* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cloze 4
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
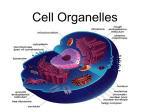
1 Cloze 4-1 The Big Idea All organisms are composed of one or more_____. Section 1 The Characteristics of Cells Key Concept Cells function similarly in all living organisms. Cells and Cell Discovery • Cells ________similarly in all living things. • A ______is the smallest structural and functional unit of living things. • In 1665, Robert Hooke built a _________and and observed box-like structures in a sample of cork. He called the structures cells. • Because animal cells lack cell_____, Hooke could not see them. He believed that only plants and fungi were made of cells. • In 1673, Dutch merchant Anton van Leeuwenhoek made a microscope and observed swimming “_________” in a sample of pond scum. • Today we call these single-celled organisms_________. • Leeuwenhooek also observed blood cells from different animals and was the first person to observe________. Cells and Cell Theory • Nearly 100 years later, Matthias Schleiden, a plant scientists, concluded that all ________parts were made of cells. • A year later, in 1839, Theodor Schwann concluded that all _________tissues were made of cells. • Schwann went on to write the first two parts of modern cell________: • All organisms are made up of one or more cells. • The cell is the basic unit of all living things. • In 1858, Rudolf Virchow added the third part of the cell theory: • All cells come from _________cells. Cell Size • The vast majority of cells are too _______to be seen without a microscope. • If the volume of a cell becomes too large, the surface area of its membrane will not be able to let in enough materials and let________ wastes. • Cells must remain small to maintain a proper surface-area-to-volume_______. Cell Membrane • Cells come in many shapes and sizes, and may be specialized for different functions. But _____cells have some parts in common. • All cells have a cell membrane. The cell membrane is a protective layer that covers the cell’s surface and acts a ________. • The cell membrane separates the cell’s contents from its____________. • The cell membrane also controls the materials going ______and out of the cell. Cytoplasm and Organelles • Most of the contents of a cell, including the fluid, is called the___________. • Organelles are part of the cytoplasm. Organelles are structures that have specific _______inside the cell. DNA and Nucleus • All cells have_____- (deoxyribonucleic acid) at some point in their lives. DNA is the genetic material that carries _________for making new cells. • In eukaryotic cells, including plants and animals, the DNA is found within the _________of the cell. • The nucleus is an organelle ____________to hold the DNA. The nucleus plays a role in growth, metabolism, and reproduction. • __________have DNA, but do not have a nucleus. Their DNA floats free in the cytoplasm. • Human blood cells have a nucleus and DNA as they are growing. Once mature, they _______their DNA and nucleus. • Most cells, however, need DNA throughout their lives. The DNA provides instructions for making ___________. Two Kinds of Cells • Cells that do not have a nucleus are called prokaryotes. Bacteria and __________ are prokaryotes. • Prokaryotic DNA is a round molecule, twisted like a ___________band. • Prokaryotes have cell walls. They lack the membrane-bound organelles found in other organisms. • Eukaryotes are organisms made up of cells that have a nucleus enclosed by a_________. • Eukaryotic cells are 10 times as large as prokaryotic cells, although most eukaryotic cells are still__________. • Eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles to carry out the functions of the cell. Section 2 Eukaryotic Cells Key Concept Eukaryotic cells have organelles that perform important functions. Cell Wall • Eukaryotic cells have many organelles in common to carry out important functions. • _________ are eukaryotes that have some structures and organelles not seen in animal cells. • Plant cells have a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane called the______ ______. Animal cells lack a cell wall. Cell Membrane • All cells have a cell membrane made up of proteins and _______________. Answers: cells, cell, all, phospholipids , microscopic , microscope, membrane, small, barrier, existing, lose , Bacteria, protests, DNA, out, plant, theory, animal, walls, bacteria, animacules, ratio, into, nucleus, jobs, instructions, Plants , archaea, function, cytoplasm , rubber, surroundings, specialized, proteins, cell wall,