macromolecules new
... • Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals, similar to starch in plants. • It is mainly found in the liver and muscles ...
... • Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals, similar to starch in plants. • It is mainly found in the liver and muscles ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration
... Fats can be used after the cell hydrolyzes them to glycerol & fatty acids. How are carbohydrates stored? Stored as a polysaccharide, such as glycogen, in our liver & muscle cells. How is glycogen used between meals? Glycogen is hydrolyzed to glucose to serve as fuel between meals. ...
... Fats can be used after the cell hydrolyzes them to glycerol & fatty acids. How are carbohydrates stored? Stored as a polysaccharide, such as glycogen, in our liver & muscle cells. How is glycogen used between meals? Glycogen is hydrolyzed to glucose to serve as fuel between meals. ...
fatty acid oxid final
... Increase requirement Pregnancy, Infections, Burns, Trauma o Losses can also occur in hemodialysis • SYMPTOMS: Hypoglycemia during fast ...
... Increase requirement Pregnancy, Infections, Burns, Trauma o Losses can also occur in hemodialysis • SYMPTOMS: Hypoglycemia during fast ...
Lipids: Membrane Structure
... acid composition with ratio of saturated to unsaturated fatty acids and chain length ...
... acid composition with ratio of saturated to unsaturated fatty acids and chain length ...
Chapter 3 – Carbon Compounds in Cells
... Structural – spider silk, hair, and fibers of tendons & ligaments, feathers and cartilage Contractile – control muscle movement Storage – (nutritious) stores amino acids such as albumin, milk, many seeds Defensive – antibodies of blood that fight infection ...
... Structural – spider silk, hair, and fibers of tendons & ligaments, feathers and cartilage Contractile – control muscle movement Storage – (nutritious) stores amino acids such as albumin, milk, many seeds Defensive – antibodies of blood that fight infection ...
Unit 3 * Chapter 3 Biochemistry
... _______________________– clusters of atoms that influence the properties of molecules they are a part of. Ex.) -OH (hydroxyl group) – if this is attached to an organic compound, it will form an alcohol. ...
... _______________________– clusters of atoms that influence the properties of molecules they are a part of. Ex.) -OH (hydroxyl group) – if this is attached to an organic compound, it will form an alcohol. ...
File
... The molecules of these organic compounds are made up of hundreds or even thousands of atoms. Such molecules are called macromolecules: large molecules that often have complex structures. ...
... The molecules of these organic compounds are made up of hundreds or even thousands of atoms. Such molecules are called macromolecules: large molecules that often have complex structures. ...
Concepts in Biochemistry 3/e
... adapts from the use of glucose as its soul fuel source to the use of ketone bodies, shift the metabolic burden form protein breakdown to fat breakdown Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which insulin either not secreted or doesn’t stimulate its target tissues → high [glucose] in the blood and urine. ...
... adapts from the use of glucose as its soul fuel source to the use of ketone bodies, shift the metabolic burden form protein breakdown to fat breakdown Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which insulin either not secreted or doesn’t stimulate its target tissues → high [glucose] in the blood and urine. ...
Q1 Describe the physiological consequences that
... Upregulates Pyruvate Dehydrogenase, Lipoprotein Lipase and Fatty Acid Synthase to facilitate the breakdown of TAGs to fatty acids for uptake by adipose tissue cells Inhibits Hormone Sensitive lipase to decrease ...
... Upregulates Pyruvate Dehydrogenase, Lipoprotein Lipase and Fatty Acid Synthase to facilitate the breakdown of TAGs to fatty acids for uptake by adipose tissue cells Inhibits Hormone Sensitive lipase to decrease ...
Fatty Acid Oxidation and Ketone Bodies OXIDATION OF FATTY
... -oxidation is a minor pathway and is brought about by cytochrome P450 in the endoplasmic reticulum. CH3 group is converted to a -CH2OH group that subsequently is oxidized to -COOH, thus forming a dicarboxylic acid. They subsequently undergo ß-oxidation and are excreted in the urine. ...
... -oxidation is a minor pathway and is brought about by cytochrome P450 in the endoplasmic reticulum. CH3 group is converted to a -CH2OH group that subsequently is oxidized to -COOH, thus forming a dicarboxylic acid. They subsequently undergo ß-oxidation and are excreted in the urine. ...
Human Physiology
... • A typical protein contains 200–300 amino acids. • Some are much smaller and some much larger • The largest protein is titin • This is found in skeletal and cardiac muscle; it contains 26,926 amino acids in a single chain! ...
... • A typical protein contains 200–300 amino acids. • Some are much smaller and some much larger • The largest protein is titin • This is found in skeletal and cardiac muscle; it contains 26,926 amino acids in a single chain! ...
Biology I SB1bc Enzymes and Macromolecules Test Study Guide
... “Reusable” proteins that put together or break down substrates to form products 2. Since enzymes are proteins they are made of ……what? Amino acids joined by peptide bonds 3. The energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called? Activation Energy (EA) 4. How do enzymes increase the rate or speed ...
... “Reusable” proteins that put together or break down substrates to form products 2. Since enzymes are proteins they are made of ……what? Amino acids joined by peptide bonds 3. The energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called? Activation Energy (EA) 4. How do enzymes increase the rate or speed ...
HS-Omega-3 Index®
... work well. When it is flexible, the chemicals that run our bodies – hormones, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, minerals, fats, etc – can move in and out of cells efficiently as needed, thus making the cells healthier, since the materials they need to function well are available. When the cells work well ...
... work well. When it is flexible, the chemicals that run our bodies – hormones, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, minerals, fats, etc – can move in and out of cells efficiently as needed, thus making the cells healthier, since the materials they need to function well are available. When the cells work well ...
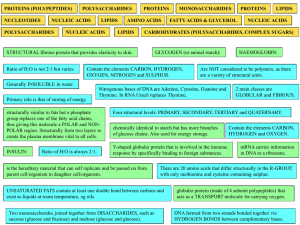
biol 3 biomolecules table activity
... structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma membrane vital to all cells. INSULIN: ...
... structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma membrane vital to all cells. INSULIN: ...
Remediation/Corrections Packet
... Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) and three fatty acid chains. This subunit is ca ...
... Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) and three fatty acid chains. This subunit is ca ...
Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs): Your Brain and Body
... called essential fatty acids (EFAs). They are occasionally also referred to as vitamin F or polyunsaturates. EFAs must be supplied through the diet. Essential fatty acids have desirable effects on many disorders. They improve the skin and hair, reduce blood pressure, aid in the prevention of arthrit ...
... called essential fatty acids (EFAs). They are occasionally also referred to as vitamin F or polyunsaturates. EFAs must be supplied through the diet. Essential fatty acids have desirable effects on many disorders. They improve the skin and hair, reduce blood pressure, aid in the prevention of arthrit ...
Triacylglycerol Metabolism Gone Bad: A major cause of disease
... – Rate limiting reaction for fatty acid synthesis – ACC1 is a liver isozyme – Small amounts of ACC2 are present in muscle where malonyl-CoA has a regulatory function (Fatty acid oxidation) ...
... – Rate limiting reaction for fatty acid synthesis – ACC1 is a liver isozyme – Small amounts of ACC2 are present in muscle where malonyl-CoA has a regulatory function (Fatty acid oxidation) ...
Option A: Human nutrition and health (15 hours)
... • Instructions that are in red refer to what I expect to see in your notebook. Any extra information is fantastic! ...
... • Instructions that are in red refer to what I expect to see in your notebook. Any extra information is fantastic! ...
Biochemistry: Monomers and Polymers
... – It serves as a form of energy storage in animals and fungi. – The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body. ...
... – It serves as a form of energy storage in animals and fungi. – The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body. ...
Abstract of the project nr. 16
... During our study, we will use fish muscle for lipid extraction based on the (Hara and Radin, 1978) method with slight modificatios and lipid content will be quantified. The lipid extracts will be then frozen in -80°C for subsequent analysis. After weighting the samples on microbalance, methylation o ...
... During our study, we will use fish muscle for lipid extraction based on the (Hara and Radin, 1978) method with slight modificatios and lipid content will be quantified. The lipid extracts will be then frozen in -80°C for subsequent analysis. After weighting the samples on microbalance, methylation o ...
biomolecule ii - UMK CARNIVORES 3
... • Long hydrocarbon chain – will not form hydrogen bonding – thus hydrophobic • Fatty acid in unesterifed or sterified – have more tendency to associate with each other or other hydrophobic structure, such as sterol and hydrophobic chain of aa • This hydrophobic character – essential for construction ...
... • Long hydrocarbon chain – will not form hydrogen bonding – thus hydrophobic • Fatty acid in unesterifed or sterified – have more tendency to associate with each other or other hydrophobic structure, such as sterol and hydrophobic chain of aa • This hydrophobic character – essential for construction ...
Exam II answer key
... converted into something that can enter a primary metabolic pathway. Draw the mechanism of this/these steps. Propionyl CoA biotin dependent carboxylation to methyl malonyl CoA, B-12 dependent rearrangement to succinyl CoA. See mechanisms on web site and book. 10. (10 pts) Describe the structure of g ...
... converted into something that can enter a primary metabolic pathway. Draw the mechanism of this/these steps. Propionyl CoA biotin dependent carboxylation to methyl malonyl CoA, B-12 dependent rearrangement to succinyl CoA. See mechanisms on web site and book. 10. (10 pts) Describe the structure of g ...