LB Metabolic Diseases
... 1) Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus reduced insulin action results in uncontrolled lipolysis ...
... 1) Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus reduced insulin action results in uncontrolled lipolysis ...
Rebecca Landerman Advanced Nutrition Science 1: 81944
... tissue is a major reason for the need for fats to be limited in the diet, but not completely cut out. Moderation is key for healthy fats since excess consumption of foods containing fatty acids will build up in fat stores on people and lead to much more serious problems like visceral fat buildup an ...
... tissue is a major reason for the need for fats to be limited in the diet, but not completely cut out. Moderation is key for healthy fats since excess consumption of foods containing fatty acids will build up in fat stores on people and lead to much more serious problems like visceral fat buildup an ...
5.6. membrane lipids
... 5.3. EICOSANOIDS: • They are derived from arachidonic acid, 20:4(5,8,11,14). ...
... 5.3. EICOSANOIDS: • They are derived from arachidonic acid, 20:4(5,8,11,14). ...
Macromolecules
... How does variation in molecular building blocks provide cells with a wider range of functions? ...
... How does variation in molecular building blocks provide cells with a wider range of functions? ...
Chapter 19 Lipid Metabolism
... 8 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP +14NADPH +14H+ → palmitic acid +14NADP + + 8CoA + 7ADP + 7Pi + 6H2 O E= fatty acid synthase-composed of all the enzymatic units necessary for FA synthesis Features of fatty acid synthesis: 1) Fatty acids are made from the addition of C2 units derived from acetyl-CoA 2) The aceta ...
... 8 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP +14NADPH +14H+ → palmitic acid +14NADP + + 8CoA + 7ADP + 7Pi + 6H2 O E= fatty acid synthase-composed of all the enzymatic units necessary for FA synthesis Features of fatty acid synthesis: 1) Fatty acids are made from the addition of C2 units derived from acetyl-CoA 2) The aceta ...
Biological Molecules
... Named according to the number of carbon atoms End in -ose triose, pentose and hexose Used mainly as an energy source (conversion between ATP and ADP) Two can monosacharide molecules can join to form a disacharide (also a sugar) ...
... Named according to the number of carbon atoms End in -ose triose, pentose and hexose Used mainly as an energy source (conversion between ATP and ADP) Two can monosacharide molecules can join to form a disacharide (also a sugar) ...
THE MOLECULES OF LIFE
... Protein catalysts that speed up a chemical reaction Lower the activation energy needed to start a reaction Each enzyme only catalyzes one reaction How enzymes work: o Substrate binds to enzyme’s active site like lock and key o In active site, substrate is converted to product o Product leave ...
... Protein catalysts that speed up a chemical reaction Lower the activation energy needed to start a reaction Each enzyme only catalyzes one reaction How enzymes work: o Substrate binds to enzyme’s active site like lock and key o In active site, substrate is converted to product o Product leave ...
Slide 1
... Nucleic acids are large organic molecules, found in the nucleus, which store and process information at the molecular level Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Determines inherited characteristics Directs protein synthesis Controls enzyme production Controls metabolism ...
... Nucleic acids are large organic molecules, found in the nucleus, which store and process information at the molecular level Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Determines inherited characteristics Directs protein synthesis Controls enzyme production Controls metabolism ...
Outline
... – a substance in food that is used by the body to promote normal growth, maintenance, and repair ...
... – a substance in food that is used by the body to promote normal growth, maintenance, and repair ...
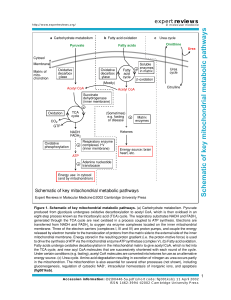
Schematic of key mitochondrial metabolic pathways
... transferred from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen via enzyme complexes located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Three of the electron carriers (complexes I, III and IV) are proton pumps, and couple the energy released by electron transfer to the translocation of protons from the matrix side to the exter ...
... transferred from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen via enzyme complexes located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Three of the electron carriers (complexes I, III and IV) are proton pumps, and couple the energy released by electron transfer to the translocation of protons from the matrix side to the exter ...
Macromolecules - Nolte Science
... glycogen is released from your liver to be used in your muscles for muscular contraction and movement. ...
... glycogen is released from your liver to be used in your muscles for muscular contraction and movement. ...
Main Concepts Muscle structure, Oxidation of fats, Muscle types
... inability of the protein albumin to move from the blood into the brain. 15. Triacylglycerols (fats) provide considerably more energy per gram than carbohydrates and are the major form of energy storage in humans. 16. To utilise the stored energy of triacylglycerols they must first be broken down int ...
... inability of the protein albumin to move from the blood into the brain. 15. Triacylglycerols (fats) provide considerably more energy per gram than carbohydrates and are the major form of energy storage in humans. 16. To utilise the stored energy of triacylglycerols they must first be broken down int ...
The Chemistry of Life
... a. All enzymes are catalysts, but not all catalysts are enzymes b. Most are proteins c. Speed up reaction or reduce activation energy required ...
... a. All enzymes are catalysts, but not all catalysts are enzymes b. Most are proteins c. Speed up reaction or reduce activation energy required ...
Biochemistry of Cells
... • Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes control the rate of chemical reactions by weakening bonds, thus lowering the amount of activation energy needed for the reaction ...
... • Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes control the rate of chemical reactions by weakening bonds, thus lowering the amount of activation energy needed for the reaction ...
Lipids • Triglycerides –Fats and oils • Phospholipids
... phospholipids –Plasma membrane –Emulsifiers ...
... phospholipids –Plasma membrane –Emulsifiers ...
Quiz Chapter 5 Organic Molecules
... 19. A particular polypeptide contains 90 amino acids. When the polypeptide is completely hydrolyzed, how many water molecules are formed during this process? a. 2 d. 89 b. 30 e 90 c. 45 20. All of the following qualities contribute to capillary action EXCEPT: a. cohesion d. hydrogen bonding b. adhes ...
... 19. A particular polypeptide contains 90 amino acids. When the polypeptide is completely hydrolyzed, how many water molecules are formed during this process? a. 2 d. 89 b. 30 e 90 c. 45 20. All of the following qualities contribute to capillary action EXCEPT: a. cohesion d. hydrogen bonding b. adhes ...
Metabolism II
... the number of acetyl CoA produced. • Example with Palmitic Acid = 16 carbons = 8 acetyl groups • Number of turns of fatty acid spiral = 8-1 = 7 turns • ATP from fatty acid spiral = 7 turns and 5 per turn = 35 ATP. [activation energy = 1 ATP] NET ATP from Fatty Acid Spiral = 35 - 1 = 34 ATP ...
... the number of acetyl CoA produced. • Example with Palmitic Acid = 16 carbons = 8 acetyl groups • Number of turns of fatty acid spiral = 8-1 = 7 turns • ATP from fatty acid spiral = 7 turns and 5 per turn = 35 ATP. [activation energy = 1 ATP] NET ATP from Fatty Acid Spiral = 35 - 1 = 34 ATP ...
Organic Molecule
... 2 Types of Fatty Acids Saturated: If each carbon atom in a lipid’s fatty acid has single covalent bonds. - Results in straight chains(Solid at room ...
... 2 Types of Fatty Acids Saturated: If each carbon atom in a lipid’s fatty acid has single covalent bonds. - Results in straight chains(Solid at room ...
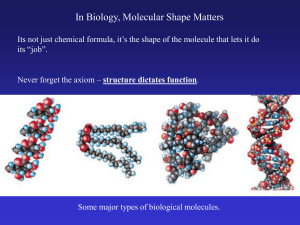
In Biology, Molecular Shape Matters
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
Fats and Lipids
... 1. Storage lipids (store energy within fat cells). Burning of fats produce 9 Kcal/g of energy and burning of carbohydrates of equal weight produces 4 kcal/g. 2. Membrane Lipids (separate compartments of aqueous solutions from each other) Lipids are insoluble in water. This is very important as most ...
... 1. Storage lipids (store energy within fat cells). Burning of fats produce 9 Kcal/g of energy and burning of carbohydrates of equal weight produces 4 kcal/g. 2. Membrane Lipids (separate compartments of aqueous solutions from each other) Lipids are insoluble in water. This is very important as most ...
Chemistry of Cells - Aditya K Panda, PhD
... • Monosaccharides generally have molecular formulas containing C,H and O in a 1:2:1 ratio. – For example, glucose has the formula C6H12O6. – Most names for sugars end in -ose. ...
... • Monosaccharides generally have molecular formulas containing C,H and O in a 1:2:1 ratio. – For example, glucose has the formula C6H12O6. – Most names for sugars end in -ose. ...
Chemistry of Cells - Marengo Community High School
... • Monosaccharides generally have molecular formulas containing C,H and O in a 1:2:1 ratio. – For example, glucose has the formula C6H12O6. – Most names for sugars end in -ose. ...
... • Monosaccharides generally have molecular formulas containing C,H and O in a 1:2:1 ratio. – For example, glucose has the formula C6H12O6. – Most names for sugars end in -ose. ...
Modern Biology (I) First Midterm (10/24/2007)
... c. DNA is a very long helix composed of two strands d. genes are associated with chromosomes 35. During DNA synthesis, one strand is synthesized ______ and the complementary strand is synthesized ______. a. 3’ to 5’; 5’ to 3’ b. 3’ to 5’; 3’ to 5’ c. 5’ to 3’; 3’ to 5’ d. 5’ to 3’; 5’ to 3’ 36. When ...
... c. DNA is a very long helix composed of two strands d. genes are associated with chromosomes 35. During DNA synthesis, one strand is synthesized ______ and the complementary strand is synthesized ______. a. 3’ to 5’; 5’ to 3’ b. 3’ to 5’; 3’ to 5’ c. 5’ to 3’; 3’ to 5’ d. 5’ to 3’; 5’ to 3’ 36. When ...