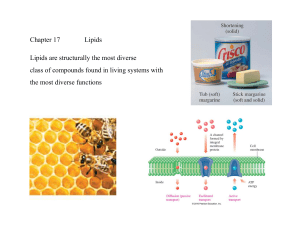
Chapter 17 Lipids Lipids are structurally the most diverse
... Remenber these acids are present as triglycerides in fish oil and other sources ...
... Remenber these acids are present as triglycerides in fish oil and other sources ...
1. Triglyceride degradation is not influenced by: A cAMP B Glucagon
... 9. Which of the following occurs when cholesterol enters cells: A Cholesterol is released from the LDL particles when the particles become internalized by lysozomes B LDL receptors on the cell surface recognize cholesterol in LDL particles C The internalized LDL receptor is degraded to amino acids t ...
... 9. Which of the following occurs when cholesterol enters cells: A Cholesterol is released from the LDL particles when the particles become internalized by lysozomes B LDL receptors on the cell surface recognize cholesterol in LDL particles C The internalized LDL receptor is degraded to amino acids t ...
投影片 1
... 18CO2 + 9CoA-SH + 9FADH2 + 27NADH + 9GTP + 27H+ 17FADH2 + 8.5O2 + 25.5ADP + 25.5Pi 17 FAD + 25.5 ATP + 17 H2O 35NADH + 35H+ + 17.5 O2 + 87.5ADP + 87.5Pi 35NAD+ + 87.5ATP + 35H2O O CH3(CH2)16C-S-CoA + 26O2 + 122 ADP + 122Pi 18CO2 + 17H2O + 122ATP + CoA-SH one 18C fatty acid ...
... 18CO2 + 9CoA-SH + 9FADH2 + 27NADH + 9GTP + 27H+ 17FADH2 + 8.5O2 + 25.5ADP + 25.5Pi 17 FAD + 25.5 ATP + 17 H2O 35NADH + 35H+ + 17.5 O2 + 87.5ADP + 87.5Pi 35NAD+ + 87.5ATP + 35H2O O CH3(CH2)16C-S-CoA + 26O2 + 122 ADP + 122Pi 18CO2 + 17H2O + 122ATP + CoA-SH one 18C fatty acid ...
Chapter 21 Biosynthetic Pathways
... • A large excess of phosphate would drive the reaction to the right; that is, drive the hydrolysis of glycogen. • To provide an alternative pathway for the synthesis of glycogen, even in the presence of excess phosphate: ...
... • A large excess of phosphate would drive the reaction to the right; that is, drive the hydrolysis of glycogen. • To provide an alternative pathway for the synthesis of glycogen, even in the presence of excess phosphate: ...