* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MACROMOLECULE SUMMARY SHEET
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
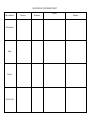
MACROMOLECULE SUMMARY SHEET Macromolecule Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Functions Monomers Structure Examples Carbohydrate Questions: 1. How are monosaccharides and polysaccharides related? 2. Compare (what’s the same) and contrast (what’s different) about starch and glycogen? Lipid Questions: 1. Explain how glycerol and fatty acids join together to form lipids. 2. Explain what is meant by “unsaturated” and “saturated” fatty acids. Nucleic Acids: 1. What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide? 2. What is the difference between the 2 types of nucleic acids? Proteins: 1. What is the one thing that makes one amino acid different from another? 2. How many amino acids are found in nature? 3. What type of bond joins one amino acid to another (use internet, not in book). MACROMOLECULE SUMMARY SHEET Macromolecule Carbohydrates Polysaccharides (Starch, glycogen, & cellulose) Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Functions Energy storage (starch in plants; glycogen in animals) Monomers Examples Structure monosaccharide Structural components (cellulose in plants) Energy storage Insulation Protects soft organs Chemical messages Waterproof coverings Glucose, fructose, galactose Sucrose, lactose, maltose Glycogen, starch, cellulose 3 Fatty Acids 1 Glycerol (Form a triglyceride) Fats - butter Waxes – plant leaf coverings Oils – vegetable oil Steroids – testosterone, estrogen Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions Structural components Transport molecules Contractile proteins in muscles Body defense Signaling Storage Amino Acids Hemoglobin Catalase Antibodies Keratin(hair, nails) Actin/Myosin (muscles) Carries genetic information Nucleotides DNA RNA