* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NME2.28: fat and carbohydrate metabolism in the
Survey
Document related concepts
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
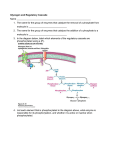
NME2.28: FAT AND CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM IN THE ABSORPTIVE STATE 05/03/08 GLYCOGEN SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION Glycogen is a branched glucose storage polymer consisting of α1-4 and α1-6 bonds o These branched bonds allow rapid degradation to generate glucose Synthesis of glycogen is catalysed by de-phosphorylated glycogen synthase (GS) o Synthase phosphatase (SP) activates GS o Synthase kinase (SK) deactivates GS Degradation of glycogen is catalysed by phosphorylated glycogen phosphorylase (GP) o Phosphorylase kinase (PK) activates GP o Phosphorylase phosphatase (PP) deactivates GP Hormonal control of glycogen synthesis and degradation is through: o Insulin – stimulates the phosphatases promoting glycogen synthesis o Glucagon – stimulates the kinases promoting glycogen degradation Non-hormonal control of glycogen synthesis and degradation is through: o Glucose-6P stimulates SP and glucose stimulates PP promoting glycogen synthesis o Adrenaline stimulates the kinases promoting glycogen degradation FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS The liver has a limited glycogen storage capacity (approximately 100g) Excess glucose and amino acids are converted to fatty acids and ultimately triglycerides to be stored Pyruvate from glycolysis enters the hepatocyte/adipocyte mitochondria o Pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA by pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) o Acetyl-CoA enters the first part of the TCA cycle (see NME 2.31) o Acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate is converted to citrate o Citrate is exported from the mitochondria Citrate is re-converted to acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate in the cytoplasm o Oxaloacetate is converted to malate which re-enters the mitochondria and the TCA cycle o Acetyl-CoA is converted to malonyl-CoA by acetyl-CoA carboxylase o Malonyl-CoA is converted into a fatty acid by fatty acid synthase using NADPH Hormonal control of fatty acid synthesis is through: o Insulin – activates PDH and acetyl-CoA carboxylase promoting fatty acid synthesis o Glucagon – inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase restricting fatty acid synthesis Non-hormonal control of fatty acid synthesis is through: o Citrate – activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase promoting fatty acid synthesis o Fatty acids – inhibit PDH and acetyl-CoA carboxylase restricting fatty acid synthesis o NADH – inhibits PDH restricting fatty acid synthesis LEARNING OUTCOMES Explain why disorders in glycogen metabolism affect blood glucose homeostasis and cause muscle fatigue Liver glycogen stores maintain blood glucose during fasting o Glycogen releases glucose-6P which is de-phosphorylated to glucose by G6Pase o G6Pase is only found in the liver Muscle glycogen stores provide energy during exercise o Glycogen is metabolised by glycolysis to generate ATP Disorders of glycogen metabolism: o Reduce the liver’s ability to replenish blood glucose levels during fasting o Restrict energy production in muscle leading to fatigue Explain why the replenishment of glycogen stores is the major priority of glucose metabolism in the liver when feeding follows a period of fasting Glycogen stores are crucial for maintaining blood glucose homeostasis during fasting