HPER 334 Nutrition Exam 2
... 43. Exercise has a very strong insulin-like effect. 44. An example of a food that contains a complete protein is peanut butter. 45. The catabolism of protein can produce ammonia, a product that is toxic to the body. 46. It has been proven that protein supplements are more effective than food protein ...
... 43. Exercise has a very strong insulin-like effect. 44. An example of a food that contains a complete protein is peanut butter. 45. The catabolism of protein can produce ammonia, a product that is toxic to the body. 46. It has been proven that protein supplements are more effective than food protein ...
Slides
... amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. ...
... amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. ...
Biochemistry_of_Cells abridged
... • Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on Earth Found in the cell walls that enclose plants It is a major component of wood It is also known as dietary fiber ...
... • Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on Earth Found in the cell walls that enclose plants It is a major component of wood It is also known as dietary fiber ...
Examination III Key
... The additional synthesis does not occur in the mitochondria, because that is where only fatty acid degradation occurs. The question hints at the fact that both lengthening and addition of cis bonds are needed since oleic acid is C18:1, while FAS only makes C16:0 ...
... The additional synthesis does not occur in the mitochondria, because that is where only fatty acid degradation occurs. The question hints at the fact that both lengthening and addition of cis bonds are needed since oleic acid is C18:1, while FAS only makes C16:0 ...
Chapter 18_CHEM 131
... • Linoleic (an omega-3 fatty acid) and linolenic (an omega-6 fatty acid) acids: • are used to produce hormonelike substances that regulate a wide range of functions and characteristics, including: • e.g. blood pressure, blood clotting, blood lipid levels, the immune response, and the inflammation re ...
... • Linoleic (an omega-3 fatty acid) and linolenic (an omega-6 fatty acid) acids: • are used to produce hormonelike substances that regulate a wide range of functions and characteristics, including: • e.g. blood pressure, blood clotting, blood lipid levels, the immune response, and the inflammation re ...
Carbohydrates
... • Starch: plants • Glycogen: animals • Cellulose: structural support in plants (wood) ...
... • Starch: plants • Glycogen: animals • Cellulose: structural support in plants (wood) ...
1 - Wsfcs
... 28. How many proteins are there? _________________ 29. To link amino acids together, a _______ must be removed from the amino group and an _______ must be removed from the COOH to form water. The covalent bond is called a _________________ 30. The ______________________ and ______________________ of ...
... 28. How many proteins are there? _________________ 29. To link amino acids together, a _______ must be removed from the amino group and an _______ must be removed from the COOH to form water. The covalent bond is called a _________________ 30. The ______________________ and ______________________ of ...
3.1 The Molecules of Life--From Structure to Function A. What Is An
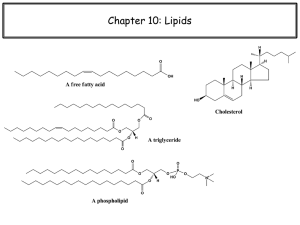
... 3. Fats are formed by the attachment of one (mono-), two (di-), or three (tri-) fatty acids to a glycerol. a. They are a rich source of energy, yielding more than twice the energy per weight basis as carbohydrates. ...
... 3. Fats are formed by the attachment of one (mono-), two (di-), or three (tri-) fatty acids to a glycerol. a. They are a rich source of energy, yielding more than twice the energy per weight basis as carbohydrates. ...
Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen
... have a second site where a coenzyme attaches to help make the substrate better fit the active site of the enzyme. Color the enzyme purple, the substrate yellow, and the coenzyme green. Also color the active site red. ...
... have a second site where a coenzyme attaches to help make the substrate better fit the active site of the enzyme. Color the enzyme purple, the substrate yellow, and the coenzyme green. Also color the active site red. ...
Basic Biochemistry
... Building blocks for most complex lipids Long chains with a carboxylic acid at 1 end Can be saturated or unsaturated Saturated only single C-C bonds Unsaturated has one or more C=C (double bond) ...
... Building blocks for most complex lipids Long chains with a carboxylic acid at 1 end Can be saturated or unsaturated Saturated only single C-C bonds Unsaturated has one or more C=C (double bond) ...
The process of beta oxidation is named after the carbon atom in the
... 8CH3-CO-S-CoA + 7FADH2 + 7NADH + 7H+ The completion of the degradation process (coenzyme oxidation) requires the citric acid cycle which yields an additional 96 mols of ATP for all 8 acetyl-CoA units oxidized in the process. The total energy yield of palmitic acid oxidation results ...
... 8CH3-CO-S-CoA + 7FADH2 + 7NADH + 7H+ The completion of the degradation process (coenzyme oxidation) requires the citric acid cycle which yields an additional 96 mols of ATP for all 8 acetyl-CoA units oxidized in the process. The total energy yield of palmitic acid oxidation results ...
lipids
... What are the characteristics of these fatty acids? • All fatty acid chains are unbranched, but they may be ...
... What are the characteristics of these fatty acids? • All fatty acid chains are unbranched, but they may be ...
word
... Two phases: preparation, and energy generating; what compartment in cell? Critical enzymes: hexokinase (glucokinase in liver), phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1), pyruvate kinase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and regulation Pyruvate as critical point – availability of oxygen determine next steps; lactic acido ...
... Two phases: preparation, and energy generating; what compartment in cell? Critical enzymes: hexokinase (glucokinase in liver), phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1), pyruvate kinase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and regulation Pyruvate as critical point – availability of oxygen determine next steps; lactic acido ...
Functional Groups, I
... • Monomer: amino acids (there are 20) bind together to form peptide bonds, during dehydration reactions. ...
... • Monomer: amino acids (there are 20) bind together to form peptide bonds, during dehydration reactions. ...
Outline06 Metabolism - Napa Valley College
... - fatty acids are synthesized from 2C units of acetyl CoA - fatty acids are combined with glycerol to form triglycerides and phospholipids 3. Tissue Utilization of Fatty Acids - triglycerides are stored mostly in adipose tissue - lipids are transported in the blood by lipoproteins: HDL, LDL - liver, ...
... - fatty acids are synthesized from 2C units of acetyl CoA - fatty acids are combined with glycerol to form triglycerides and phospholipids 3. Tissue Utilization of Fatty Acids - triglycerides are stored mostly in adipose tissue - lipids are transported in the blood by lipoproteins: HDL, LDL - liver, ...
File
... • C) Polysaccharidecomplex sugars made of 3 or more sugars ex. Starch (plants store food as starch) Glycogen (stored in liver and muscles for quick energy) Cellulose (structural support for plants) ...
... • C) Polysaccharidecomplex sugars made of 3 or more sugars ex. Starch (plants store food as starch) Glycogen (stored in liver and muscles for quick energy) Cellulose (structural support for plants) ...
Macromolecules - Van Buren Public Schools
... • Large! • Accomplish all life functions • Types: Carbohydrates, lipids*, proteins, nucleic acids ...
... • Large! • Accomplish all life functions • Types: Carbohydrates, lipids*, proteins, nucleic acids ...
Organic Molecules: The Molecules of Life
... Fats- found in animals We can think of body fat and the derived products of lard and butter Oils are derived from plants. Ie) olive oil, canola oil…. Made of a glycerol backbone that has 3 fatty acid chains attached to it. Think of a big letter E. Fatty acids are chains of Carbon (16-18 or so) have ...
... Fats- found in animals We can think of body fat and the derived products of lard and butter Oils are derived from plants. Ie) olive oil, canola oil…. Made of a glycerol backbone that has 3 fatty acid chains attached to it. Think of a big letter E. Fatty acids are chains of Carbon (16-18 or so) have ...
02-3 Carbon Compounds
... Polysaccharides • Polysaccharides are large molecules composed of individual monosaccharide units. • Ex) starch, glycogen, cellulose ...
... Polysaccharides • Polysaccharides are large molecules composed of individual monosaccharide units. • Ex) starch, glycogen, cellulose ...
carbs and lipids
... • The formation of a glycosidic bond involves the formation of water as a by-product and is a dehydration synthesis reaction. (aka: condensation reaction) ...
... • The formation of a glycosidic bond involves the formation of water as a by-product and is a dehydration synthesis reaction. (aka: condensation reaction) ...
Organ Integration and Control
... In this mode glucose can be made from a number of sources including: 1. Glycerol from fat breakdown 2. Alanine from protein breakdown – alanine cycle 3. Lactate (Red blood cells, Muscle) – Cori Cycle ...
... In this mode glucose can be made from a number of sources including: 1. Glycerol from fat breakdown 2. Alanine from protein breakdown – alanine cycle 3. Lactate (Red blood cells, Muscle) – Cori Cycle ...