* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mrs. LeCompte
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
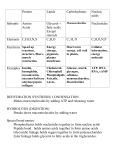
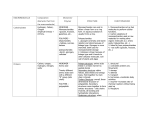
3-2: Carbs 4 MAJOR CLASSES OF BIOMOLECULES 1. CARBOHYDRATES = sugars and their polymers Used for ENERGY and CARBON sources 3 Types: a) Monosaccharides = monomers of sugars in which C, H, and O occur in the ratio of 1:2:1 (CH2O)n Ex. C6H12O6 o Major E SOURCE for cells (GLUCOSE is the most common) o Store energy in their chemical bonds o Carbon skeletons are raw materials for other organic molecules o Characteristics: An –OH group is attached to each C except one, which is doublebonded to an oxygen Size of the carbon skeleton varies from 3 to 7 carbons Spatial arrangement around asymmetric carbons may vary In aqueous solutions, many monosaccharides form rings b) Disaccharide = a double sugar that is made of 2 monosaccharides monomers joined by a glycosidic linkage o Ex. Sucrose = glucose + fructose c) Polysaccharides = macromolecules that are polymers of a few hundred or thousand monosaccharides o Formed by dehydration reactions o Tend to be linear in shape o Two Types: STORAGE Polysaccharides (for energy and carbon) Starch = storage polysaccharide for glucose in plants o Most animals have digestive enzymes to break down starch Glycogen = storage polysaccharide for glucose in animals o Stored in the liver and muscle of humans other vertebrates o Insulin triggers its creation from glucose molecules, glucagon causes its breakdown into glucoses STRUCTURAL Polysaccharides = for cell/body support Cellulose – structural polysaccharide in plant cells walls o Is the most abundant organic molecule on Earth o Cannot be digested by most animals, since they lack the enzyme that can hydrolyze the β-linkage Peptidoglycan in bacteria Chitin – structural polysaccharide of an amino sugar (with a Ncontaining group that replaces a hydroxyl) o Found in exoskeletons of arthropods and cells walls of Fungi 2. LIPIDS = diverse group of organic compounds that are insoluble in water A) Fats and Oils (a.k.a. Triglycerides) = Macromolecules made of: Glycerol – a 3-C alcohol with three –OH groups attached 3 Fatty Acids o Hydrocarbon chain has a long C-skeleton usually with an even number of carbon atoms (most with 16-18 carbons) o Nonpolar C-H bonds make the chain hydrophobic and not water soluble o Attached to the glycerol by an ester linkage = bond formed between a –OH group and a –COOH group Variation is in the fatty acid composition o Fatty acids may all be the same or they may differ o Fatty acids may vary in length o Fatty acids may vary in the number and location of double bonds between C’s SATURATED FAT NO double bonds between C’s in fatty acid UNSATURATED FAT One or more double bonds… tails - Bonded to maximum # of H’s (“saturated”) Tail kinks at each C=C, so molecules do not Straight chains pack closely Solids at room temperature Liquids at room temperature Animal fats (ex. Lard and Butter) Plant fats (ex. Olive oil) Functions of Fats: o Energy storage o LONG-TERM fuel reservoir Gram-for-gram, fats store 4x more energy than glycogen o Cushion vital organs o Protects against heat loss (ex. Blubber) B) Phospholipids = glycerol + 2 fatty acids + one phosphate group o 3rd C of glycerol is joined to a negatively charged phosphate group Often the phosphate will have additional side groups attached to it o Shows ambivalent behavior toward water. o Tails are hydrophobic, but phosphate “head” is polar and hydrophilic o Are major constituents of cell membranes!!! Form the Lipid Bilayer C) Steroids = lipids which have 4 fused C-rings with various functional groups attached o “Honeycomb, honeycomb, honeycomb, house” o Cholesterol is an important steroid Precursor to sex hormones, bile acids, etc. Common component of animal cell membranes Can contribute to atherosclerosis D) Waxes = long-chain fatty acids bonded with long-chain alcohols o High melting points at normal temperatures (solid) o Hydrophobic repel water and resist degradation o Form a protective cuticle on the outsides of plants, preventing water loss