Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in
... monoacylglycerols, free fatty acids, and glycerol. Both free fatty acids and monoacylglycerols enter the glyoxysome (see p 485 in your text), whereas most of the glycerol is metabolized in the plant cell cytosol. A membrane-bound lipase in the glyoxysome converts monoacylglycerols to free fatty acid ...
... monoacylglycerols, free fatty acids, and glycerol. Both free fatty acids and monoacylglycerols enter the glyoxysome (see p 485 in your text), whereas most of the glycerol is metabolized in the plant cell cytosol. A membrane-bound lipase in the glyoxysome converts monoacylglycerols to free fatty acid ...
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... 16. Describe the part of the glycolytic pathway from fructose 6-phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3phosphate. Show structures of intermediates, enzyme names, and indicate where any cofactors ...
... 16. Describe the part of the glycolytic pathway from fructose 6-phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3phosphate. Show structures of intermediates, enzyme names, and indicate where any cofactors ...
Practice Quiz
... 13. Weak acids and weak bases help the body to resist shifts in pH and are therefore called ____________. 14. A common example of a monosaccharide is _________________. 15. The monomer units of a triglyceride are: three ______________ and one ____________. 16. The monomer unit of a protein is a(n) _ ...
... 13. Weak acids and weak bases help the body to resist shifts in pH and are therefore called ____________. 14. A common example of a monosaccharide is _________________. 15. The monomer units of a triglyceride are: three ______________ and one ____________. 16. The monomer unit of a protein is a(n) _ ...
Lipids
... • 3 fatty acid molecules joined to a glycerol • Each fatty acid consists of an acid COOH group joined to a long hydrocarbon chain consisting of carbon and hydrogen • The length of the hydrocarbon chain varies but in many of the fatty acids in triglycerides there are between 14 and 16 carbon atoms ...
... • 3 fatty acid molecules joined to a glycerol • Each fatty acid consists of an acid COOH group joined to a long hydrocarbon chain consisting of carbon and hydrogen • The length of the hydrocarbon chain varies but in many of the fatty acids in triglycerides there are between 14 and 16 carbon atoms ...
Lipids_Notes
... Lipids are formed by condensation reactions between fatty acids and an alcohol Fatty Acids Contain the acidic carboxyl –COOH group. Have the general formula R.COOH where R is hydrogen or a group such as CH3, C2H5, or C3H7 and so on. Usually many carbons in the fatty acids used to make lipids ...
... Lipids are formed by condensation reactions between fatty acids and an alcohol Fatty Acids Contain the acidic carboxyl –COOH group. Have the general formula R.COOH where R is hydrogen or a group such as CH3, C2H5, or C3H7 and so on. Usually many carbons in the fatty acids used to make lipids ...
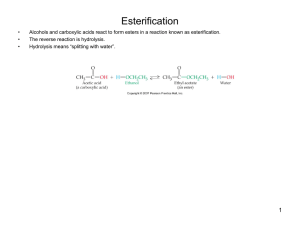
Esterification
... Prostaglandins and Pain Arachadonic acid is synthesized from an essential omega-6-fatty acid that must be obtained from diet. Arachadonic acid is used by the body to make prostaglandins. Cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes are needed for these reactions to occur. Since prostaglandin production is responsi ...
... Prostaglandins and Pain Arachadonic acid is synthesized from an essential omega-6-fatty acid that must be obtained from diet. Arachadonic acid is used by the body to make prostaglandins. Cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes are needed for these reactions to occur. Since prostaglandin production is responsi ...
Acyl-CoA synthetases : Fatty acid +CoA + ATP → fatty acyl
... • Ketone bodies in the blood and urine of untreated diabetics can reach extraordinary levels, a condition called ketosis. • In individuals on every low-calorie diets, using the fats stored in adipose tissue as their major energy source, levels of ketone bodies in the blood and urine must be monitor ...
... • Ketone bodies in the blood and urine of untreated diabetics can reach extraordinary levels, a condition called ketosis. • In individuals on every low-calorie diets, using the fats stored in adipose tissue as their major energy source, levels of ketone bodies in the blood and urine must be monitor ...
NME2.29 - Fat and Carbohydrate Metabolism 2
... o Sequence of enzymatic reactions resulting in production of acetoacetate / 3-hydroxybutyrate o HMG-CoA lyase, the enzyme that produces acetoacetate, is only found in the liver Ketone bodies are synthesised in starvation and diabetes in response to: o High levels of circulating free fatty acids (e.g ...
... o Sequence of enzymatic reactions resulting in production of acetoacetate / 3-hydroxybutyrate o HMG-CoA lyase, the enzyme that produces acetoacetate, is only found in the liver Ketone bodies are synthesised in starvation and diabetes in response to: o High levels of circulating free fatty acids (e.g ...
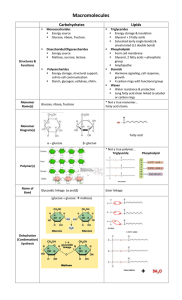
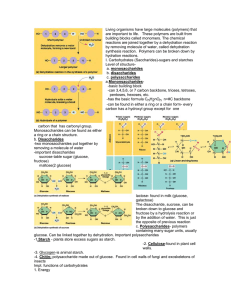
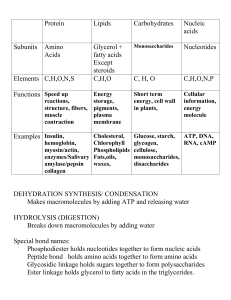
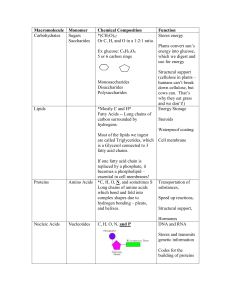
Living organisms have large molecules (polymers) that are
... have a carboxyl group and a hydrocarbon tail.Palmic acid is a saturated fatty acid with the maximum amount of hydrogens. Linoleic acid is called an unsaturated fatty acid. This means that it contains double bonds and is missing some hydrogen. Synthesis of a triglyceride involves 3 fatty acids and a ...
... have a carboxyl group and a hydrocarbon tail.Palmic acid is a saturated fatty acid with the maximum amount of hydrogens. Linoleic acid is called an unsaturated fatty acid. This means that it contains double bonds and is missing some hydrogen. Synthesis of a triglyceride involves 3 fatty acids and a ...
LIPIDS
... Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain, solid at room temperature (animal fats, butter, lard). Unsaturated fatty acids do have double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain, liquid at room temperature, known as oils (plant fats). ...
... Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain, solid at room temperature (animal fats, butter, lard). Unsaturated fatty acids do have double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain, liquid at room temperature, known as oils (plant fats). ...
Lecture Slides for Fatty Acid Catabolism
... • Lack of intrinsic factor results in impaired B12 absorption, pernicious anemia, death in 1-3 years • Original treatment (1920’s) was ½ lb. of raw liver daily • Concentrated liver juice (yum) became available in 1928 • B12 isolated in 1948, synthesized in 1973 • Now treated with large doses (severa ...
... • Lack of intrinsic factor results in impaired B12 absorption, pernicious anemia, death in 1-3 years • Original treatment (1920’s) was ½ lb. of raw liver daily • Concentrated liver juice (yum) became available in 1928 • B12 isolated in 1948, synthesized in 1973 • Now treated with large doses (severa ...
Digestion and Respiration MMHS Anatomy Chitraroff
... Digestion and Respiration MMHS Anatomy Chitraroff ...
... Digestion and Respiration MMHS Anatomy Chitraroff ...
Document
... Phospholipid Facts • Polar Phospholipids make up most of a cell membrane • Made of a polar “head” with a + AND - charge ...
... Phospholipid Facts • Polar Phospholipids make up most of a cell membrane • Made of a polar “head” with a + AND - charge ...
File
... Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Can occur in the cytoplasm of most animal cells, but the liver is the major site for this process Fatty acids are synthesized when the diet is low in fat or high in carbohydrate or protein (most from glucose via pyruvate) A large quantity of NADPH is needed for this process a ...
... Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Can occur in the cytoplasm of most animal cells, but the liver is the major site for this process Fatty acids are synthesized when the diet is low in fat or high in carbohydrate or protein (most from glucose via pyruvate) A large quantity of NADPH is needed for this process a ...
Lipids (fats)
... Also known as fats Made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen When your body breaks down lipids, it turns it into fatty acids and glycerol ...
... Also known as fats Made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen When your body breaks down lipids, it turns it into fatty acids and glycerol ...
Text S3: Fatty acid synthesis and catabolism
... Text S3: Fatty acid synthesis and catabolism Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 is able to synthesize fatty acids de novo from acetyl-CoA and incorporate them into phospholipids. This strain has an absolute requirement for several volatile acids for growth [1], utilizing isobutyrate and valerate for produ ...
... Text S3: Fatty acid synthesis and catabolism Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 is able to synthesize fatty acids de novo from acetyl-CoA and incorporate them into phospholipids. This strain has an absolute requirement for several volatile acids for growth [1], utilizing isobutyrate and valerate for produ ...