Chap 23 –Nutrition, Part III
... • Almost completely ____________ • Requires ___ • Completes the breakdown of foods • Produces ____, ________, and large amounts of ______ ...
... • Almost completely ____________ • Requires ___ • Completes the breakdown of foods • Produces ____, ________, and large amounts of ______ ...
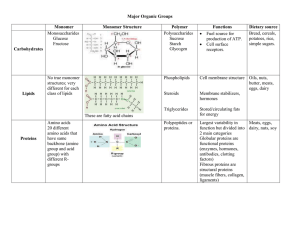
Biological Molecules wHelp Sheet
... 23. Metabolism is the collective term used to describe all the chemical reactions taking place inside living organisms. Why is water so important for metabolic reactions? ...
... 23. Metabolism is the collective term used to describe all the chemical reactions taking place inside living organisms. Why is water so important for metabolic reactions? ...
Macromolecules Notes Macromolecules Notes
... •20 different kinds of amino acids 5 functions of proteins: • Transport (e.g., hemoglobin) • Provides immunity (e.g., immune system) • Regulate the body (e.g., hormones, enzymes, metabolism) • Muscle tissue (e.g., movement) • Structural components of the body (e.g., membranes, hair, nails, etc.) Mac ...
... •20 different kinds of amino acids 5 functions of proteins: • Transport (e.g., hemoglobin) • Provides immunity (e.g., immune system) • Regulate the body (e.g., hormones, enzymes, metabolism) • Muscle tissue (e.g., movement) • Structural components of the body (e.g., membranes, hair, nails, etc.) Mac ...
PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
... b) Anaerobic glycolysis can not be accelerated enough to compensate its inefficient ATP production. ...
... b) Anaerobic glycolysis can not be accelerated enough to compensate its inefficient ATP production. ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide
... 3. Using the “lock and key model’, explain why an enzyme is only able to catalyze one specific ...
... 3. Using the “lock and key model’, explain why an enzyme is only able to catalyze one specific ...
LECTURE #1 STUDY GUIDE
... Complete the following chemical equation: NADH + H+ + 3ADP + 3 P + 1/2 O2 –––––––> ...
... Complete the following chemical equation: NADH + H+ + 3ADP + 3 P + 1/2 O2 –––––––> ...
BIO C211 - BITS Pilani
... Course Handout (Part II) In addition to Part One (General Handout for all courses appended to the time table) this part gives further specific details regarding the course. Course No. ...
... Course Handout (Part II) In addition to Part One (General Handout for all courses appended to the time table) this part gives further specific details regarding the course. Course No. ...
NotesMacromolecules
... 2. List the monomer building block in each disaccharide or polysaccharide you eat. ...
... 2. List the monomer building block in each disaccharide or polysaccharide you eat. ...
Organic Compounds
... • Mostly contain C and H atoms. • Secondary functions of lipids are as structural components (the major building block in cell membranes) and as "messengers" (hormones) that play roles in communications within and between cells. ...
... • Mostly contain C and H atoms. • Secondary functions of lipids are as structural components (the major building block in cell membranes) and as "messengers" (hormones) that play roles in communications within and between cells. ...
Classifying Organic Molecules Lab
... 10. Proteins are molecules that play many important roles in the body; muscle structure, hormones, antibodies, hemoglobin for carrying oxygen, transport proteins for carrying molecules across cell membranes, chemical messengers in the nervous system and enzymes to control chemical reactions. Each am ...
... 10. Proteins are molecules that play many important roles in the body; muscle structure, hormones, antibodies, hemoglobin for carrying oxygen, transport proteins for carrying molecules across cell membranes, chemical messengers in the nervous system and enzymes to control chemical reactions. Each am ...
Lipids WORD 1000 KB - Science Learning Hub
... Sterols like cholesterol Fats and oils Fats and oils are the fatty acid esters of glycerol and are an important source of energy in the diet. They are also referred to as triglycerides. A triglyceride molecule if formed by reacting a molecule of glycerol (an alcohol) with long chain fatty acids su ...
... Sterols like cholesterol Fats and oils Fats and oils are the fatty acid esters of glycerol and are an important source of energy in the diet. They are also referred to as triglycerides. A triglyceride molecule if formed by reacting a molecule of glycerol (an alcohol) with long chain fatty acids su ...
Chapter 3: Molecules of Life The molecules of life contain a high
... group bonded to a carbon of an organic compound; imparts a specific chemical property ...
... group bonded to a carbon of an organic compound; imparts a specific chemical property ...
UNIT 1: Cell Biology Chemical Foundations of Life ALL matter is
... o Obtained from ______________ such as sunflower or olive oils ...
... o Obtained from ______________ such as sunflower or olive oils ...
Synopsis - Challenge:Future
... Algae are photosynthetic organisms that occur in most habitats, ranging from marine and freshwater to desert sands and from hot boiling springs to snow and ice. They exhibit a wide range of reproductive strategies, from simple, asexual cell division to complex forms of sexual reproduction. Algae are ...
... Algae are photosynthetic organisms that occur in most habitats, ranging from marine and freshwater to desert sands and from hot boiling springs to snow and ice. They exhibit a wide range of reproductive strategies, from simple, asexual cell division to complex forms of sexual reproduction. Algae are ...
Chem331 Lect 13 Lipids - University of San Diego Home Pages
... (NOT HIGH ENERGY BONDS!) -These are highly reduced molecules with low amounts of water associated. The result is a molecule that can undergo repeated oxidation steps transferring the energy to form ATP. -The low water content increases the gram per gram energy available vs. carbohydrates Phospholipi ...
... (NOT HIGH ENERGY BONDS!) -These are highly reduced molecules with low amounts of water associated. The result is a molecule that can undergo repeated oxidation steps transferring the energy to form ATP. -The low water content increases the gram per gram energy available vs. carbohydrates Phospholipi ...
1 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... A. Pyridoxine B. Cobalamine C. Thiamine D. Niacin 61. An increase in which of the following minerals causes a decrease in blood pressure? A. Potassium B. Na C. Chloride D. P 62. Dietary vitamin E is absorbed in the intestines by? A. Amino acids B. Carbohydrates C. Lipids D. Biotin and thiamine 63. D ...
... A. Pyridoxine B. Cobalamine C. Thiamine D. Niacin 61. An increase in which of the following minerals causes a decrease in blood pressure? A. Potassium B. Na C. Chloride D. P 62. Dietary vitamin E is absorbed in the intestines by? A. Amino acids B. Carbohydrates C. Lipids D. Biotin and thiamine 63. D ...
Answers - Shelton State
... carries oxygen. 10. Which of the following are macromolecules? proteins and carbohydrates but not lipids 11. What is the net charge on cysteine, pI=5.1, when the pH=6.3? negative Which way will it move during electrophoresis? Toward the positive electrode. 12. The names of enzymes often identify the ...
... carries oxygen. 10. Which of the following are macromolecules? proteins and carbohydrates but not lipids 11. What is the net charge on cysteine, pI=5.1, when the pH=6.3? negative Which way will it move during electrophoresis? Toward the positive electrode. 12. The names of enzymes often identify the ...
Integration of Mammalian Metabolism
... •generated by the oxidation of fuel molecules: NADH and FADH2 shuttle electrons to the ETC where the bulk of ATP is formed via ...
... •generated by the oxidation of fuel molecules: NADH and FADH2 shuttle electrons to the ETC where the bulk of ATP is formed via ...
Name______Answer Key__________________
... 5. Draw a triglyceride and label the parts of the molecule. (You get to choose whether you draw a saturated or unsaturated triglyceride ) ...
... 5. Draw a triglyceride and label the parts of the molecule. (You get to choose whether you draw a saturated or unsaturated triglyceride ) ...
week 7_lipid - UniMAP Portal
... 1. TAGs are hydrophobic, they coalesce into compact, anhydrous droplets within cells. Adipocyte stores TAG. - Glycogen binds to water- the anhydrous TAG store equivalent amount of energy in about 1-8th of glycogen vol. 2. TAG are less oxidized than carbohydrate. TAG release more energy when they are ...
... 1. TAGs are hydrophobic, they coalesce into compact, anhydrous droplets within cells. Adipocyte stores TAG. - Glycogen binds to water- the anhydrous TAG store equivalent amount of energy in about 1-8th of glycogen vol. 2. TAG are less oxidized than carbohydrate. TAG release more energy when they are ...
NSC 602 - Department of Nutritional Sciences
... from Acetyl-CoA. Detail the steps of eta-oxidation of fatty acids and calculate the total number of ATP molecules that can be obtained from complete oxidation, this means all the way down to the Krebs cycle and respiratory chain. Be aware of differences in the oxidation of saturated and unsaturated ...
... from Acetyl-CoA. Detail the steps of eta-oxidation of fatty acids and calculate the total number of ATP molecules that can be obtained from complete oxidation, this means all the way down to the Krebs cycle and respiratory chain. Be aware of differences in the oxidation of saturated and unsaturated ...