CHEM 2414
... cycloalkane two hydrogen atoms, one from each end of the chain, must be lost. Hence the general formula for a cycloalkane composed of n carbons is CnH2n. Although a cycloalkane has two fewer hydrogens than the equivalent alkane, each carbon is bonded to four other atoms so such compounds are still c ...
... cycloalkane two hydrogen atoms, one from each end of the chain, must be lost. Hence the general formula for a cycloalkane composed of n carbons is CnH2n. Although a cycloalkane has two fewer hydrogens than the equivalent alkane, each carbon is bonded to four other atoms so such compounds are still c ...
Name
... b. C=O- carbonyl c. COOH- carboxyl d. NH2- amino e. OPO32-- phosphate f. CH3- methyl 5. What is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid? (1) Saturated fats do not have double bonded C and have the max number of H possible. Unsaturated have double bonds and not the max number ...
... b. C=O- carbonyl c. COOH- carboxyl d. NH2- amino e. OPO32-- phosphate f. CH3- methyl 5. What is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid? (1) Saturated fats do not have double bonded C and have the max number of H possible. Unsaturated have double bonds and not the max number ...
Markovnikov`s Rule
... What's the rxn of ethene and hydrogen bromide get you? How about hydrogen chloride and cyclohexene? ...
... What's the rxn of ethene and hydrogen bromide get you? How about hydrogen chloride and cyclohexene? ...
Organic Chemistry Review
... Isomer: compounds that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structures. Unsaturated compound: an organic compound with one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. Saturated compound: an organic compound in which all carbon atoms are joined by single covalent bonds; it contain ...
... Isomer: compounds that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structures. Unsaturated compound: an organic compound with one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. Saturated compound: an organic compound in which all carbon atoms are joined by single covalent bonds; it contain ...
Development of New Organic Reactions by Exploiting Sulfur
... Therefore, exploration of a new method for oxidation is worth challenging. Based on the idea that a new reactivity would be created in sulfur-based oxidation by utilizing a sufur-nitrogen bond, we found N-tert-butylbenzenesulfinimidoyl chloride (1) as a unique oxidizing agent in organic synthesis. F ...
... Therefore, exploration of a new method for oxidation is worth challenging. Based on the idea that a new reactivity would be created in sulfur-based oxidation by utilizing a sufur-nitrogen bond, we found N-tert-butylbenzenesulfinimidoyl chloride (1) as a unique oxidizing agent in organic synthesis. F ...
Eliminations
... As with SN2, the rate is dependent on both the concentration of the base and the electrophile. The transition state involves the anti-‐periplanar arrangement of the hydrogen with the leaving group: they ...
... As with SN2, the rate is dependent on both the concentration of the base and the electrophile. The transition state involves the anti-‐periplanar arrangement of the hydrogen with the leaving group: they ...
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
... Ozone is generated by passing a stream of oxygen through a highvoltage electrical discharge Ozone adds rapidly to C=C bond at low temperature to give molozonide which spontaneously rearranges to ozonide Ozonide is treated with reducing agent to convert it to carbonyl ...
... Ozone is generated by passing a stream of oxygen through a highvoltage electrical discharge Ozone adds rapidly to C=C bond at low temperature to give molozonide which spontaneously rearranges to ozonide Ozonide is treated with reducing agent to convert it to carbonyl ...
Chapter 16 Alkanes and alkenes
... alkenes alkenes a group of hydrocarbons with the general formula, CnH2n where n is the number of carbon atoms in one molecule contain the C=C functional group (unsaturated hydrocarbons) names of alkenes end with -ene are molecular compounds have low boiling points; gases under room conditi ...
... alkenes alkenes a group of hydrocarbons with the general formula, CnH2n where n is the number of carbon atoms in one molecule contain the C=C functional group (unsaturated hydrocarbons) names of alkenes end with -ene are molecular compounds have low boiling points; gases under room conditi ...
Chapter 5. An Overview of Organic Reactions
... C-H bonds only (no functional groups) Connecting carbons can lead to large or small molecules The formula for an alkane with no rings in it must be CnH2n+2 where the number of C’s is n Alkanes are saturated with hydrogen (no more can be added They are also called aliphatic compounds ...
... C-H bonds only (no functional groups) Connecting carbons can lead to large or small molecules The formula for an alkane with no rings in it must be CnH2n+2 where the number of C’s is n Alkanes are saturated with hydrogen (no more can be added They are also called aliphatic compounds ...
SCH4C Organic Test
... C) are very reactive, while alkenes are unreactive D) contain only single bonds, while alkenes have at least one triple bond ____ 17. Alkynes contain A) one or more C–C double bonds B) only single C–C bonds C) one or more C–C triple bonds D) contain one or more H–H double bonds ____ 18. The number o ...
... C) are very reactive, while alkenes are unreactive D) contain only single bonds, while alkenes have at least one triple bond ____ 17. Alkynes contain A) one or more C–C double bonds B) only single C–C bonds C) one or more C–C triple bonds D) contain one or more H–H double bonds ____ 18. The number o ...
lecture 11 catalysis_hydrogenation of alkenes
... The protons of a dihydrogen ligand are known to be more acidic than those of free H2, and many H2 complexes can be deprotonated by NEt3. ...
... The protons of a dihydrogen ligand are known to be more acidic than those of free H2, and many H2 complexes can be deprotonated by NEt3. ...
Petroleum C Notes
... The single and double bonds between C’s are covalent bonds - occur between two nonmetals that share electrons ...
... The single and double bonds between C’s are covalent bonds - occur between two nonmetals that share electrons ...
슬라이드 1
... Nickel carbonyl is an extremely toxic compound, and a number of other nickel reagents with generally similar reactivity can be used in its place. ...
... Nickel carbonyl is an extremely toxic compound, and a number of other nickel reagents with generally similar reactivity can be used in its place. ...
Lesson 4 halogenoalkanes
... IF there was enough energy in the collision. • The O-C bond forms completely, the C-Br bond breaks completely NB - If the initial halogenalkane is chiral (see later) this causes an inversion of chirality. For this reason the 3-D representation of this mechanism IS IMPORTANT!! ...
... IF there was enough energy in the collision. • The O-C bond forms completely, the C-Br bond breaks completely NB - If the initial halogenalkane is chiral (see later) this causes an inversion of chirality. For this reason the 3-D representation of this mechanism IS IMPORTANT!! ...
Chemistry: The Central Science, 12e (Brown et al
... C) nucleic acids D) amino acids E) salts 24) __________ is a disaccharide. A) Glucose B) Galactose C) Sucrose D) Ribose E) Fructose 25) The principal difference between fructose and glucose is that __________. A) fructose is a disaccharide and glucose is a monosaccharide B) fructose is a monosacchar ...
... C) nucleic acids D) amino acids E) salts 24) __________ is a disaccharide. A) Glucose B) Galactose C) Sucrose D) Ribose E) Fructose 25) The principal difference between fructose and glucose is that __________. A) fructose is a disaccharide and glucose is a monosaccharide B) fructose is a monosacchar ...
Alkenes
... lies in the range 100 to 10,000. The end groups constitute such a small fraction of the polymer molecule that they are usually omitted. Under the right conditions, ethene molecules will add to each other to form a giant molecule (a polymer) by the process of addition polymerisation. The backbone of ...
... lies in the range 100 to 10,000. The end groups constitute such a small fraction of the polymer molecule that they are usually omitted. Under the right conditions, ethene molecules will add to each other to form a giant molecule (a polymer) by the process of addition polymerisation. The backbone of ...
Organic Reactions Note – Student.DOC
... Oxidation of a secondary (2°) alcohol produces a ketone ...
... Oxidation of a secondary (2°) alcohol produces a ketone ...
TYPES OF REACTIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... ~ Esters are formed when an alcohol and a carboxylic acid react together, (condensation reaction) ~ The H attached to the -OH group in the carboxylic acid molecule has been replaced by the alkyl group, it is a type of substitution reaction. ~ The reverse reaction of esterification is called hydrolys ...
... ~ Esters are formed when an alcohol and a carboxylic acid react together, (condensation reaction) ~ The H attached to the -OH group in the carboxylic acid molecule has been replaced by the alkyl group, it is a type of substitution reaction. ~ The reverse reaction of esterification is called hydrolys ...
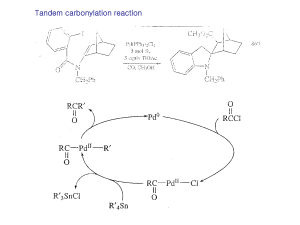
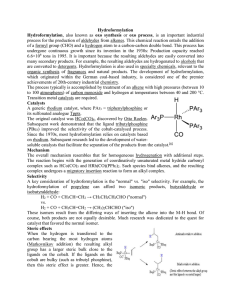
Hydroformylation Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or
... 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic s ...
... 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic s ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.