2.3 Biomolecules Hon
... Organic: contains carbon and hydrogen ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon and hydrogen ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
Unit 2: Metabolic Processes Metabolism and Energy
... - Point of entry depends on amino acid - Eg: leucine acetyl-CoA ...
... - Point of entry depends on amino acid - Eg: leucine acetyl-CoA ...
The pathway from “activated acetic acid” to fatty acids and terpenes
... Triglycerides are also stored in muscle ...
... Triglycerides are also stored in muscle ...
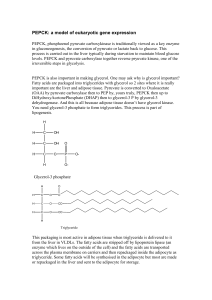
PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression
... PEPCK, phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase is traditionally viewed as a key enzyme in gluconeogenesis, the conversion of pyruvate or lactate back to glucose. This process is carried out in the liver typically during starvation to maintain blood glucose levels. PEPCK and pyruvate carboxylase together ...
... PEPCK, phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase is traditionally viewed as a key enzyme in gluconeogenesis, the conversion of pyruvate or lactate back to glucose. This process is carried out in the liver typically during starvation to maintain blood glucose levels. PEPCK and pyruvate carboxylase together ...
Principles of Biochemistry 4/e
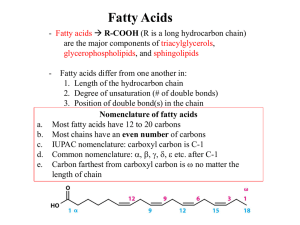
... Fatty acids differ from one another in: 1. Length of the hydrocarbon chain 2. Degree of unsaturation (# of double bonds) 3. Position of double bond(s) in the chain Nomenclature of fatty acids Most fatty acids have 12 to 20 carbons Most chains have an even number of carbons IUPAC nomenclature: carbox ...
... Fatty acids differ from one another in: 1. Length of the hydrocarbon chain 2. Degree of unsaturation (# of double bonds) 3. Position of double bond(s) in the chain Nomenclature of fatty acids Most fatty acids have 12 to 20 carbons Most chains have an even number of carbons IUPAC nomenclature: carbox ...
Metabolism of the whole organism
... • uses keto acids for fuel • Kidney: needs energy for active transport • uses FA, KB, glucose, amino acids, • gluneogenic tissue ...
... • uses keto acids for fuel • Kidney: needs energy for active transport • uses FA, KB, glucose, amino acids, • gluneogenic tissue ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis Chapter 28, Stryer Short Course
... receptors in non-liver cells • HDLs are “good cholesterol” ...
... receptors in non-liver cells • HDLs are “good cholesterol” ...
Nutrition & Metabolism
... Relationship of height and weight Formula: weight (lb) / [height (in)]2 x 703 ...
... Relationship of height and weight Formula: weight (lb) / [height (in)]2 x 703 ...
2-A Chemical Compounds of Life Organic Compounds
... 1.Carbohydrates (sugars) a)Used to store energy and for structure in plants & some animals b)H:O ratio = 2:1 c)Monosaccharide = simple sugar ...
... 1.Carbohydrates (sugars) a)Used to store energy and for structure in plants & some animals b)H:O ratio = 2:1 c)Monosaccharide = simple sugar ...
biological_molecules_facts
... coiled forming a compact molecule. It is used for storage. Starch is tested with iodine solution, giving a blue-black colour change. Glycogen is a polysaccharide formed in animal cells. It is very branched. Cellulose is a polysaccharide formed from -glucose molecules. It has straight chains that ar ...
... coiled forming a compact molecule. It is used for storage. Starch is tested with iodine solution, giving a blue-black colour change. Glycogen is a polysaccharide formed in animal cells. It is very branched. Cellulose is a polysaccharide formed from -glucose molecules. It has straight chains that ar ...
Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... – Small, simple molecules – Amino acid, fatty acid, nucleotide, monosaccharide ...
... – Small, simple molecules – Amino acid, fatty acid, nucleotide, monosaccharide ...
Organic Molecules - Mr. Swords` Classes
... Speeds up reaction, can be used over and over again. The reaction does not change it (like a key!) ...
... Speeds up reaction, can be used over and over again. The reaction does not change it (like a key!) ...
Compounds of Life Chart
... Polysaccharides – made of two or more monosaccharides o Starch (how plants store glucose) o Cellulose (dietary fiber in animals, component of cell walls in plants) o Glycogen (how animals store glucose) ...
... Polysaccharides – made of two or more monosaccharides o Starch (how plants store glucose) o Cellulose (dietary fiber in animals, component of cell walls in plants) o Glycogen (how animals store glucose) ...
Fatty Acid Oxidation and Ketone Bodies
... Fed state: Malonyl-CoA formed in the fed state is a potent inhibitor of CPT-1. Under these conditions, free fatty acids enter the liver cell in low concentrations and are nearly all esterified to acylglycerols and transported out as VLDL. Starvation: Free fatty acid concentration increases with sta ...
... Fed state: Malonyl-CoA formed in the fed state is a potent inhibitor of CPT-1. Under these conditions, free fatty acids enter the liver cell in low concentrations and are nearly all esterified to acylglycerols and transported out as VLDL. Starvation: Free fatty acid concentration increases with sta ...
Lipids
... • Important cell component – animal cell membranes – precursor of all other steroids • including vertebrate sex hormones ...
... • Important cell component – animal cell membranes – precursor of all other steroids • including vertebrate sex hormones ...
Solgar® Earth Source® Organic Flaxseed Oil
... Solgar ® Earth Source ® Organic Flaxseed Oil provides one of the most concentrated vegan plant sources of omega-3 fatty acids found in nature. It also supplies the omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids linoleic acid and oleic acid. Fatty acids play a role in providing an energy source for the body and sup ...
... Solgar ® Earth Source ® Organic Flaxseed Oil provides one of the most concentrated vegan plant sources of omega-3 fatty acids found in nature. It also supplies the omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids linoleic acid and oleic acid. Fatty acids play a role in providing an energy source for the body and sup ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
CH 5: Carbs, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids – Study Chart I
... Directions: Use your textbook, class notes, and/or internet resources to complete the charts below. In the “box” to the right of each molecule, write a brief description explaining what the molecule is, or does, or is used for, in living things. ...
... Directions: Use your textbook, class notes, and/or internet resources to complete the charts below. In the “box” to the right of each molecule, write a brief description explaining what the molecule is, or does, or is used for, in living things. ...
Biology Study Guide for Section (Macromolecules) Test
... Energy-The main function of carbohydrates in animal cells. Sugars- Similar to starch, cellulose is a complex carbohydrate. This compound makes up cellulose. Nitrogen- Carbohydrates contain all C,H,O but no nitrogen. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. Glucose-is also called a monosacchar ...
... Energy-The main function of carbohydrates in animal cells. Sugars- Similar to starch, cellulose is a complex carbohydrate. This compound makes up cellulose. Nitrogen- Carbohydrates contain all C,H,O but no nitrogen. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. Glucose-is also called a monosacchar ...
lecture_22 - WordPress.com
... Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase: an enzyme similar to succinate dehydrogenase ...
... Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase: an enzyme similar to succinate dehydrogenase ...
Ex. glucose, fructose and galactose: these are isomers
... D. Functions: there are many different kinds of proteins each with different roles. 1. Provide________________ ________________ and _______________________ in cells. Example: Keratin and Collagen. 2. Control the __________ of ________________ reactions: enzymes 3. Carry and transport substances in a ...
... D. Functions: there are many different kinds of proteins each with different roles. 1. Provide________________ ________________ and _______________________ in cells. Example: Keratin and Collagen. 2. Control the __________ of ________________ reactions: enzymes 3. Carry and transport substances in a ...
Slide 1
... Fat catabolism: generation of energy by fatty acid oxidation Fat (triacylglycerol) and Fatty Acids: 90% of dietary lipids are tryacylglycerol, a hydrophobic, neutral molecule made from reaction of OH group of glycerol and COO- group of fatty acids. Fatty acids are made up of a long hydrophobic hydro ...
... Fat catabolism: generation of energy by fatty acid oxidation Fat (triacylglycerol) and Fatty Acids: 90% of dietary lipids are tryacylglycerol, a hydrophobic, neutral molecule made from reaction of OH group of glycerol and COO- group of fatty acids. Fatty acids are made up of a long hydrophobic hydro ...
FATS - Catherine Huff`s Site
... component of cell membranes building blocks for other molecules acts as a water proofing substance ...
... component of cell membranes building blocks for other molecules acts as a water proofing substance ...