Chemistry Honors Study Guide – Organic Chemistry You should be
... Compare straight-chain and branched hydrocarbons, in terms of structure, viscosity, and boiling point ...
... Compare straight-chain and branched hydrocarbons, in terms of structure, viscosity, and boiling point ...
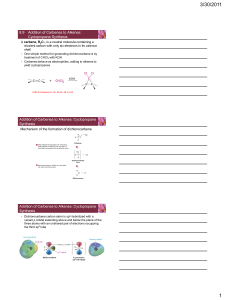
Mechanism of Dissolving Metal Reduction
... ring opens up affording a single chain with two carbonyls at the carbons where the double bonds were originally. • Oxidative cleavage is a valuable tool in structure determination, helping to pinpoint the location of double bonds in complex alkene structures. ...
... ring opens up affording a single chain with two carbonyls at the carbons where the double bonds were originally. • Oxidative cleavage is a valuable tool in structure determination, helping to pinpoint the location of double bonds in complex alkene structures. ...
Chapter 6: Alkynes, reactions of alkynes, and multistep synthesis
... 3. if 2 triple bonds, diyne a. if 3 trple bonds, triyne b. if 4, tetrayne, then pentayne, hexayne, heptayne, etc 4. with number (#) as prefix a. funct grp has priority with numbering 5. if more than 1 subst., place all in alphabetical order in front 6. if counting from either end is tie in yne #, us ...
... 3. if 2 triple bonds, diyne a. if 3 trple bonds, triyne b. if 4, tetrayne, then pentayne, hexayne, heptayne, etc 4. with number (#) as prefix a. funct grp has priority with numbering 5. if more than 1 subst., place all in alphabetical order in front 6. if counting from either end is tie in yne #, us ...
7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis
... • Oxidizing reagents other than ozone also cleave alkenes • Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) can produce carboxylic acids and carbon dioxide if H’s are present on C=C O ...
... • Oxidizing reagents other than ozone also cleave alkenes • Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) can produce carboxylic acids and carbon dioxide if H’s are present on C=C O ...
Alkenes—The Products of Elimination
... • Removal of the elements HX is called dehydrohalogenation. • Dehydrohalogenation is an example of elimination. • The curved arrow formalism shown below illustrates how four bonds are broken or formed in the process. ...
... • Removal of the elements HX is called dehydrohalogenation. • Dehydrohalogenation is an example of elimination. • The curved arrow formalism shown below illustrates how four bonds are broken or formed in the process. ...
Chapter 22 Organic chemistry
... Sources and uses of alkanes Most from petroleum & natural gas e.g. natural gas is 90 % methane gasoline: heptane, isooctane, …. ...
... Sources and uses of alkanes Most from petroleum & natural gas e.g. natural gas is 90 % methane gasoline: heptane, isooctane, …. ...
1 - Rosshall Academy
... Name the straight chain alkanes C1 to C8 from molecular formulae, shortened and full structural formulae. Write molecular formulae and draw full and shortened structural formulae given the names of straight-chain alkanes C1 to C8 Give the systematic names of branched chain alkanes from shortened and ...
... Name the straight chain alkanes C1 to C8 from molecular formulae, shortened and full structural formulae. Write molecular formulae and draw full and shortened structural formulae given the names of straight-chain alkanes C1 to C8 Give the systematic names of branched chain alkanes from shortened and ...
UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS
... 1. Write the equation for chemical reaction H2SO4 C2H5OH → C2H4 + H2O 2. Find the mole number of ethyl alcohol n= m/ M = 23/ 46 = 0,5 mole According to chemical equation n(ethanol)= n (ethylene) = 0,5 mole 3. Find the mass of ethylene m= 0,5 * 28 = 14 g 4. Since the yield of product is only 70% - m ...
... 1. Write the equation for chemical reaction H2SO4 C2H5OH → C2H4 + H2O 2. Find the mole number of ethyl alcohol n= m/ M = 23/ 46 = 0,5 mole According to chemical equation n(ethanol)= n (ethylene) = 0,5 mole 3. Find the mass of ethylene m= 0,5 * 28 = 14 g 4. Since the yield of product is only 70% - m ...
Organometallic Compounds
... (named after the chemical companies of the same name) originally referred to the oxidation of ethylene to acetaldehyde by oxygen in water in the presence of a tetrachloropalladate catalyst. This chemical reaction, a German invention, was the first organometallic and organopalladium reaction applied ...
... (named after the chemical companies of the same name) originally referred to the oxidation of ethylene to acetaldehyde by oxygen in water in the presence of a tetrachloropalladate catalyst. This chemical reaction, a German invention, was the first organometallic and organopalladium reaction applied ...
Organic Chemistry
... Contain 1 or more triple bonds “unsaturated” Not common in nature All 3 hydrocarbons have weak van der Waals forces—low boiling points Example C2H2 H—C=C—H Ethyne ...
... Contain 1 or more triple bonds “unsaturated” Not common in nature All 3 hydrocarbons have weak van der Waals forces—low boiling points Example C2H2 H—C=C—H Ethyne ...
types of organic reactions
... One product will be there in greater amounts than the other and is called the major product (the other is called the minor product). To decide which is the major product, Markovnikov’s rule is used: The hydrogen atom of the addition reagent goes to the carbon atom of the double bond, that is attache ...
... One product will be there in greater amounts than the other and is called the major product (the other is called the minor product). To decide which is the major product, Markovnikov’s rule is used: The hydrogen atom of the addition reagent goes to the carbon atom of the double bond, that is attache ...
Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes – Properties and Synthesis
... Chapter 11. Alcohols and Ethers Ch 11.1–11.10: Structure and nomenclature Synthesis of alcohols and ethers Reactions of alcohols (as an acid, to alkyl halides with PBr3 and SOCl2, to sulfonates) Ch 11.11–11.12: Synthesis of Ethers–Williamson ether synthesis ...
... Chapter 11. Alcohols and Ethers Ch 11.1–11.10: Structure and nomenclature Synthesis of alcohols and ethers Reactions of alcohols (as an acid, to alkyl halides with PBr3 and SOCl2, to sulfonates) Ch 11.11–11.12: Synthesis of Ethers–Williamson ether synthesis ...
World of Chemistry Chapter 20—Organic Chemistry
... Section 20.1—Carbon bonding A. There are several million known carbon-chain (organic) molecules which are the basis for respiration and reproduction in all plants and animals. B. Carbon forms strong bonds to itself and to many other elements C. More than any other element, carbon can form long chain ...
... Section 20.1—Carbon bonding A. There are several million known carbon-chain (organic) molecules which are the basis for respiration and reproduction in all plants and animals. B. Carbon forms strong bonds to itself and to many other elements C. More than any other element, carbon can form long chain ...
Document
... change in the receptor site. Not produced by the body. An organic molecule containing a carbon atom with a + charge. Intermediates in the electrophilic addition reactions of alkenes. A carbon atom with 4 different atoms or groups of atoms attached. A reaction in which two molecules join together and ...
... change in the receptor site. Not produced by the body. An organic molecule containing a carbon atom with a + charge. Intermediates in the electrophilic addition reactions of alkenes. A carbon atom with 4 different atoms or groups of atoms attached. A reaction in which two molecules join together and ...
Organic Objectives
... build models using single, double and triple bonds and describe which rotate. demonstrate cis- and trans- isomerism, example: dichloroethene, C2H2Cl2. recognize whether the molecule is an alkane, alkene, or alkyne given the formula. name a molecule, given the structural formula. write the ...
... build models using single, double and triple bonds and describe which rotate. demonstrate cis- and trans- isomerism, example: dichloroethene, C2H2Cl2. recognize whether the molecule is an alkane, alkene, or alkyne given the formula. name a molecule, given the structural formula. write the ...
C14_-_Organic_Chemistry
... alkanes and alkenes (not cistrans), containing up to four carbon atoms per molecule. ...
... alkanes and alkenes (not cistrans), containing up to four carbon atoms per molecule. ...
Chapter 1--Title
... A compound with general formula CnH2n-2 can have a triple bond, two double bonds, a double bond and a ring or two rings Index of Hydrogen Deficiency: the number of pairs of hydrogen atoms that must be subtracted from the molecular formula of the corresponding alkane to give the molecular formula o ...
... A compound with general formula CnH2n-2 can have a triple bond, two double bonds, a double bond and a ring or two rings Index of Hydrogen Deficiency: the number of pairs of hydrogen atoms that must be subtracted from the molecular formula of the corresponding alkane to give the molecular formula o ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.