* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Synthesis and Mutations Review Sheet 2014
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
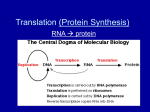
Protein Synthesis and Mutations Review Sheet Directions: Write the answers to each of the questions on a separate sheet of paper or flash cards. For the terms, either use them in your answers or separately define or describe their relation to the concepts of protein synthesis or mutations. Protein Synthesis: Chapter 8.4 and 8.5 1. What are three differences between DNA and RNA? 2. Where does transcription take place and describe each step. Use the following terms: RNA polymerase, mRNA nucleotides, start codon, stop codon, nitrogen bases (A, U, G, C). 3. Where does translation occur and describe the steps. Use the following terms: Ribosome, tRNA, anti-codon, mRNA codons, amino acids, protein. 4. Starting with a sequence of DNA nitrogen bases, be able to match up mRNA nucleotides that contain the proper nitrogen base (A, U, G or C). Then match the mRNA sequence to tRNA anticodons and use a chart (in your textbook, previous handout, or online) to figure out the amino acid sequence. EX: DNA TACGGCATAACT mRNA AUGCCGUAUUGA tRNA anticodon UACGGCAUAACU amino acids meth pro tyro STOP (not an amino acid) *Now you do it for this sequence: TACGGATTGCATATT Terms to know and apply: DNA Codons mRNA nucleotides RNA polymerase mRNA Codons Ribosome Start codon Anticodons Transcription Translation Amino Acid Chain Protein Stop codon Mutations: Chapter 8.7 5. What is the difference between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation? 6. Which one (frameshift or point mutation) causes more problems in terms of reading the genetic code? Explain. 7. When can the other type of mutation cause major problems? 8. What happens to cause a monosomy disease? Trisomy disease? What causes Down syndrome?