Exam 3: Biochem 2 Fill in the Blank
... 1. Glycogen phosphorylase switches from _______ to ___________ form 2. Glycogen synthetase switches form __________ to ___________ form ii. Glycogen synthesis from G-1P 1. Glycogen phosphorylase switches from _______ to ___________ form 2. Glycogen synthetase switches from __________ to ___________ ...
... 1. Glycogen phosphorylase switches from _______ to ___________ form 2. Glycogen synthetase switches form __________ to ___________ form ii. Glycogen synthesis from G-1P 1. Glycogen phosphorylase switches from _______ to ___________ form 2. Glycogen synthetase switches from __________ to ___________ ...
Sample exam questions Chapter 11 Carbohydrates
... 24) All of the following statements concerning the citric acid cycle are true EXCEPT A. The cycle starts with the four-carbon compound oxaloacetate, adds two carbons from acetyl-CoA, stepwise loses two carbons as CO2, and regenerated the fourcarbon compound oxaloacetate. B. For each molecule of gluc ...
... 24) All of the following statements concerning the citric acid cycle are true EXCEPT A. The cycle starts with the four-carbon compound oxaloacetate, adds two carbons from acetyl-CoA, stepwise loses two carbons as CO2, and regenerated the fourcarbon compound oxaloacetate. B. For each molecule of gluc ...
chemistryandmacromolecules3
... • formed by interactions of lipid monomers, such as fatty acids and glycerol backbones. • Contain hydrocarbons (composed of C and H atoms); they are insoluble in water because of many nonpolar covalent bonds. • When close together, weak but additive van der Waals interactions hold them together. Sto ...
... • formed by interactions of lipid monomers, such as fatty acids and glycerol backbones. • Contain hydrocarbons (composed of C and H atoms); they are insoluble in water because of many nonpolar covalent bonds. • When close together, weak but additive van der Waals interactions hold them together. Sto ...
Exam 4, 2015 - Biochemistry at CSU, Stanislaus
... 14. (24 points) Describe how liver cells are controlled so that glycolysis and gluconeogenesis do not occur simultaneously in the liver. Give specific details about the regulation by insulin and glucagon. Give specific details about the reactions that are regulated. What enzyme, how is it regulated? ...
... 14. (24 points) Describe how liver cells are controlled so that glycolysis and gluconeogenesis do not occur simultaneously in the liver. Give specific details about the regulation by insulin and glucagon. Give specific details about the reactions that are regulated. What enzyme, how is it regulated? ...
Chapter Eight Lipids and Proteins Are Associated in Biological
... organic compounds classified together on the basis of common solubility properties • insoluble in water, but soluble in aprotic organic solvents including ______________________________________ ...
... organic compounds classified together on the basis of common solubility properties • insoluble in water, but soluble in aprotic organic solvents including ______________________________________ ...
(Macromolecules) Outline
... a. Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on Earth. 4. Chitin – This is the exoskeleton of some animals and also Fungi cell walls. ...
... a. Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on Earth. 4. Chitin – This is the exoskeleton of some animals and also Fungi cell walls. ...
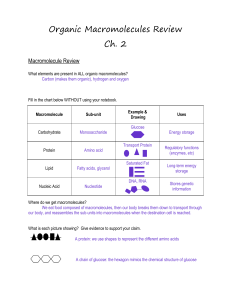
Organic Macromolecules Review Ch. 2
... Regulatory functions (enzymes, etc) Long-term energy storage Stores genetic information ...
... Regulatory functions (enzymes, etc) Long-term energy storage Stores genetic information ...
Document
... Ex. Glucose, fructose, galactose (sugars), cellulose (starch in plants), glycogen (starch stored in the liver) Provide energy for cells Indicator: Iodine (tests for starch): yellow to blue/black Benedicts (tests for sugar): blue + heat changes to orange ...
... Ex. Glucose, fructose, galactose (sugars), cellulose (starch in plants), glycogen (starch stored in the liver) Provide energy for cells Indicator: Iodine (tests for starch): yellow to blue/black Benedicts (tests for sugar): blue + heat changes to orange ...
Biological Molecules
... The shape of a protein determines its function. The shape of an individual protein is determined by the order of amino acids in the primary chain, which affects how the amino acid chain twists and folds into the final shape of the protein. DNA contains the code that instructs the cell machinery to ...
... The shape of a protein determines its function. The shape of an individual protein is determined by the order of amino acids in the primary chain, which affects how the amino acid chain twists and folds into the final shape of the protein. DNA contains the code that instructs the cell machinery to ...
Anatomy I - Unit 3: Basic Biochemistry
... Living things require millions of chemical reactions within the body, just to survive. Metabolism = all the chemical reactions occurring in the body. Organic molecules: ...
... Living things require millions of chemical reactions within the body, just to survive. Metabolism = all the chemical reactions occurring in the body. Organic molecules: ...
Anatomy I - Unit 3: Basic Biochemistry
... Living things require millions of chemical reactions within the body, just to survive. Metabolism = all the chemical reactions occurring in the body. Organic molecules: ...
... Living things require millions of chemical reactions within the body, just to survive. Metabolism = all the chemical reactions occurring in the body. Organic molecules: ...
fatty acids synthesis
... FATTY ACIDS SYNTHESIS A large proportion of the fatty acids used by the body are supplied by the diet. Carbohydrates, protein, and other molecules obtained from the diet in excess of the body's needs for these compounds can be converted to fatty acids, which are stored as triacylglycerols. In humans ...
... FATTY ACIDS SYNTHESIS A large proportion of the fatty acids used by the body are supplied by the diet. Carbohydrates, protein, and other molecules obtained from the diet in excess of the body's needs for these compounds can be converted to fatty acids, which are stored as triacylglycerols. In humans ...
Chemistry of Cooking, Chemisty in the Kitchen
... 12. Fe(II) wheel 13. a 'carboxylic acid' that fuels living cells 16. uncommon in nature - ie: elaidic acid 17. element Fe: blood, Flatirons are red b/c of this 18. one of 3 main nutrients: chain of amino acids 19. chemical used to test for presence of CO2 21. element C: found in abundance in stars, ...
... 12. Fe(II) wheel 13. a 'carboxylic acid' that fuels living cells 16. uncommon in nature - ie: elaidic acid 17. element Fe: blood, Flatirons are red b/c of this 18. one of 3 main nutrients: chain of amino acids 19. chemical used to test for presence of CO2 21. element C: found in abundance in stars, ...
Ch5LIPIDS
... • Trans fatty acids tend to raise total blood cholesterol levels, but less than more saturated fatty acids • Trans fatty acids also tend to raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL cholesterol • It is not clear if trans fats that occur naturally have the same effect as those produced by ...
... • Trans fatty acids tend to raise total blood cholesterol levels, but less than more saturated fatty acids • Trans fatty acids also tend to raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL cholesterol • It is not clear if trans fats that occur naturally have the same effect as those produced by ...
biochemistry - Bioscience High School
... maximum number of hydrogens bonded to the carbons (a double bond between carbons) Saturated fatty acids have the maximum number of hydrogens bonded to the carbons (all single bonds ...
... maximum number of hydrogens bonded to the carbons (a double bond between carbons) Saturated fatty acids have the maximum number of hydrogens bonded to the carbons (all single bonds ...
Biochemistry
... Explain the difference between acids and bases and be able to identify an acid or base by its position on the pH scale. Also explain how a buffer affects the pH of a solution. Explain the role of condensation and hydrolysis reactions in the formation and break down of organic compounds (notes and fi ...
... Explain the difference between acids and bases and be able to identify an acid or base by its position on the pH scale. Also explain how a buffer affects the pH of a solution. Explain the role of condensation and hydrolysis reactions in the formation and break down of organic compounds (notes and fi ...
fatty acid metabolism
... – ACC inhibited by FA-CoA – no malonyl-CoA to inhibit CAT-1 – net effect: FA oxidation ...
... – ACC inhibited by FA-CoA – no malonyl-CoA to inhibit CAT-1 – net effect: FA oxidation ...
10.2: Chemical Digestion and Absorption Which nutrients are
... Pancreatic Lipase: Trypsin: Chymotripsin: Peptidases: Absorption: How are the following absorbed? How are they transported? Monosaccharides: ...
... Pancreatic Lipase: Trypsin: Chymotripsin: Peptidases: Absorption: How are the following absorbed? How are they transported? Monosaccharides: ...
Examination III Key
... palmitoyl-CoA inside the mitochondrial matrix palmitoyl-ACP outside the mitochondrial matrix pallmitoyl-ACP inside the mitochondrial matrix palmitoyl-carnitine outside the mitochondrial matrix palmitoyl-carnitine inside the mitochondrial matrix palmitoyl-CoA then palmitoyl-carnitine outside the mito ...
... palmitoyl-CoA inside the mitochondrial matrix palmitoyl-ACP outside the mitochondrial matrix pallmitoyl-ACP inside the mitochondrial matrix palmitoyl-carnitine outside the mitochondrial matrix palmitoyl-carnitine inside the mitochondrial matrix palmitoyl-CoA then palmitoyl-carnitine outside the mito ...
Biochemistry - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... by addition of a water molecule one molecule gets an H+ & one gets OH – It is used to turn ATP into ADP ...
... by addition of a water molecule one molecule gets an H+ & one gets OH – It is used to turn ATP into ADP ...