Midterm Review Project Ch 5
... (covalent bond formed by a dehydration reaction: either alpha or beta linkage depending on location of hydroxyl group in glucose monomers), then polysaccharides if multiple monosaccharides polysaccharides’ function: storage material hydrolyzed for sugar, building material for structures that protect ...
... (covalent bond formed by a dehydration reaction: either alpha or beta linkage depending on location of hydroxyl group in glucose monomers), then polysaccharides if multiple monosaccharides polysaccharides’ function: storage material hydrolyzed for sugar, building material for structures that protect ...
Macromolecules - Haiku Learning
... Three major lipids in the body Triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesterol ...
... Three major lipids in the body Triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesterol ...
I The THREE types of LIPIDS
... foods that provide unsaturated fats such as: ________________________________ Keep saturated less than ______ of Calories, trans fat as _____ as possible and cholesterol less than _______ per day _____ of seafood per week. 4. Nutritional Disadvantages of a lowfat diet: a. hard to get enough __FA b. ...
... foods that provide unsaturated fats such as: ________________________________ Keep saturated less than ______ of Calories, trans fat as _____ as possible and cholesterol less than _______ per day _____ of seafood per week. 4. Nutritional Disadvantages of a lowfat diet: a. hard to get enough __FA b. ...
The Origins Of Life
... These monomers are used to build nucleic acids The acids can be used for various functions in life such as storage, transfer of vital information, and even enzymes ...
... These monomers are used to build nucleic acids The acids can be used for various functions in life such as storage, transfer of vital information, and even enzymes ...
Section 1 Workbook Unit 1 ANSWERS File
... that the functions are all involved in Protein Synthesis (building proteins) ...
... that the functions are all involved in Protein Synthesis (building proteins) ...
Practice Exam I
... 14. The active site of an enzyme a. is similar to that of any other enzyme b. is the part of the enzyme where the substrate can fit c. is only used once d. is usually not affected by pH or temperature 15. All the chemical reactions that occur in the cell a. metabolism b. free energy c. kinetic energ ...
... 14. The active site of an enzyme a. is similar to that of any other enzyme b. is the part of the enzyme where the substrate can fit c. is only used once d. is usually not affected by pH or temperature 15. All the chemical reactions that occur in the cell a. metabolism b. free energy c. kinetic energ ...
Biological_Molecules worksheet - answers
... alcohol/ethanol 4. List 3 functions of fats in the human body: a. They make up cell membranes b. Long term energy source – they release as twice as much energy as carbohydrates/protein. c. Good thermal insulators, reducing heat loss. ...
... alcohol/ethanol 4. List 3 functions of fats in the human body: a. They make up cell membranes b. Long term energy source – they release as twice as much energy as carbohydrates/protein. c. Good thermal insulators, reducing heat loss. ...
File - Mrs Jones A
... Rest is changed to glycogen or fat During fasting/starvation /prolonged exercise: Protein is then hydrolysed (split with water) to amino acids which can be respired Some can be converted to pyruvate, or acetate and then is carried to Krebs cycle Some can enter Krebs directly Number of hydrogen atoms ...
... Rest is changed to glycogen or fat During fasting/starvation /prolonged exercise: Protein is then hydrolysed (split with water) to amino acids which can be respired Some can be converted to pyruvate, or acetate and then is carried to Krebs cycle Some can enter Krebs directly Number of hydrogen atoms ...
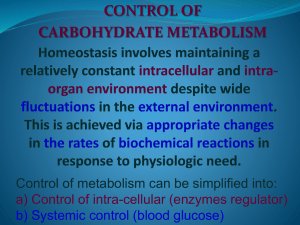
Control of intra-cellular (enzyme regulator)
... polysaccharides reside inside organelles called lysosomes. Fatty acid biosynthesis occurs in the cytosol, whereas fatty acid oxidation takes place within mitochondria Segregation of certain metabolic pathways within specialized cell types can provide further physical compartmentation. ...
... polysaccharides reside inside organelles called lysosomes. Fatty acid biosynthesis occurs in the cytosol, whereas fatty acid oxidation takes place within mitochondria Segregation of certain metabolic pathways within specialized cell types can provide further physical compartmentation. ...
Metabolic Characteristics of the Major Organs and Tissues
... The cells in adipose tissue are called adipocytes. A 70 kg human male is about 17% triacylglycerol, stored in adipose tissue. This represents 110,000 kcal of stored energy, or enough to sustain life for a few months. When chylomicrons from the intestines reach adipocytes, lipoprotein lipase on the a ...
... The cells in adipose tissue are called adipocytes. A 70 kg human male is about 17% triacylglycerol, stored in adipose tissue. This represents 110,000 kcal of stored energy, or enough to sustain life for a few months. When chylomicrons from the intestines reach adipocytes, lipoprotein lipase on the a ...
1. Amino Acids,Peptides, Proteins
... Hormones of Pancreas and Gastrointestinal Tract - The photocopy from the 25th edition 23. Thyroid Hormones and Adrenal Medulla Hormones The photocopy from the 25th edition 24. Cholesterol and Bile Acids Ch. 26. Cholesterol Synthesis, Transport, & Excretion - without chemical structures on Figure ...
... Hormones of Pancreas and Gastrointestinal Tract - The photocopy from the 25th edition 23. Thyroid Hormones and Adrenal Medulla Hormones The photocopy from the 25th edition 24. Cholesterol and Bile Acids Ch. 26. Cholesterol Synthesis, Transport, & Excretion - without chemical structures on Figure ...
... A fat that is solid at room temperature, found in animal fats such as lard and butter. All of its carbon to carbon bonds are single. Too much of this can increase the chance of cardiovascular disease 11. What are unsaturated fats? A fat that contains fewer numbers of hydrogen (less stored energy) a ...
* Abundant! * Able to share 4 outer valence electrons! * Versatile
... • Used in the body to form tissues, cell membrane gates • Functional Group – NH2 • Made up of monomers called amino acids • Single amino acids are bonded together using peptide bonds. • EX: Meat, eggs, fish ...
... • Used in the body to form tissues, cell membrane gates • Functional Group – NH2 • Made up of monomers called amino acids • Single amino acids are bonded together using peptide bonds. • EX: Meat, eggs, fish ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 1. DNA and RNA are examples of ___nucleic acids______________. 2. Carbohydrates and lipids both contain the elements ____carbon__________, __hydrogen__________, and ________oxygen_________. 3. Proteins are made of ___amino acids________________ 4. __polynucleotides or nucleic acids____________ are m ...
... 1. DNA and RNA are examples of ___nucleic acids______________. 2. Carbohydrates and lipids both contain the elements ____carbon__________, __hydrogen__________, and ________oxygen_________. 3. Proteins are made of ___amino acids________________ 4. __polynucleotides or nucleic acids____________ are m ...
CM 65% IL red
... is unable to work. Some enzymes have a second site where a coenzyme attaches to help make the substrate better fit the active site of the enzyme. Color the enzyme purple, the substrate yellow, and the coenzyme green. Also color the active site red. ...
... is unable to work. Some enzymes have a second site where a coenzyme attaches to help make the substrate better fit the active site of the enzyme. Color the enzyme purple, the substrate yellow, and the coenzyme green. Also color the active site red. ...
Correlation - EngineeringDuniya.com
... same is the case with [NADH]/[NAD+] and [NADPH]/[NADP+] ratio. One important mediator of regulation is AMP dependent protein kinase (AMPK). The action of AMPK increases glucose transport and activates glycolysis and fatty acid oxidation while suppressing energy requiring processes like fatty acid sy ...
... same is the case with [NADH]/[NAD+] and [NADPH]/[NADP+] ratio. One important mediator of regulation is AMP dependent protein kinase (AMPK). The action of AMPK increases glucose transport and activates glycolysis and fatty acid oxidation while suppressing energy requiring processes like fatty acid sy ...
Nutrients and the structure of macromolecules File
... Fats – made up of glycerol and fatty acid chains (chains of C, H, and O). Naming fats: 1. The fatty acid chains can be different lengths. This is partly how fats get their name i.e. C18 or C12 (Lorenzo’s Oil). 2. These chains can also be saturated with Hydrogen molecules so there are only single bo ...
... Fats – made up of glycerol and fatty acid chains (chains of C, H, and O). Naming fats: 1. The fatty acid chains can be different lengths. This is partly how fats get their name i.e. C18 or C12 (Lorenzo’s Oil). 2. These chains can also be saturated with Hydrogen molecules so there are only single bo ...
Biology 105
... temperature. Known as trans fatty acids. Partially hydrogenated oil means that the hydrogenation process stopped short of a full solid, reaching a more ...
... temperature. Known as trans fatty acids. Partially hydrogenated oil means that the hydrogenation process stopped short of a full solid, reaching a more ...
Dr Azis Ariffin and Dr Nora. UPM.
... The omega-6 (C18:2, linoleic) and omega-3 (C18:3, linolenic acid) fatty acids which are necessary but cannot be synthesized by the body. Some plants have oils with exceptionally high content of essential fatty acids. Plant oil rich in essential acids may not have the aromatic compound or “essence” t ...
... The omega-6 (C18:2, linoleic) and omega-3 (C18:3, linolenic acid) fatty acids which are necessary but cannot be synthesized by the body. Some plants have oils with exceptionally high content of essential fatty acids. Plant oil rich in essential acids may not have the aromatic compound or “essence” t ...
Triacylglycerol Metabolism Gone Bad: A major cause of disease
... transport of lipid out of the liver – If protein synthesis is reduced (e.g. by malnutrition) fat droplets accumulate in the liver. – If the rate of lipid synthesis is greatly elevated with respect to protein synthesis (e.g. in type I diabetes or glucose 6-phosphatase deficiency) fat droplets accumul ...
... transport of lipid out of the liver – If protein synthesis is reduced (e.g. by malnutrition) fat droplets accumulate in the liver. – If the rate of lipid synthesis is greatly elevated with respect to protein synthesis (e.g. in type I diabetes or glucose 6-phosphatase deficiency) fat droplets accumul ...
Lab Time
... 4. How can the rapid breakdown of fat result in a dangerous decrease in blood pH? Hint – Ketone bodies Hydrolysis of triglycerides within adipose tissue releases glycerol and free fatty acids into the blood which are both used as an energy source by many organs; they can also be converted by the liv ...
... 4. How can the rapid breakdown of fat result in a dangerous decrease in blood pH? Hint – Ketone bodies Hydrolysis of triglycerides within adipose tissue releases glycerol and free fatty acids into the blood which are both used as an energy source by many organs; they can also be converted by the liv ...
What molecules make up living things
... • Used in the presence of oxygen to generate cellular energy (ATP)= cellular respiration • Carbohydrates make up part of our cell membrane (hydrophobic) • Sweet in flavor – ______ is an important complex carbohydrate made from glucose – _________ is a carbohydrate that make up plant cell walls raw ...
... • Used in the presence of oxygen to generate cellular energy (ATP)= cellular respiration • Carbohydrates make up part of our cell membrane (hydrophobic) • Sweet in flavor – ______ is an important complex carbohydrate made from glucose – _________ is a carbohydrate that make up plant cell walls raw ...
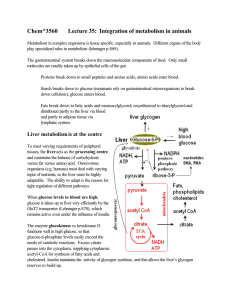
Chem*3560 Lecture 35: Integration of metabolism in animals
... from amino acid oxidation Amino acids in blood may be derived from dietary protein. If this source is insufficient, breakdown of tissue proteins occurs, mostly from body muscle mass (which is why starvation dieting is ill-advised). The liver has very active protein synthesis and degradation, and als ...
... from amino acid oxidation Amino acids in blood may be derived from dietary protein. If this source is insufficient, breakdown of tissue proteins occurs, mostly from body muscle mass (which is why starvation dieting is ill-advised). The liver has very active protein synthesis and degradation, and als ...
C483 Study Guide for Exam 2 Fall 2015 Basic Information Exam 3
... Bring your student ID. Failure to do so will result in getting your exam back later. You may use a NON-PROGRAMMABLE calculator. All papers, books, phones, and electronic devices must be in a sealed bag under your seat. The exam will cover chapters 13-15 and 17, which includes Glycolysis, glu ...
... Bring your student ID. Failure to do so will result in getting your exam back later. You may use a NON-PROGRAMMABLE calculator. All papers, books, phones, and electronic devices must be in a sealed bag under your seat. The exam will cover chapters 13-15 and 17, which includes Glycolysis, glu ...