Unit 3: Chemistry of Life
... State one function of glucose, lactose and glycogen in animals, and of fructose, sucrose and cellulose in plants. ...
... State one function of glucose, lactose and glycogen in animals, and of fructose, sucrose and cellulose in plants. ...
biochem2
... the structure. These are clusters of atoms that behave in a particular manner regardless of how the rest of the molecule looks. ...
... the structure. These are clusters of atoms that behave in a particular manner regardless of how the rest of the molecule looks. ...
Organic Compounds
... the structure. These are clusters of atoms that behave in a particular manner regardless of how the rest of the molecule looks. ...
... the structure. These are clusters of atoms that behave in a particular manner regardless of how the rest of the molecule looks. ...
Fermentation and Biosynthetic Pathways File
... intermediates produced during glycolysis, Krebs cycle and from lipids or amino acids. Bacteria may assemble it into the more complex polysaccharides. Biosynthesis of Lipids Lipids vary in chemical composition, cells synthesize fats by joining glycerol and fatty acids. The glycerol portion of the fat ...
... intermediates produced during glycolysis, Krebs cycle and from lipids or amino acids. Bacteria may assemble it into the more complex polysaccharides. Biosynthesis of Lipids Lipids vary in chemical composition, cells synthesize fats by joining glycerol and fatty acids. The glycerol portion of the fat ...
Table S1.
... Resulting HMGCoA reductase enzyme is the rate reductase limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis. Mevalonate kinase Catabolizes mevalonate to mevalonate-5P D-7 dehydrocholesterol reductase Catalyzes the conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to cholesterol. Isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase Isomerase th ...
... Resulting HMGCoA reductase enzyme is the rate reductase limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis. Mevalonate kinase Catabolizes mevalonate to mevalonate-5P D-7 dehydrocholesterol reductase Catalyzes the conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to cholesterol. Isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase Isomerase th ...
MAKEUP: Briefly discuss functions of the liver
... • Once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolised to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fatty acid Cholesterol / phospholipid formation o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CHO: Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o Fats ...
... • Once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolised to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fatty acid Cholesterol / phospholipid formation o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CHO: Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o Fats ...
Chemistry of Life - Haughton Science
... that holds amino acids together in protein molecules dipeptide bond = two connected amino acids polypeptide bond = 3 or more connected amino acids ...
... that holds amino acids together in protein molecules dipeptide bond = two connected amino acids polypeptide bond = 3 or more connected amino acids ...
Lipids
... Fatty acids and glycerol are released into bloodstream and taken up by body cells Remnants of the chylomicron are brought to liver VLDL – very low density lipoproteins – lipoprotein created in the liver that carries cholesterol and lipids newly synthesized by the liver Once in blood, triglycer ...
... Fatty acids and glycerol are released into bloodstream and taken up by body cells Remnants of the chylomicron are brought to liver VLDL – very low density lipoproteins – lipoprotein created in the liver that carries cholesterol and lipids newly synthesized by the liver Once in blood, triglycer ...
The Mac Daddies of Molecules
... ENZYMES (promote chemical reactions) Provide structure (hair, bones, muscles) Antibodies (fight infection) Carry things (oxygen from lungs to rest of body) ...
... ENZYMES (promote chemical reactions) Provide structure (hair, bones, muscles) Antibodies (fight infection) Carry things (oxygen from lungs to rest of body) ...
Fatty acids and their derivatives
... ◦ structural components in cell membranes (e.g phospolipids) ◦ means to store energy (e.g triacylglycerols) ◦ chemical signals, vitamins, or pigments, ◦ protective molecules (outer coatings for cells). ...
... ◦ structural components in cell membranes (e.g phospolipids) ◦ means to store energy (e.g triacylglycerols) ◦ chemical signals, vitamins, or pigments, ◦ protective molecules (outer coatings for cells). ...
b-oxidation - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... • Some of the acetyl-CoA produced by fatty acid oxidation in liver mitochondria is converted to acetone, acetoacetate and b-hydroxybutyrate • These are called "ketone bodies" • Source of fuel for brain, heart and muscle • Major energy source for brain during starvation • They are transportable forms ...
... • Some of the acetyl-CoA produced by fatty acid oxidation in liver mitochondria is converted to acetone, acetoacetate and b-hydroxybutyrate • These are called "ketone bodies" • Source of fuel for brain, heart and muscle • Major energy source for brain during starvation • They are transportable forms ...
Test 2 - HCC Learning Web
... 4. Stanley Miller's 1953 experiments proved that. Explain? 5. Why are hydrocarbons insoluble in water? 6. Humans can digest starch but not cellulose because. Explain? 7. How does RNA differ from DNA? 8. Explain how ATP functions as the primary energy transfer molecule in living cells 9. What aspects ...
... 4. Stanley Miller's 1953 experiments proved that. Explain? 5. Why are hydrocarbons insoluble in water? 6. Humans can digest starch but not cellulose because. Explain? 7. How does RNA differ from DNA? 8. Explain how ATP functions as the primary energy transfer molecule in living cells 9. What aspects ...
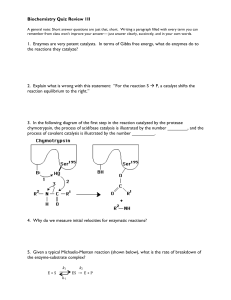
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1II 1. Enzymes are very potent catalysts
... the breakdown of fructose, lactose, or sucrose are defective. However, there are very few cases of people having a genetic disease in which one of the enzymes of glycolysis is severely affected. Why do you suppose such mutations are seen so rarely? ...
... the breakdown of fructose, lactose, or sucrose are defective. However, there are very few cases of people having a genetic disease in which one of the enzymes of glycolysis is severely affected. Why do you suppose such mutations are seen so rarely? ...
Biomolecules Fill in the crossword puzzle by using
... amino acids examples are insulin,hemglobin and enzymes. are the small building blocks of polymers ...
... amino acids examples are insulin,hemglobin and enzymes. are the small building blocks of polymers ...
Fatty acid breakdown
... cis conformation, enoyl-CoA hydratase cannot work on as it requires a trans bond • The actions of an isomerase and a reductase convert the cis bond to trans, resulting in a substrate for b-oxidation ...
... cis conformation, enoyl-CoA hydratase cannot work on as it requires a trans bond • The actions of an isomerase and a reductase convert the cis bond to trans, resulting in a substrate for b-oxidation ...
LB Fat metabolism A
... Unlike glucose and amino acids, most lipids from a meal do not directly enter the bloodstream. Instead, they are packaged into chylomicrons and released into the lymph. The lymph dumps into the aortic arch (near the heart), where it then is transported through the bloodstream to be cleared (taken up ...
... Unlike glucose and amino acids, most lipids from a meal do not directly enter the bloodstream. Instead, they are packaged into chylomicrons and released into the lymph. The lymph dumps into the aortic arch (near the heart), where it then is transported through the bloodstream to be cleared (taken up ...
Trans Fatty Acids
... • Well, since this drastic change in conformation changes how the fatty acid functions in the roles it holds. This has implicated it in many health problems – Increase in coronary disease, and arteriosclerosis rates ...
... • Well, since this drastic change in conformation changes how the fatty acid functions in the roles it holds. This has implicated it in many health problems – Increase in coronary disease, and arteriosclerosis rates ...
4. DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION OF LIPIDS
... components. • This is necessary for their absorption, since the cells lining the intestine are able to absorb them into the bloodstream only as relatively small molecules. ...
... components. • This is necessary for their absorption, since the cells lining the intestine are able to absorb them into the bloodstream only as relatively small molecules. ...
Fatty Acid Spiral
... Our diets must contain a reasonable ratio of the essential amino acids in order for our bodies to maintain health. – Meat, eggs, soy and milk contain the essential amino acids in a similar ratio to that needed by humans. – Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains tend to be high in some and low i ...
... Our diets must contain a reasonable ratio of the essential amino acids in order for our bodies to maintain health. – Meat, eggs, soy and milk contain the essential amino acids in a similar ratio to that needed by humans. – Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains tend to be high in some and low i ...
Document
... Our diets must contain a reasonable ratio of the essential amino acids in order for our bodies to maintain health. – Meat, eggs, soy and milk contain the essential amino acids in a similar ratio to that needed by humans. – Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains tend to be high in some and low i ...
... Our diets must contain a reasonable ratio of the essential amino acids in order for our bodies to maintain health. – Meat, eggs, soy and milk contain the essential amino acids in a similar ratio to that needed by humans. – Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains tend to be high in some and low i ...
NUTRIENT Handout
... All of the nutrients fit into one of these classes. Sometimes the things we ANALYZE, however, are not so clear cut. For example, we don't analyze just for "carbohydrates" because some of the carbohydrates are very digestible and some are very indigestible. For purposes of ANALYSIS, we often use a ve ...
... All of the nutrients fit into one of these classes. Sometimes the things we ANALYZE, however, are not so clear cut. For example, we don't analyze just for "carbohydrates" because some of the carbohydrates are very digestible and some are very indigestible. For purposes of ANALYSIS, we often use a ve ...