* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classification Graphic Organizer
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
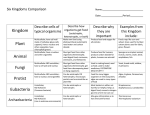
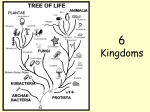
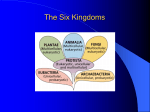
Name: ____________________________ Classification Graphic Organizer Period: ____ Date:__________ Definitions: classification: process of grouping things autotrophs: organisms that can make their own food taxonomy: study of classification heterotrophs: organisms that cannot make their own food-They eat nucleus: Cell part with DNA aurotrophs. (chemical instructions that direct the cell’s activities) unicellular: organisms that are made of only one cell prokaryotes: cell with no nucleus multicellular: organisms that are made of more than one cell eukaryotes: cell with a nucleus All Living Things: organisms are grouped by their: 1. cell type 2.number of cells 3.ability to obtain food into 3 domains Bacteria: prokaryote, autotrophs, & heterotrophs, unicellular Archaea: prokaryote, autotrophs, & heterotrophs, unicellular Eukarya: eukaryotes, autotrophs, & heterotrophs, mostly multicellular into 1 kingdom: into 1 kingdom: eubacteria archaebacteria into 4 kingdoms: Plants: multicellular, autotrophs Animals: multicellular, heterotrophs Fungi: multicellular & unicellular, heterotrophs Protists: most unicellular some multicellular, heterotrophs & autotrophs