* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes 2-4
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
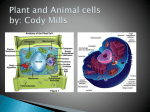
7th Grade Life Science Mr. Fisk Chapter 2 – Living Things Engage: Show Cells - Discuss Objectives: 1. Identify the role of the cell wall and the cell membrane in the cell. 2. Describe the functions of cell organelles. 3. Explain how cells are organized into manycelled organisms. Introduction Page 1 of 8 7th Grade Life Science Mr. Fisk 2-4: LOOKING INSIDE CELLS A. Introduction -- Let’s go for an imaginary journey inside a living organism visiting its tiny cells. 1. Cells -- very small. (Exception -- egg yolk) 2. Structures in cell functions: a. Protection b. Support c. Barrier d. Building & repairing cell parts e. Transporting material f. Storing & releasing energy g. Getting rid of wastes h. Increasing in number Introduction Page 2 of 8 7th Grade Life Science Mr. Fisk Journey Through the Trunk of Oak Tree: B. Cell Wall -- Support & Protection 1. Strong & stiff. 2. Made of cellulose -- non-living material -- long chain of sugar molecules. 3. Plant cells only. 4. H2 O, O2 & CO2 can pass through. C. Cell Membrane -- Doorway of the cell – like a window screen. 1. Plant Cell -- just inside cell wall. 2. Animal Cell -- outer covering of cell. 3. Jobs: a. Protection & support. Cholesterol strengthens cell membrane. b. Control movement of materials into and out of the cell. c. Help maintain homeostasis. Introduction Page 3 of 8 7th Grade Life Science Mr. Fisk D. Nucleus -- Control center of the cell. 1. Control center. 2. “Brain” of the cell. 3. Nuclear Membrane (envelope) -- like cell membrane. 4. Chromosomes (Chromatin): a. Rod-like objects. b. Direct all the activities of the cell (growth & reproduction). c. Pass on traits to new cells. d. Made of nucleic acids -- store information that helps a cell make the proteins it requires (like enzymes & hormones). 2 Nucleic Acids: DNA -- Store information remaining in nucleus. RNA -- Carrying its protein building instruction leaves the nucleus through pores in the nuclear membrane. Introduction Page 4 of 8 7th Grade Life Science Mr. Fisk 5. Nucleolus -- “little nucleus” Site of ribosome production. E. Endoplasmic Reticulum: Transportation system of the cell. 1. Cytoplasm -- Region between the nucleus & cell membrane. (thick jelly-like substance). 2. E.R. -- Clear, tubular passageways 3. Job -- Transportation of protein. F. Golgi Bodies – “Cells Mail Room” – receive protein & other newly formed materials from the endoplasmic reticulum – package them & distributes them to other parts of the cell. Introduction Page 5 of 8 7th Grade Life Science Mr. Fisk G. Ribosome -- Protein factories of the cell. 1. Attached to surface of E.R. 2. Made of RNA. Protein-making sites of the cell. 3. Some ribosomes also found in cytoplasm. H. Mitochondria -- Powerhouse of the cell. 1. 2. 3. 4. Introduction Supply energy. Rod-shaped. Respiration – Sugar → Energy. The more active the cell, the more mitochondua. (i.e. human lives - 1000). Page 6 of 8 7th Grade Life Science I. Mr. Fisk Vacuoles -- Storage tanks for cells. 1. 2. 3. 4. Round water-filled sac. Plants -- large. Animals -- small. Store -- food, wastes, & H2 O. J. Lysosomes -- Clean-up crews for cells. 1. Digestive activities. 2. Job: a. Enzymes break down food molecules into smaller ones. b. Digest old cell parts. K. Chloroplasts -- Energy-Producers for cells. 1. Green -- Chlorophyll. 2. Photosynthesis. Introduction Page 7 of 8 7th Grade Life Science Mr. Fisk L. Cell Specialization 1. In multicellular organisms cells are different – specialized to perform specific functions. Example: Nerve Cells – Transmit information from one part of the body to another. Red blood cells carry oxygen throughout your body. 2. Cells → Tissues → Organs → Systems → Organism Introduction Page 8 of 8