NSC 602 - Department of Nutritional Sciences
... from Acetyl-CoA. Detail the steps of eta-oxidation of fatty acids and calculate the total number of ATP molecules that can be obtained from complete oxidation, this means all the way down to the Krebs cycle and respiratory chain. Be aware of differences in the oxidation of saturated and unsaturated ...
... from Acetyl-CoA. Detail the steps of eta-oxidation of fatty acids and calculate the total number of ATP molecules that can be obtained from complete oxidation, this means all the way down to the Krebs cycle and respiratory chain. Be aware of differences in the oxidation of saturated and unsaturated ...
1. Identify the structural formula. Use these choices - burgess
... 17. All organic compounds are compounds that contain oxygen. _false - carbon_ 18. Isomers are organic molecules that have the same chemical formula, but different structural formulas. _true_ ...
... 17. All organic compounds are compounds that contain oxygen. _false - carbon_ 18. Isomers are organic molecules that have the same chemical formula, but different structural formulas. _true_ ...
07-Quiz 3 Key
... a. They cause obesity and should be totally eliminated from a healthful diet. b. They are metabolized in the body, producing energy. c. They can be produced in plants by photosynthesis in an endothermic reaction. d. Simple carbohydrates, such as monosaccharides, are made up of C, H, and 0 in a 1: ...
... a. They cause obesity and should be totally eliminated from a healthful diet. b. They are metabolized in the body, producing energy. c. They can be produced in plants by photosynthesis in an endothermic reaction. d. Simple carbohydrates, such as monosaccharides, are made up of C, H, and 0 in a 1: ...
Carbohydrates
... mainly in nucleus Also in mitochondria Provides all instructions for protein building ...
... mainly in nucleus Also in mitochondria Provides all instructions for protein building ...
www.eastpenn.k12.pa.us
... -Lipids are polymers formed from two monomers: glycerol and fatty acids -Saturated: when each carbon atom in the fatty acid chain is joined to another carbon atom by a single bond. Saturated means the fatty acids contain the max possible number of hydrogen atoms (butter, cheese, meat contain a lot o ...
... -Lipids are polymers formed from two monomers: glycerol and fatty acids -Saturated: when each carbon atom in the fatty acid chain is joined to another carbon atom by a single bond. Saturated means the fatty acids contain the max possible number of hydrogen atoms (butter, cheese, meat contain a lot o ...
Grade 12 University Biology
... Unsaturated fats come from plant sources such as olive oil, canola oil, and avocado. The kinks formed between the double bonds of the carbons in the fatty acid tail do not allow for tight packing of molecules which is why unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature. ...
... Unsaturated fats come from plant sources such as olive oil, canola oil, and avocado. The kinks formed between the double bonds of the carbons in the fatty acid tail do not allow for tight packing of molecules which is why unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature. ...
Document
... The brain problem… Most energy stored as fatty acids Brain only uses Glc Fatty acids Glc? How does brain function during starvation? ...
... The brain problem… Most energy stored as fatty acids Brain only uses Glc Fatty acids Glc? How does brain function during starvation? ...
Lipids: Are heterogeneous group of compounds related to the fatty
... alcohol; 3 fatty acids+ Glycerol Diglyceride; 2 fatty acids+ Glycerol Monoglycride: 1 fatty acid+ Glycerol. TG represents(its function) the principal storage form of energy in adipose tissues that needed physiologically in prolonged fasting and starvation and pathologically, for example in uncontrol ...
... alcohol; 3 fatty acids+ Glycerol Diglyceride; 2 fatty acids+ Glycerol Monoglycride: 1 fatty acid+ Glycerol. TG represents(its function) the principal storage form of energy in adipose tissues that needed physiologically in prolonged fasting and starvation and pathologically, for example in uncontrol ...
Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... polysaccharides.Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on earth. It is made of glucose, like starch, but they differ in the type of 1-4 linkage. Instead of an @ linkage as in starch cellulose contains a B 1-4 linkage • Enzymes find it difficult to brake the B 14 linkage. ...
... polysaccharides.Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on earth. It is made of glucose, like starch, but they differ in the type of 1-4 linkage. Instead of an @ linkage as in starch cellulose contains a B 1-4 linkage • Enzymes find it difficult to brake the B 14 linkage. ...
Structure and Function of Macromolecules What is a Macromolecule?
... polysaccharides.Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on earth. It is made of glucose, like starch, but they differ in the type of 1-4 linkage. Instead of an @ linkage as in starch cellulose contains a B 1-4 linkage • Enzymes find it difficult to brake the B 14 linkage. ...
... polysaccharides.Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on earth. It is made of glucose, like starch, but they differ in the type of 1-4 linkage. Instead of an @ linkage as in starch cellulose contains a B 1-4 linkage • Enzymes find it difficult to brake the B 14 linkage. ...
Digestive System Learning Targets 6-10
... carbohydrates, proteins & fats. State the functions of glucose, fats & amino acids in the body. Define the terms essential fatty acid, essential amino acid ...
... carbohydrates, proteins & fats. State the functions of glucose, fats & amino acids in the body. Define the terms essential fatty acid, essential amino acid ...
The six elements that make up 99.9% of all living things include
... Which of the following describes the function of proteins? 1. energy formation and storage 2. energy used in muscles and reaction 3. structural use and enzyme formation 4. heredity and genetic code carriers ...
... Which of the following describes the function of proteins? 1. energy formation and storage 2. energy used in muscles and reaction 3. structural use and enzyme formation 4. heredity and genetic code carriers ...
macromolecules powerpoint
... • Consist of peptide bonds between 20 possible amino acid monomers • Have a 3 dimensional globular shape • Each Protein has a specific order and number of Amino Acids ...
... • Consist of peptide bonds between 20 possible amino acid monomers • Have a 3 dimensional globular shape • Each Protein has a specific order and number of Amino Acids ...
Organic Compounds
... This game is open to the public The first hundred puzzles are known proteins But many proteins are not decoded and scientists are asking for our help to figure them out http://fold.it/ ...
... This game is open to the public The first hundred puzzles are known proteins But many proteins are not decoded and scientists are asking for our help to figure them out http://fold.it/ ...
Biochemistry Jeopardy C.P. Bio.
... is formed by chemically bonding two of these monosaccharides. ...
... is formed by chemically bonding two of these monosaccharides. ...
EXAM2
... “You’ll find me in the mitochondria and cytosol. I am not very big, but my function is extensive. I am one of the big four in a major pathway and I have 4 carbons. I play a prominent role in C4 plants. You may say that I catch CO2, but that is wrong. Some consider me the great communicator. I even h ...
... “You’ll find me in the mitochondria and cytosol. I am not very big, but my function is extensive. I am one of the big four in a major pathway and I have 4 carbons. I play a prominent role in C4 plants. You may say that I catch CO2, but that is wrong. Some consider me the great communicator. I even h ...
Biology 211 Anatomy & Physiology I
... Diglycerides and triglycerides are energy-storage molecules. They can be found in most type of cells, but are primarily found in adipocytes, in which they form large fat droplets in the center. When needed for energy, fatty acids can be released and broken down to release energy to form ATP ...
... Diglycerides and triglycerides are energy-storage molecules. They can be found in most type of cells, but are primarily found in adipocytes, in which they form large fat droplets in the center. When needed for energy, fatty acids can be released and broken down to release energy to form ATP ...
Document
... (E) Nutrients used for growth, repair, maintenance. Macronutrients needed in large quantities: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, water. Micronutrients = vitamins and minerals. RDAs (recommended daily allowances) have been long determined. Recent recommendations refine diet to prevent chronic disease. ...
... (E) Nutrients used for growth, repair, maintenance. Macronutrients needed in large quantities: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, water. Micronutrients = vitamins and minerals. RDAs (recommended daily allowances) have been long determined. Recent recommendations refine diet to prevent chronic disease. ...
Chemical Compounds in Cells and in Our Food
... • In the cell, used as: -part of cell membranes -structures of organelles -muscles in the body ...
... • In the cell, used as: -part of cell membranes -structures of organelles -muscles in the body ...
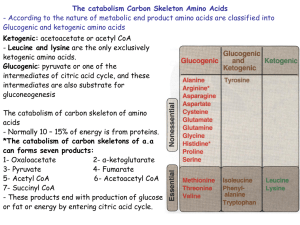
The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...