* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Metabolism of lipids
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
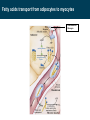
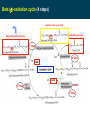
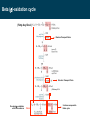
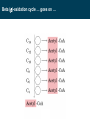
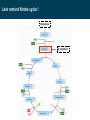
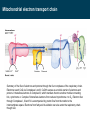
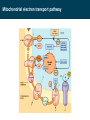
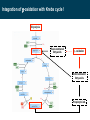
BIOQUÍMICA E BIOLOGIA CELULAR António Ascensão, José Magalhães Metabolism of lipids Faculdade de Desporto, Universidade do Porto, 1º Ciclo, 1º Ano 2011_20012 Metabolic conversions of nutrients Metabolic pathways overview Molecular structure of triglycerides Adapted from “Understanden human anatomy and physiology”, 5fh Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2004 Steps of lipid catabolism • Mobilization - hydrolysis of TG stored on adipocytes • Circulation – Plasmatic transport of free fatty acids with albumin to muscle • Absortion - entrance of fatty acids in muscle (FABP) • Activation – formation of fatty acyl-CoA in cytosol (ATP dependent) • Translocation – Transport of fatty acyl-CoA to mitochondria through carnitine shuttle • Beta-oxidation – production of NADH, FADH2 and acetyl-CoA from fatty acyl-CoA • Mitochondrial oxidation – Krebs cycle and electron transport chain The example of G Protein on lipolysis … ↑ Catecolamines ↑ Glucagon Triacylglycerols Lipase Fatty acids transport from adipocytes to myocytes ↑ Catecolamines ↑ Glucagon Lipid metabolism animation http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/ animations/fatty_acid_metabolism/ fatty_acid_metabolism.htm Entry of fatty acids into mitochondria – the Carnitine Shuttle (fatty acid binding proteins) 1 2 Carnitine Shuttle (3 steps process) 3 β - oxidation Carnitine Shuttle (rate limiting step for fatty acids oxidation) 2 Acyl-CoA synthetase Carnitine acyltransferase I 1 3 Carnitine acyltransferase II Beta (β)-oxidation cycle (4 steps) (continues for new cycle) (end of the process) (beginning of the process) 1º Step 4º Step FADH2 H+ + NADH 2º Step (HADH) 3º Step Beta (β)-oxidation cycle ( Fatty-Acyl CoA ) Electron Transport Chain Electron Transport Chain Re-enters β - oxidation with 2 less carbons 2 carbon compound to Krebs cycle Steps of Beta (β) oxidation cycle (summary) • Reaction 1 (1st Step) • – Oxidation of fatty Acyl-CoA Reaction 3 (3rd Step) – Oxidation – Catalyzed by Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase – Catalyzed by Hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase – Generates 1 FADH2 (ETC) – Generates 1 NADH (ETC) • Reaction 2 (2nd Step) – Hydration • Reaction 4 (4th Step) – Catalyzed by Enoyl-CoA Hydratase – Bond Cleavage between β and α carbon – Forms β-Hydroxyacyl-CoA – Catalyzed by Thiolase – Requires CoA – Forms Acetyl-CoA (enters Krebs cycle) – Forms Fatty Acyl-CoA (2 carbons shorter (re-enters β - oxidation) Beta (β)-oxidation • Breakdown of fats into – Acetyl coenzyme A (CoA) --> Kreb Cycle – FADH2 --> Oxidative Phosphorylation – NADH --> Oxidative Phosphorylation • Breaks off two carbons at a time to acetyl CoA – Remaining Acyl-CoA goes another round Beta (β)-oxidation cycle … goes on … Beta (β)-oxidation … an example γ β α O CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – C SCoA 14 carbon fatty acid 6 rounds on Beta-oxidation 7 acetyl-CoA formed Beta (β)-oxidation cycle interconnections Lets remind Krebs cycle ! Lets remind Krebs cycle ! Glycolysis β - oxidation Mitochondrial electron transport chain Summary of the flow of electrons and protons through the four complexes of the respiratory chain. Electrons reach CoQ via Complexes I and II. CoQH2 serves as a mobile carrier of electrons and protons. It transfers electrons to Complex III, which transfers them to another mobile connecting link, cytochrome c. Complex IV transfers electrons from reduced cytochrome c to O2. Electron flow through Complexes I, III and IV is accompanied by proton flow from the matrix to the intermembrane space. Electrons from fatty acid b-oxidation can also enter the respiratory chain though UQ. Mitochondrial electron transport pathway Beta (β)-oxidation cycle … an example ! Fatty acids oxidation … the energetic yelding ! Beta (β)-oxidation of odd-numbered fatty acids Integration of β-oxidation with Krebs cycle ! Glycolysis Even-numbered fatty acids β - oxidation Odd-numbered fatty acids Propionyl-CoA Ketogenesis (formation of ketone bodies) Physiological condition Biochemical impact Ketogenesis Ketone bodies Ketosis Fasted-state (starvation) Prolonged exercise Diabetes … Glycogen deplection (↓ oxaloacetate - gluconeogenesis) Excess of β-oxidation (↑ acetyl-CoA) Liver Acetoacetate Acetone β-hydroxybutyrate Metabolic acidosis ↑ plasma ketonic bodies Ketogenesis (formation of ketone bodies) in liver X Ketogenesis (formation of ketone bodies) Extreme ketogenesis … the case of diabetes Mitochondrial metabolism_overview