* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
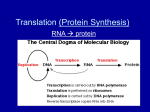
Download In this activity you will be translating the mRNA codons into the final
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Rosetta@home wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
RNA-binding protein wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Alpha helix wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
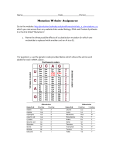
HUMAN INSULIN TRANSLATION & MUTATIONS PRACTICE WORKSHEET In this activity you will be translating the mRNA codons into the final amino acid chain that makes up the protein insulin. The mRNA DOES NOT start with AUG since that amino acid is cut out of the final working protein. Part 1: Use the mRNA codon chart in your textbook or online to translate the following mRNA into a protein. Place the 3 or 1 letter amino acid abbreviation in the corresponding bubbles in the insulin diagram below. HINT: put lines to separate each of the codons in the mRNA sequence. Insulin amino acid sequence and 2 dimensional structure: Part 2: Analysis 1. How many amino acid chains make up the human insulin protein? 2. What do you notice about the amino acids in all the -s-s- areas? (The –s-s- is representing a type of covalent bond called a disulfide bond.) 3. What do you think would happen to this protein if codon #7 changed to GGU? Would the protein still work? Why or why not? 4. What do you think would happen to this protein if codon #7 was instead changed to UGA? Would the protein still work? Why or why not? 5. What would deletion of the 15th nucleotide base in the mRNA sequence do to the protein? Would the protein still work? Why or why not? What other type of mutation would cause the same basic result in the protein sequence? Explain. 6. Give an example of a mutation in the mRNA strand that would be considered to be a silent mutation. Explain why it would be an example of a silent mutation? 7. In general, why are frameshift mutations (question 5) worse than substitution mutations (questions 3 & 6)? Explain. 8. Based on this exercise, are all mutations in DNA bad? Give some specific reasons. Is it ever possible for a mutation to be good? Why or why not?