Lipids (PowerPoint)
... Lipids are hydrophobic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. They contain fewer polar O-H bonds and more nonpolar C-H bonds than do carbohydrates, thus they are insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar substances. Why are lipids important? Organisms use lipids for: 1. Storing energy 2 ...
... Lipids are hydrophobic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. They contain fewer polar O-H bonds and more nonpolar C-H bonds than do carbohydrates, thus they are insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar substances. Why are lipids important? Organisms use lipids for: 1. Storing energy 2 ...
nucleic acid - 4J Blog Server
... • The cellular functions of lipids. • How the sequence and subcomponents of lipids determine their properties. • The basic structure of a nucleic acid. ...
... • The cellular functions of lipids. • How the sequence and subcomponents of lipids determine their properties. • The basic structure of a nucleic acid. ...
Lipid Metabolizması - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Fat catabolism: generation of energy by fatty acid oxidation Fat (triacylglycerol) and Fatty Acids: 90% of dietary lipids are tryacylglycerol, a hydrophobic, neutral molecule made from reaction of OH group of glycerol and COO- group of fatty acids. Fatty acids are made up of a long hydrophobic hydro ...
... Fat catabolism: generation of energy by fatty acid oxidation Fat (triacylglycerol) and Fatty Acids: 90% of dietary lipids are tryacylglycerol, a hydrophobic, neutral molecule made from reaction of OH group of glycerol and COO- group of fatty acids. Fatty acids are made up of a long hydrophobic hydro ...
Document
... G. Importance of lipids- alternate energy source other than monosaccharides; fats are lighter than polysacc. and take up less space ...
... G. Importance of lipids- alternate energy source other than monosaccharides; fats are lighter than polysacc. and take up less space ...
Macromolecules 9-3
... molecule joins monomers together to form polymers a. This process can reverse b. The adding of a water molecule to a polymer, which breaks the polymer into a monomer is called hydrolysis Lipids a. DO NOT FORM POLYMERS b. “Water-Fearing” i. HYDROPHOBIC c. Three classes of biologically important lipid ...
... molecule joins monomers together to form polymers a. This process can reverse b. The adding of a water molecule to a polymer, which breaks the polymer into a monomer is called hydrolysis Lipids a. DO NOT FORM POLYMERS b. “Water-Fearing” i. HYDROPHOBIC c. Three classes of biologically important lipid ...
Ch.24Pt.4_000
... Pancreatic lipase (PL) hydrolyzes insoluble triglyceride by binding to the bile-salt micelles TAGs are partially hydrolyzed: 2 of the 3 F.A.s have ester linkages hydrolyzed and are released. Monoacylglycerol remains = glycerol and 1 fatty acid ...
... Pancreatic lipase (PL) hydrolyzes insoluble triglyceride by binding to the bile-salt micelles TAGs are partially hydrolyzed: 2 of the 3 F.A.s have ester linkages hydrolyzed and are released. Monoacylglycerol remains = glycerol and 1 fatty acid ...
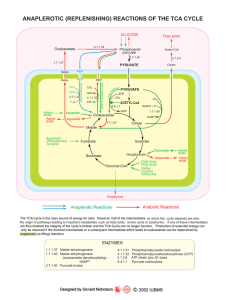
anaplerotic (replenishing) reactions of the tca cycle - Sigma
... The TCA Cycle is the main source of energy for cells. However, half of the intermediates on which the cycle depends are also the origin of pathways leading to important metabolites such as fatty acids , amino acids or porphyrins. If any of these intermediates are thus diverted the integrity of the c ...
... The TCA Cycle is the main source of energy for cells. However, half of the intermediates on which the cycle depends are also the origin of pathways leading to important metabolites such as fatty acids , amino acids or porphyrins. If any of these intermediates are thus diverted the integrity of the c ...
Respiratory Substrates
... • Number of hydrogen atoms per mole accepted by NAD then used in electron transport chain is slightly more than the number of hydrogen atoms per mole of glucose, so proteins release slightly more energy than equivalent masses of glucose ...
... • Number of hydrogen atoms per mole accepted by NAD then used in electron transport chain is slightly more than the number of hydrogen atoms per mole of glucose, so proteins release slightly more energy than equivalent masses of glucose ...
碩命題橫式 - 國立彰化師範大學圖書館
... 10. The direct sources of nitrogen that are used to make urea via the Urea Cycle are: (a). citrulline and ornithine (b). arginine and aspartate (c). arginine and citrulline (d). ammonia and arginine (e). aspartate and ammonia 11. Which product in glycolysis also involve in serine synthesis? (a) G6P. ...
... 10. The direct sources of nitrogen that are used to make urea via the Urea Cycle are: (a). citrulline and ornithine (b). arginine and aspartate (c). arginine and citrulline (d). ammonia and arginine (e). aspartate and ammonia 11. Which product in glycolysis also involve in serine synthesis? (a) G6P. ...
Biological Molecules - Princeton High School
... R group = red (varies in each AA and determines the AA’s form and function ...
... R group = red (varies in each AA and determines the AA’s form and function ...
Kevin Ahern's Biochemistry Course (BB 350) at Oregon State University
... enzyme catalyzes conversion of cis bonds between carbons 3 and 4 to trans bonds between carbons 2 and 3 so it can be oxidized in beta oxidation. Dina catalyzes conversion of two double bonds into one cis double bond between carbons 3 and 4, which is, in turn, converted to a trans between carbons 2 a ...
... enzyme catalyzes conversion of cis bonds between carbons 3 and 4 to trans bonds between carbons 2 and 3 so it can be oxidized in beta oxidation. Dina catalyzes conversion of two double bonds into one cis double bond between carbons 3 and 4, which is, in turn, converted to a trans between carbons 2 a ...
Biomolecules Review
... Is it a chiral molecule? ____ 5. What structural characteristics distinguish fatty acid from other carboxylic acids? ...
... Is it a chiral molecule? ____ 5. What structural characteristics distinguish fatty acid from other carboxylic acids? ...
Fish Oil - Sundown Naturals
... Health experts agree: not all fat is bad for you. Omega-3 fatty acids are considered some of the “good” fats important for cellular, heart and metabolic health.* Getting an adequate amount of fatty acids to promote heart health is not easy.* Sundown Naturals’ Fish Oil 1000 mg contains eicosapentaeno ...
... Health experts agree: not all fat is bad for you. Omega-3 fatty acids are considered some of the “good” fats important for cellular, heart and metabolic health.* Getting an adequate amount of fatty acids to promote heart health is not easy.* Sundown Naturals’ Fish Oil 1000 mg contains eicosapentaeno ...
Apoptosis
... • Abundant in nervous system • Has structural similarity to phospholipids – Ceramide tells cells to undergo apoptosis – Sphingosine tells cells to grow, divide and migrate ...
... • Abundant in nervous system • Has structural similarity to phospholipids – Ceramide tells cells to undergo apoptosis – Sphingosine tells cells to grow, divide and migrate ...
Ch7METABOLISM
... compounds, making new compounds, and transporting compounds from place to place. ...
... compounds, making new compounds, and transporting compounds from place to place. ...
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS - anderson1.k12.sc.us
... made of carbon atoms (with hydrogen and oxygen) most molecules with carbon are organic ...
... made of carbon atoms (with hydrogen and oxygen) most molecules with carbon are organic ...
Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol
... • sphingomyelin *** Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol (lecithin, phosphatidylcholine phosphatidylserine and cardiolipin). Sphingomyelin contains a sphingosine backbone instead of glycerol. Phospholipids are lipids. Each molecule is made up of one glycerol molecule attached to two fatty ac ...
... • sphingomyelin *** Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol (lecithin, phosphatidylcholine phosphatidylserine and cardiolipin). Sphingomyelin contains a sphingosine backbone instead of glycerol. Phospholipids are lipids. Each molecule is made up of one glycerol molecule attached to two fatty ac ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Seventeen arachidonic acid (17.2) a fatty acid that is derived from linolenic acid; the precursor of the prostaglandins. atherosclerosis (17.4) deposition of excess plasma cholesterol and other lipids and proteins on the walls of arteries, resulting in a decreased ar ...
... Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Seventeen arachidonic acid (17.2) a fatty acid that is derived from linolenic acid; the precursor of the prostaglandins. atherosclerosis (17.4) deposition of excess plasma cholesterol and other lipids and proteins on the walls of arteries, resulting in a decreased ar ...
myelin sheath
... (cells that protect the body by destroying foreign microorganisms. Galactocerebroside is found almost exclusively in the membranes of brain cells. ...
... (cells that protect the body by destroying foreign microorganisms. Galactocerebroside is found almost exclusively in the membranes of brain cells. ...