* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hindlimb - bthsresearch
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
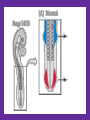
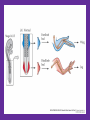
Development of the Tetrapod Limb - Placement on the Axis, Forelimb Vs. Hindlimb Gilbert - Chapter 16 Today’s Goals • Become familiar with several aspects of limb formation in the tetrapod – Limb initiation • Forelimb vs. hindlimb • Where to make a limb? • Examine molecules involved in specification of the above – Limb patterning • Dorsal/ventral • Anterior/Posterior • Proximal/distal Position of the tetrapod limb is conserved: Forelimb always at cervical to thoracic transition Hindlimb always at lumbosacral transition Evidence that Limb field is Specified • If remove presumptive limb field, no limb will form • If move limb field tissue to new axial level (flank), a limb will form in the flank • Fate mapping presumptive limb field shows those cells participate in limb formation Hox Genes and Limb Field Specification • Different Hox genes are expressed at different points along the A-P axis – “Hox code” • Expression of certain Hox genes maps to the level of limb formation • Conserved throughout the tetrapod organisms • Thought to be important for establishing limb field, level of limb field What about snakes? In snakes • Radical change to the body plan • No Limbs! – Lost them through evolution – First the forelimb and then the hindlimb! – Fossils have been found of snakes w/ hindlimb, but no forelimb! – Primitive snakes develop a rudimentary femur (pythons) • Don’t continue to form (no SHH to extend limb - we’ll see more later. . . ) – Can be explained by Hox expression • Hox C6 and C8 expressed through most of body -> ribs throughout From Specification to Induction • Once limb field is set-up, how does the embryo begin to form a limb? – Mesenchyme cells in somatopleure LP proliferate – Myotome from somite proliferates – These 2 cell types form a bulge or limb bud • Cells in limb field were specified from A-P signals – Now must signal locally to form this swelling Primaxial Abaxial Limb Bud Formation • Lateral plate mesoderm cells – Secrete FGF-10 (fibroblast growth factor) – Appears to be important for limb bud formation – HOW CAN WE TEST THIS?? • Is it in the right place? • Is it sufficient to form a limb? (Over-express) • Is it necessary to form a limb? (Knockout) FGF-10 and Limb bud formation • FGF-10 is expressed in the lateral plate mesoderm at the presumptive limb field regions (correlative evidence) • Ectopic expression of FGF-10 results in ectopic limb formation (gain-of-function evidence) • FGF-10 null mutant mice (Knockouts) do not form limb outgrowths (loss-of-function evidence) Forelimb or Hindlimb? • Depending on placement of the ectopic FGF-10 protein in the flank either forelimb or hindlimb will form – If placed closest to forelimb, ectopic forelimb – If placed closest to hindlimb, ectopic hindlimb – If place directly at midpoint, chimeric fore/hindlimb forms Specifying Forelimbs and Hindlimbs • Members of a family of transcription factors related to T(Brachyury) called T-box genes have been implicated – Tbx-4, Tbx-5 – Transcription factors • Initially, expression data showed Tbx-5 expressed only in mouse forelimb, Tbx-4 only in mouse hindlimb – CORRELATIVE evidence Tbx-5 Loss of Function • Humans with heterozygous for TBX5 have upper limb abnormalities – Not completely show support for upper limb specification – Not turn upper limb into a lower limb – Good enough evidence to continue to pursue these genes Tbx genes: Gain-of-Function evidence • FGF-bead experiments. If FGF placed: – Closest to forelimb • Ectopic forelimb formed • Tbx-5 expression induced in new bud – Closest to hindlimb • Ectopic hindlimb formed • Tbx-4 expression induced in new bud – Between fore and hindlimb • Ectopic chimeric fore/hindlimb • Anterior 1/2 expresses Tbx-5, posterior 1/2 expression Tbx-4 Tbx-5 Tbx-4 Viral Misexpression of Chick Proteins • In Chick embryos, avian viruses can be engineered to express a gene of interest • The embryo can then be injected with the virus at an early stage • As virus spreads through the developing tissue, gene expression is turned on • In this way we can express genes ectopically in chick tissue – Like a gain of function mutation in a mouse, but limited to a specific cell population Viral misexpression of Tbx proteins in chick • Tbx-4 misexpression throughout the flank of the embryo – Then an FGF bead is placed in flank • Results in formation of mostly ectopic hindlimbs • This further supports Tbx genes in hindlimb vs. forelimb identity – NOT YET PROVEN! • BUT: it is necessary to establish the expression of Tbx genes – This occurs further upstream: ??HOX??