A, C
... A. What kind of reaction is this? B. How many bonds are formed? C. Is water a reactant (used) or a product (formed)? D. How many water molecules are involved? ...
... A. What kind of reaction is this? B. How many bonds are formed? C. Is water a reactant (used) or a product (formed)? D. How many water molecules are involved? ...
Ch 28 Reading guide
... 3. What is the role of citrate lyase? What hormone leads to its activation? 4. The synthesis of palmitate requires _____ molecules of NADPH as well as __________. 5. The shuttle that returns oxaloacetate back to the matrix also produces _____________, which is needed in fatty acid synthesis. 6. Draw ...
... 3. What is the role of citrate lyase? What hormone leads to its activation? 4. The synthesis of palmitate requires _____ molecules of NADPH as well as __________. 5. The shuttle that returns oxaloacetate back to the matrix also produces _____________, which is needed in fatty acid synthesis. 6. Draw ...
3.2 Carbohydrates, lipids annd proteins
... 3.2.5: Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides. ...
... 3.2.5: Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides. ...
essential fatty acids
... fat When fat enters the small intestine, the gallbladder secretes bile. Bile has an affinity for both fat and water, so it can bring the fat into the water. ...
... fat When fat enters the small intestine, the gallbladder secretes bile. Bile has an affinity for both fat and water, so it can bring the fat into the water. ...
Sample exam 1
... 6. How many ATP molecules will the following fatty acids make? Give a reasonably detailed accounting to justify your answers. a. 16:0 b. 20:4 7. Gastric juice has a pH of 1.5 and is produced by pumping HCl from blood plasma (pH 7.4) into the stomach. a. Calculate the free energy required to concentr ...
... 6. How many ATP molecules will the following fatty acids make? Give a reasonably detailed accounting to justify your answers. a. 16:0 b. 20:4 7. Gastric juice has a pH of 1.5 and is produced by pumping HCl from blood plasma (pH 7.4) into the stomach. a. Calculate the free energy required to concentr ...
Food Chemistry for 1..
... • Peptide bonds can be broken apart if the temperature is higher • Peptide bonds can also be broken apart by acid ...
... • Peptide bonds can be broken apart if the temperature is higher • Peptide bonds can also be broken apart by acid ...
Organic chemistry ppt
... • Most abundant carbon compounds found in living things • Sugars (example) = quick energy • Monosaccharides- simple sugars » Glucose ...
... • Most abundant carbon compounds found in living things • Sugars (example) = quick energy • Monosaccharides- simple sugars » Glucose ...
Week 4 - Composition of Cells
... they have one glycerol molecule and three fatty acid tails. Phospholipids are the main constituent of plasma membranes. They have a phosphate group attached to the glycerol and two fatty acid tails. ...
... they have one glycerol molecule and three fatty acid tails. Phospholipids are the main constituent of plasma membranes. They have a phosphate group attached to the glycerol and two fatty acid tails. ...
Key: Biomolecule Study Guide 1) In animals, excess carbohydrates
... They must fit the molecules that they interact with (Lock and Key) 10) What does it mean to say an enzyme is “denatured”? It has changed its 3-D shape 11) What are 2 ways to denature an enzyme? Change the temperature or pH ...
... They must fit the molecules that they interact with (Lock and Key) 10) What does it mean to say an enzyme is “denatured”? It has changed its 3-D shape 11) What are 2 ways to denature an enzyme? Change the temperature or pH ...
Delivery of Nutrients to Cells
... Hepatic Portal Vein: Carries blood from another source ( e.g. from the intestine) to the liver which then leads to the general circulation. ...
... Hepatic Portal Vein: Carries blood from another source ( e.g. from the intestine) to the liver which then leads to the general circulation. ...
Sample exam 1
... 6. Gastric juice has a pH of 1.5 and is produced by pumping HCl from blood plasma (pH 7.4) into the stomach. a. Calculate the free energy required to concentrate the H+ in 1 L of gastric juice at 37°C. For this problem, you can ignore the effects of the transmembrane electrical potential difference. ...
... 6. Gastric juice has a pH of 1.5 and is produced by pumping HCl from blood plasma (pH 7.4) into the stomach. a. Calculate the free energy required to concentrate the H+ in 1 L of gastric juice at 37°C. For this problem, you can ignore the effects of the transmembrane electrical potential difference. ...
NORTH NTR W4 reading
... NOTE: SKIP the Focus on Alcohol information. We will cover that information later! Objectives ...
... NOTE: SKIP the Focus on Alcohol information. We will cover that information later! Objectives ...
lecture4
... (also called neutral fats or triglycerides), which are uncharged esters of fatty acids with glycerol (Figure 22.1). Fatty acids mobilized from triacylglycerols are oxidized to meet the energy needs of a cell or organism. Fourth, fatty acid derivatives serve as hormones and intracellular messengers. ...
... (also called neutral fats or triglycerides), which are uncharged esters of fatty acids with glycerol (Figure 22.1). Fatty acids mobilized from triacylglycerols are oxidized to meet the energy needs of a cell or organism. Fourth, fatty acid derivatives serve as hormones and intracellular messengers. ...
Fatty Acid Oxidation
... pathological states. Following this lecture students should understand that ...
... pathological states. Following this lecture students should understand that ...
Hein and Arena - University of Wisconsin–Eau Claire
... because they contain more saturated fatty acid residues and have melting points above room temperature. • Vegetable oils, on the other hand, are liquids at room temperature because they contain a high percentage of unsaturated fatty acid residues and have melting points below room temperature. ...
... because they contain more saturated fatty acid residues and have melting points above room temperature. • Vegetable oils, on the other hand, are liquids at room temperature because they contain a high percentage of unsaturated fatty acid residues and have melting points below room temperature. ...
Chapter 19
... • Excess of acetyl-CoA is converted to ketone bodies (acetoacetate + β-hydroxybutyrate) in mitochondria of liver cells. Ketone bodies are used as energy source. • 3 Acetyl-CoA are condensed to β-hydroxyl-β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), and then break down to acetoacetate & acetyl-CoA by HMG-CoA lyas ...
... • Excess of acetyl-CoA is converted to ketone bodies (acetoacetate + β-hydroxybutyrate) in mitochondria of liver cells. Ketone bodies are used as energy source. • 3 Acetyl-CoA are condensed to β-hydroxyl-β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), and then break down to acetoacetate & acetyl-CoA by HMG-CoA lyas ...
Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... • Fatty Acids (FA) and Triglycerides (TG) – high density energy store ...
... • Fatty Acids (FA) and Triglycerides (TG) – high density energy store ...
03. Lipids. Classification, structure and biological role
... estimated that a 60 kg person has a total of about 175 g of cholesterol distributed throughout the body. Much of this cholesterol is bonded through ester links to fatty acids, but some is found as the free alcohol. Gallstones, for example, are nearly purecholesterol. • Cholesterol serves two importa ...
... estimated that a 60 kg person has a total of about 175 g of cholesterol distributed throughout the body. Much of this cholesterol is bonded through ester links to fatty acids, but some is found as the free alcohol. Gallstones, for example, are nearly purecholesterol. • Cholesterol serves two importa ...
C383 Study Guide for the Final Exam Spring 2016 Basic Information
... molecule that you store in your liver. Circle the pathways/cycles below that are part of this overall transformation. Cross out any that are not. Gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, citric acid cycle B. Trace the metabolic path of this glutamate molecule throu ...
... molecule that you store in your liver. Circle the pathways/cycles below that are part of this overall transformation. Cross out any that are not. Gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, citric acid cycle B. Trace the metabolic path of this glutamate molecule throu ...
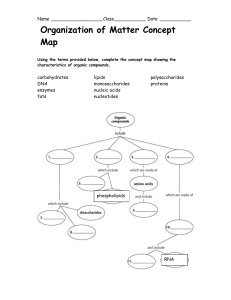
Polymers vs. monomers wkst. and concept map
... 8-18. Complete the chart below. Remember mono means one and poly means many. ...
... 8-18. Complete the chart below. Remember mono means one and poly means many. ...