Pathology Ketone bodies are created at moderate
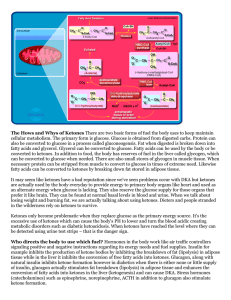
... synthesis occurs in response to low glucose, and after exhaustion of glycogen. The production of ketone bodies is then initiated to make available energy that is stored as fatty acids which are enzymatically broken down in β-oxidation to form acetyl-CoA. Normally, acetyl-CoA is further oxidized and ...
... synthesis occurs in response to low glucose, and after exhaustion of glycogen. The production of ketone bodies is then initiated to make available energy that is stored as fatty acids which are enzymatically broken down in β-oxidation to form acetyl-CoA. Normally, acetyl-CoA is further oxidized and ...
Fatty Acid Activation Fatty acid activation
... Breaks down triacylglycerols in adipose tissue to fatty acids and glycerol. ...
... Breaks down triacylglycerols in adipose tissue to fatty acids and glycerol. ...
Name Class Date Reviewing Key Concepts Identifying On the lines
... Identifying On the lines provided, identify each statement as describing carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, or proteins. 1. the main source of energy for living things 2. help carry out chemical reactions 3. important parts of biological membranes 4. contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus ...
... Identifying On the lines provided, identify each statement as describing carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, or proteins. 1. the main source of energy for living things 2. help carry out chemical reactions 3. important parts of biological membranes 4. contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus ...
1. The table shows the number of carbon atoms contained in some
... The diagrams show four types of linkage, A to D, which occur in biological molecules. Amino acid H C H ...
... The diagrams show four types of linkage, A to D, which occur in biological molecules. Amino acid H C H ...
Biochemistry
... have been linked and a water lost The bond holding the sugars together is a glycosidic bond Isomers—same chemical formula with different structures ...
... have been linked and a water lost The bond holding the sugars together is a glycosidic bond Isomers—same chemical formula with different structures ...
Lecture 7
... This mixed triglyceride includes a saturated fatty acid, a monounsaturated fatty acid, and a polyunsaturated fatty acid. ...
... This mixed triglyceride includes a saturated fatty acid, a monounsaturated fatty acid, and a polyunsaturated fatty acid. ...
Fatty Acid oxidation
... These reactions produce no ATP ß-oxidation in the peroxisomes ends at octanoyl-CoA (C 8). It is subsequently removed from the peroxisomes in the form of octanoyl and acetylcarnitine and both are further oxidized in mitochondria. ...
... These reactions produce no ATP ß-oxidation in the peroxisomes ends at octanoyl-CoA (C 8). It is subsequently removed from the peroxisomes in the form of octanoyl and acetylcarnitine and both are further oxidized in mitochondria. ...
Sample Exam 1
... 47. The extracellular fluid (ECF) is also known as the cytosol. 48. Cholesterol is a hydrophobic molecule. 49. A molecule of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is most similar in structure to a molecule of cholesterol. 50. Non-essential amino acids can only be obtained through the diet (eating). 51. Nucle ...
... 47. The extracellular fluid (ECF) is also known as the cytosol. 48. Cholesterol is a hydrophobic molecule. 49. A molecule of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is most similar in structure to a molecule of cholesterol. 50. Non-essential amino acids can only be obtained through the diet (eating). 51. Nucle ...
Document
... Thioester enolize more readily than esters. The enol can react with electrophile to afford -substitution products ...
... Thioester enolize more readily than esters. The enol can react with electrophile to afford -substitution products ...
Biomolecules
... Polysaccharide found in plant cell walls • For humans cellulose is indigestible and forms dietary fiber • Made up entirely of β glucoses – Structure is constrained into straight microfibrils ...
... Polysaccharide found in plant cell walls • For humans cellulose is indigestible and forms dietary fiber • Made up entirely of β glucoses – Structure is constrained into straight microfibrils ...
Answer
... 45. After the reaction, what happens to the products? Can the enzyme be re-used & why? Products are released and the enzyme shape returns to normal. The enzyme is recycled. 46. Besides temperature, what else can affect how an enzyme works by changing the enzyme's shape? Can the reaction still take p ...
... 45. After the reaction, what happens to the products? Can the enzyme be re-used & why? Products are released and the enzyme shape returns to normal. The enzyme is recycled. 46. Besides temperature, what else can affect how an enzyme works by changing the enzyme's shape? Can the reaction still take p ...
Chapter 5 - glenbrook s hs
... One monomer provides a hydroxyl group while the other provides a hydrogen to form a water molecule ...
... One monomer provides a hydroxyl group while the other provides a hydrogen to form a water molecule ...
2.1 Molecules and metabolism
... • Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules including the formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions. • Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers. Applications ...
... • Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules including the formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions. • Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers. Applications ...
Biochemistry Test Review KEY
... 12. What is the name of the structure above and what is its function? Nucleic acid 13. What is a common element found in all organic compounds? Carbon 14. What effect does pH levels have on a certain enzyme? Slows or speeds up rate of reaction, as well as the modifies the enzyme’s shape 15. Describ ...
... 12. What is the name of the structure above and what is its function? Nucleic acid 13. What is a common element found in all organic compounds? Carbon 14. What effect does pH levels have on a certain enzyme? Slows or speeds up rate of reaction, as well as the modifies the enzyme’s shape 15. Describ ...
Carbon Compounds In Cells
... Glycogen • Sugar storage form in animals • Large stores in muscle and liver cells • When blood sugar decreases, liver cells degrade glycogen, release glucose ...
... Glycogen • Sugar storage form in animals • Large stores in muscle and liver cells • When blood sugar decreases, liver cells degrade glycogen, release glucose ...
AS-biology answers
... Triglycerides are made from a glycerol molecule (1) and three molecules of fatty acids (1). They are formed by condensation reactions (1). These reactions result in the formation of ester bonds (1) between the fatty acid and glycerol molecules, with the production of a molecule of water for each fat ...
... Triglycerides are made from a glycerol molecule (1) and three molecules of fatty acids (1). They are formed by condensation reactions (1). These reactions result in the formation of ester bonds (1) between the fatty acid and glycerol molecules, with the production of a molecule of water for each fat ...
Lecture 14: Alternative Pathways in Cell respiration
... tied to cellular respiration • Excess intermediates of glycolysis and the Kreb’s cycle can be converted to stored carbohydrates, fats and proteins. ...
... tied to cellular respiration • Excess intermediates of glycolysis and the Kreb’s cycle can be converted to stored carbohydrates, fats and proteins. ...
Short- and long-term effects of fatty acids on pancreatic alpha cell
... Palmitate acutely stimulated glucagon release in a concentrationdependent manner. The longer the chain length of saturated fatty acids, the higher glucagon responses were obtained. Saturated fatty acids were more potent than unsaturated fatty acids in stimulating glucagon secretion. At equimolar con ...
... Palmitate acutely stimulated glucagon release in a concentrationdependent manner. The longer the chain length of saturated fatty acids, the higher glucagon responses were obtained. Saturated fatty acids were more potent than unsaturated fatty acids in stimulating glucagon secretion. At equimolar con ...
Macromolecules Review ws Name the 6 main elements that make
... 12. What are disaccharides & give an example? 2 monosaccharide - sucrose ...
... 12. What are disaccharides & give an example? 2 monosaccharide - sucrose ...
document - Food Standards Australia New Zealand
... CHD. This is because the relationships we are reviewing all stop at blood cholesterol. We are considering how to deal with the extension to CHD risk as part of a separate process. Yes, we are happy for more than one expert to work together to prepare these reviews. However for contractual reasons, w ...
... CHD. This is because the relationships we are reviewing all stop at blood cholesterol. We are considering how to deal with the extension to CHD risk as part of a separate process. Yes, we are happy for more than one expert to work together to prepare these reviews. However for contractual reasons, w ...
biologically important molecules
... INSULIN hormone causes glucose to enter LIVER and MUSCLE where it is condensed into GLYCOGEN for storage. GLUCAGON hormone causes GLYCOGEN to be hydrolyzed back into individual glucose monomers and released into the bloodstream where it is transported to cells and used for energy. ...
... INSULIN hormone causes glucose to enter LIVER and MUSCLE where it is condensed into GLYCOGEN for storage. GLUCAGON hormone causes GLYCOGEN to be hydrolyzed back into individual glucose monomers and released into the bloodstream where it is transported to cells and used for energy. ...
Unit 1: The Chemistry of Life
... 8. Distinguish between an oil and a fat and between a saturated fat, an unsaturated fat, and a polyunsaturated fat. Are unsaturated fats more common in animal tissue? Explain (pg75) . • Oil liquid at room temperature • Fat solid at room temperature • Saturated C-C single bonds, most H’s – Ex ...
... 8. Distinguish between an oil and a fat and between a saturated fat, an unsaturated fat, and a polyunsaturated fat. Are unsaturated fats more common in animal tissue? Explain (pg75) . • Oil liquid at room temperature • Fat solid at room temperature • Saturated C-C single bonds, most H’s – Ex ...