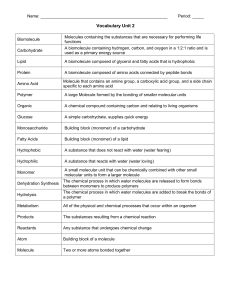
Name: Period: _____ Vocabulary Unit 2 Biomolecule Molecules
... A biomolecule containing hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio and is used as a primary energy source ...
... A biomolecule containing hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio and is used as a primary energy source ...
Fill in the Captions AP Lesson #26 Are our diets only glucose? How
... – Catabolism of carbohydrates, fats & proteins • all break down through same pathways • enter at different points as intermediates – cell extracts energy from every source ...
... – Catabolism of carbohydrates, fats & proteins • all break down through same pathways • enter at different points as intermediates – cell extracts energy from every source ...
Bio102 Problems
... membrane. This is because the greater bend or kink in the linderic acid means that the fatty acid tails of the phospholipids will pack together less efficiently and thus have a lower density. 11C. How would a membrane built only of lauric acid change if it was built only of palmitic acid molecules? ...
... membrane. This is because the greater bend or kink in the linderic acid means that the fatty acid tails of the phospholipids will pack together less efficiently and thus have a lower density. 11C. How would a membrane built only of lauric acid change if it was built only of palmitic acid molecules? ...
Carbon and Macromolecules Notes
... ORGANIC is derived from ORGANISM because all living things are made up of carbon based compounds ...
... ORGANIC is derived from ORGANISM because all living things are made up of carbon based compounds ...
Macromolecules - Uplift Education
... 2. Name 3 examples of lipids in the body. 3. Why would we store excess energy as Fat, rather than carbohydrates? ...
... 2. Name 3 examples of lipids in the body. 3. Why would we store excess energy as Fat, rather than carbohydrates? ...
Biochemistry - Circle of Docs
... 17. _______________ is a source of ribose for nucleotide formation: a. pentose phosphate pathway 18. fasting causes low serum ________ levels. a. Insulin b. Cortisol c. Glucagons d. Adrenalin 19. Which reacts with acetyl CoA to form citrate: a. Malate b. Oxaloacetate c. Pyruvate d. Glutamate 20. The ...
... 17. _______________ is a source of ribose for nucleotide formation: a. pentose phosphate pathway 18. fasting causes low serum ________ levels. a. Insulin b. Cortisol c. Glucagons d. Adrenalin 19. Which reacts with acetyl CoA to form citrate: a. Malate b. Oxaloacetate c. Pyruvate d. Glutamate 20. The ...
Biomolecules are organic molecules built and used inside of cells
... organelle membranes • “phospholipid bilayer” forms when put in aqueous solution ...
... organelle membranes • “phospholipid bilayer” forms when put in aqueous solution ...
Answers for extension worksheet – Option C
... amino acids, which are then deaminated (the NH2 group is removed). The remainder of the molecule enters the respiratory process. Some amino acids are converted to pyruvate, others enter the Krebs cycle. In either case, ATP is synthesised in the usual way. This only occurs during starvation because t ...
... amino acids, which are then deaminated (the NH2 group is removed). The remainder of the molecule enters the respiratory process. Some amino acids are converted to pyruvate, others enter the Krebs cycle. In either case, ATP is synthesised in the usual way. This only occurs during starvation because t ...
IB104 - Lecture 7 - Molecules of life
... Starch is the plant storage form and has linear stiff chains. It is therefore useful for making collars on shirts stiff. Animals eat starch in plants like corn and potatoes, etc., hydrolyse it to glucose, and then store it as glycogen. ...
... Starch is the plant storage form and has linear stiff chains. It is therefore useful for making collars on shirts stiff. Animals eat starch in plants like corn and potatoes, etc., hydrolyse it to glucose, and then store it as glycogen. ...
9AD Biomolecules
... nucleotides. Other macromolecules are ATP, hormones, and vitamins. 2. Carbohydrates are polysaccharides that store energy and provide structure for cells. Lipids are composed of fatty acids (hydrocarbon chains) and are used for energy storage and found in membranes. 3. Proteins are composed of amino ...
... nucleotides. Other macromolecules are ATP, hormones, and vitamins. 2. Carbohydrates are polysaccharides that store energy and provide structure for cells. Lipids are composed of fatty acids (hydrocarbon chains) and are used for energy storage and found in membranes. 3. Proteins are composed of amino ...
Carbon Compounds
... (Mostly carbon & hydrogen. Very little oxygen) Examples - Fats, oils, waxes, sterols (hormones) Functions • Stored energy (fats) • Structural- part of the cell membrane (phospholipids) • Repel water because they are nonpolar (even distribution of charge across the molecule) Ex- waxes. Helps to ‘wate ...
... (Mostly carbon & hydrogen. Very little oxygen) Examples - Fats, oils, waxes, sterols (hormones) Functions • Stored energy (fats) • Structural- part of the cell membrane (phospholipids) • Repel water because they are nonpolar (even distribution of charge across the molecule) Ex- waxes. Helps to ‘wate ...
Answer the following short questions Q 1
... Uridine diphosphate glucose (UDPG) can be formed directly from UDP- galactose by the enzyme UDP-glucose 4-epimerase Q2 The process of fatty acid biosynthesis shows several features which distinguish it clearly from fatty acid oxidation, these include the requirement for NADPH and biotin Q3 The pento ...
... Uridine diphosphate glucose (UDPG) can be formed directly from UDP- galactose by the enzyme UDP-glucose 4-epimerase Q2 The process of fatty acid biosynthesis shows several features which distinguish it clearly from fatty acid oxidation, these include the requirement for NADPH and biotin Q3 The pento ...
Biomolecules are organic molecules built and used inside of cells
... • The function of monosaccharides is to ______________ for a short term • Monosaccharides are broken down in cellular ________________ into carbon dioxide and water • The energy released from the broken bonds is used to form molecules of ______ (the energy currency of the cell) • Examples of monosac ...
... • The function of monosaccharides is to ______________ for a short term • Monosaccharides are broken down in cellular ________________ into carbon dioxide and water • The energy released from the broken bonds is used to form molecules of ______ (the energy currency of the cell) • Examples of monosac ...
Biochem
... • “Trans” double bonds are not naturally found in biological systems • When unsat. fats are “hydrogenated” to become sat. fat (easier to store, ship,use), the H’s can rearrange and ‘straighten out’ the molecule • Trans fat is bad (?) b/c it is not recognized by our body’s enzymes (?) ...
... • “Trans” double bonds are not naturally found in biological systems • When unsat. fats are “hydrogenated” to become sat. fat (easier to store, ship,use), the H’s can rearrange and ‘straighten out’ the molecule • Trans fat is bad (?) b/c it is not recognized by our body’s enzymes (?) ...
Lipid metabolism
... to acetyl-CoA (→ citric acid cycle) • is located in matrix of mitochondria of the peripheral tissues • is significant in skeletal muscles, heart and also in the brain if lack of Glc occurs ...
... to acetyl-CoA (→ citric acid cycle) • is located in matrix of mitochondria of the peripheral tissues • is significant in skeletal muscles, heart and also in the brain if lack of Glc occurs ...
Organic Molecules
... covalently bonded. -Glycogen, animal sugar (storage of glucose). Stored in liver and muscle. -Starch, plant sugar (storage of glucose). -glucose is stored as a large molecule rather than individual molecules. Prevents osmotic damage to the cell. ...
... covalently bonded. -Glycogen, animal sugar (storage of glucose). Stored in liver and muscle. -Starch, plant sugar (storage of glucose). -glucose is stored as a large molecule rather than individual molecules. Prevents osmotic damage to the cell. ...
+ fatty acid - Cloudfront.net
... • Hydrophobic tails “hide” from H2O – can self-assemble into “bubbles” • bubble = “micelle” • can also form a phospholipid bilayer • early evolutionary stage of cell? ...
... • Hydrophobic tails “hide” from H2O – can self-assemble into “bubbles” • bubble = “micelle” • can also form a phospholipid bilayer • early evolutionary stage of cell? ...
CH 3
... •commonly occur as storage fats in, for example, adipose tissue; they provide a reservoir of energy •they are neutral fats •they comprise 3 fatty acids combined with glycerol •note that mono and diglycerides also exist as storage fats ...
... •commonly occur as storage fats in, for example, adipose tissue; they provide a reservoir of energy •they are neutral fats •they comprise 3 fatty acids combined with glycerol •note that mono and diglycerides also exist as storage fats ...
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... • Formed by removal of hydrogen atoms from carbon skeleton. • Form good fats - liquid at room temperature (oils) ...
... • Formed by removal of hydrogen atoms from carbon skeleton. • Form good fats - liquid at room temperature (oils) ...
Organic compounds
... Used by cells to store and release energy Carbohydrates: example glucose ...
... Used by cells to store and release energy Carbohydrates: example glucose ...
Carbohydrates
... Carboxyl: carboxylic acids *Note that properties such as boiling and melting point change due to functional groups ...
... Carboxyl: carboxylic acids *Note that properties such as boiling and melting point change due to functional groups ...