* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Preparation of Azeleic Acid from Castor Oil Saponification and
Survey
Document related concepts
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
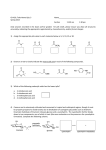
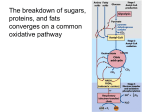
Preparation of Azeleic Acid from Castor Oil Saponification and Oxidation reactions (Please read Experiment 25.3 on page 569) This week's reaction: saponification of castor oil OH O O O OH 1. KOH, H2O, heat OH 2. H2SO4 OH O O OH O OH + 3 HO OH O Triricinoleylglycerol (castor oil) glycerol ricinoleic acid 1. Set up the reaction apparatus inside your hood; 2. Load all reactants and reagents; 3. Heat the flask directly on a hot plate at medium setting; 4. Stirring for two hours; 5. Work up the reaction. Saponification is a process that produces soap, usually from fatty esters. In chemistry terms, saponification involves base (usually NaOH or KOH) hydrolysis of triglycerides, which are esters of fatty acids, to form the sodium salt of a carboxylate. In addition to soap, such traditional saponification processes produces glycerol. Mechanism of saponification O R O O R O O OH- HO O 3 NaOH, H2O + 3 R heat OH ONa HO R glycerol O Triglycerides Next week's reaction: O OH HO KMnO4 O HO ricinoleic acid O O + + CO2 + MnO2 OH azeleic acid 2-octanone Oxidation and decarboxylation reactions. O heat RH + CO2 R OH O O gentle heating O O H O + CO2 HO O β-ketocarboxylic acid 2-octanone Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. Decarboxylation is especially easy in βketocarboxylic acids due to the concerted movement of three pairs of electrons. Biochemical decarboxylation is common. One example is pyruvate to acetyl co-A. CoA + NAD+ O OH CO2 + NADH O S CoA O pyruvate acetyl-CoA