lec---10
... 1. A polypeptide is a polymer of amino acids connected in a specific sequence 2. A protein’s function depends on its specific conformation ...
... 1. A polypeptide is a polymer of amino acids connected in a specific sequence 2. A protein’s function depends on its specific conformation ...
Mid-Term Exam 1a - Buffalo State College Faculty and Staff Web
... _____ 21. Unsaturated fatty acids cause membranes to remain fluid at low temperatures. What is the chemical property of these phospholipids that promotes membrane fluidity? A. The double bonds in the hydrocarbon chains causes kinks that prevent the chains from packing tightly together B. The loss of ...
... _____ 21. Unsaturated fatty acids cause membranes to remain fluid at low temperatures. What is the chemical property of these phospholipids that promotes membrane fluidity? A. The double bonds in the hydrocarbon chains causes kinks that prevent the chains from packing tightly together B. The loss of ...
palm butter - In
... skin soft and acts as an antioxidant active in that it is rich of tocopherols and tocotrienols delivered to the skin. Palm Butter has the follow characteristics: It contains triglycerids with saturated fatty acids which allow the cream to obtain the consistency required without having to go through ...
... skin soft and acts as an antioxidant active in that it is rich of tocopherols and tocotrienols delivered to the skin. Palm Butter has the follow characteristics: It contains triglycerids with saturated fatty acids which allow the cream to obtain the consistency required without having to go through ...
Unit 1 Page 1 Unit Vocabulary Terms Carbohydrate
... ● Carbohydrate - A group that includes sugar and starch that is used for energy or structure; can be small molecules (monosaccharides or disaccharides) or large molecules (polysaccharides such as starch and cellulose.) ● Proteins - A three-dimensional biological macromolecule constructed from a set ...
... ● Carbohydrate - A group that includes sugar and starch that is used for energy or structure; can be small molecules (monosaccharides or disaccharides) or large molecules (polysaccharides such as starch and cellulose.) ● Proteins - A three-dimensional biological macromolecule constructed from a set ...
Macromolecules
... (Scientists are lazy: Fatty acids are often shown as wavy lines instead of drawing out all the atoms) ...
... (Scientists are lazy: Fatty acids are often shown as wavy lines instead of drawing out all the atoms) ...
Overview of Fasting
... Ketogenesis is favored when the concentration of acetyl CoA, produced from fatty acid metabolism, exceeds the oxidative capacity of the TCA cycle. Significant ketogenesis starts during the first days of fasting . The availability of circulating ketone bodies is important in fasting because they can ...
... Ketogenesis is favored when the concentration of acetyl CoA, produced from fatty acid metabolism, exceeds the oxidative capacity of the TCA cycle. Significant ketogenesis starts during the first days of fasting . The availability of circulating ketone bodies is important in fasting because they can ...
Fatty acids in food supplements: Can you assume what you
... Objective 3: Determine the molecular structures of the fatty acids and their distributions In order to determine the distributions of individual fatty acids in your saponified extract, you will need to use a technique that combines a separation component with a detection method. From your Session 2 ...
... Objective 3: Determine the molecular structures of the fatty acids and their distributions In order to determine the distributions of individual fatty acids in your saponified extract, you will need to use a technique that combines a separation component with a detection method. From your Session 2 ...
Preparation of Azeleic Acid from Castor Oil Saponification and
... (usually NaOH or KOH) hydrolysis of triglycerides, which are esters of fatty acids, to form the sodium salt of a carboxylate. In addition to soap, such traditional saponification processes produces glycerol. ...
... (usually NaOH or KOH) hydrolysis of triglycerides, which are esters of fatty acids, to form the sodium salt of a carboxylate. In addition to soap, such traditional saponification processes produces glycerol. ...
Macromolecule Lecture
... • subunits called amino acids • the covalent bond linking two amino acids together is called a peptide bond • the assembled polymer is called a ...
... • subunits called amino acids • the covalent bond linking two amino acids together is called a peptide bond • the assembled polymer is called a ...
Fatty Acid Metabolism
... Occurs during starvation or prolonged exercise – result of elevated FFA • high HSL activity ...
... Occurs during starvation or prolonged exercise – result of elevated FFA • high HSL activity ...
SBI3U
... Glycogen – energy storage in animals (liver and muscle) Cellulose – structural molecule in cell walls ...
... Glycogen – energy storage in animals (liver and muscle) Cellulose – structural molecule in cell walls ...
Traffic Lights Biological Cpds
... 31. Projecting from the helix are -R groups which may interact to form bonds which help to maintain the tertiary structure’s three dimensional shape. 32. Able to identify disulphide, ionic, hydrogen and hydrophobic bonds between -R groups. 33. The quaternary structure is where two or more polypeptid ...
... 31. Projecting from the helix are -R groups which may interact to form bonds which help to maintain the tertiary structure’s three dimensional shape. 32. Able to identify disulphide, ionic, hydrogen and hydrophobic bonds between -R groups. 33. The quaternary structure is where two or more polypeptid ...
Molecules of Life Online Organizer
... Enzymes are / are not changed in a chemical reaction. Circle the correct answer ...
... Enzymes are / are not changed in a chemical reaction. Circle the correct answer ...
Dr. Ryals will give a seminar at IGBMC, focusing on global
... Dr. Ryals will give a seminar at IGBMC, focusing on global metabolism and the latest metabolom profiling technologies. Specifically, an overview of Metabolon’s global biochemical profiling technology platform will be presented with focus on the analytical approaches as well as applications to biolog ...
... Dr. Ryals will give a seminar at IGBMC, focusing on global metabolism and the latest metabolom profiling technologies. Specifically, an overview of Metabolon’s global biochemical profiling technology platform will be presented with focus on the analytical approaches as well as applications to biolog ...
Biology
... Water is released and energy is stored in the newly formed chemical bonds. • 4. Hydrolysis: A chemical process where a large molecule is broken down into smaller molecules. Water is required and energy is released. Digestion is a series of hydrolytic ...
... Water is released and energy is stored in the newly formed chemical bonds. • 4. Hydrolysis: A chemical process where a large molecule is broken down into smaller molecules. Water is required and energy is released. Digestion is a series of hydrolytic ...
Antioxidant Activity Associated with Lipid and
... germinated seeds of this tree for food uses is not known. This study reports some biochemical changes during seed germination associated with antioxidant activity and the mobilization of lipids and phenolics. Lipid content decreased, whereas the dominant fatty acids did not change significantly. The ...
... germinated seeds of this tree for food uses is not known. This study reports some biochemical changes during seed germination associated with antioxidant activity and the mobilization of lipids and phenolics. Lipid content decreased, whereas the dominant fatty acids did not change significantly. The ...
NME2.28: fat and carbohydrate metabolism in the
... o Glucagon – stimulates the kinases promoting glycogen degradation Non-hormonal control of glycogen synthesis and degradation is through: o Glucose-6P stimulates SP and glucose stimulates PP promoting glycogen synthesis o Adrenaline stimulates the kinases promoting glycogen degradation ...
... o Glucagon – stimulates the kinases promoting glycogen degradation Non-hormonal control of glycogen synthesis and degradation is through: o Glucose-6P stimulates SP and glucose stimulates PP promoting glycogen synthesis o Adrenaline stimulates the kinases promoting glycogen degradation ...
Main concepts Carbohydrates Fats, Proteins and Enzymes
... 6. Disaccharides (two sugars), including sucrose, lactose and maltose, are formed from the condensation reaction between two monosaccharide molecules. 7. Polysaccharides (many sugars), including starch, glycogen and cellulose, are formed from the condensation reactions between many monosaccharide mo ...
... 6. Disaccharides (two sugars), including sucrose, lactose and maltose, are formed from the condensation reaction between two monosaccharide molecules. 7. Polysaccharides (many sugars), including starch, glycogen and cellulose, are formed from the condensation reactions between many monosaccharide mo ...
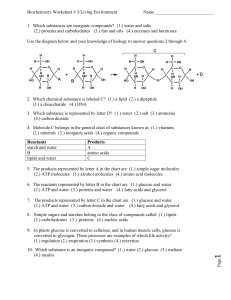
1. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
... 4. Molecule C belongs in the general class of substances known as (1.) vitamins (2.) minerals (3.) inorganic acids (4.) organic compounds ...
... 4. Molecule C belongs in the general class of substances known as (1.) vitamins (2.) minerals (3.) inorganic acids (4.) organic compounds ...
The Four major Groups of
... • Polymers can be broken down into their monomer components through hydrolysis. ...
... • Polymers can be broken down into their monomer components through hydrolysis. ...
Lecture: Fasting and gene expression, Part 1
... FASTING LED TO A SUSTAINED TRANSCRIPTION OF THE GENES ...
... FASTING LED TO A SUSTAINED TRANSCRIPTION OF THE GENES ...