* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Genetics: Senior Exam Review Chapter 1: Introduction to
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
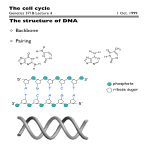
Honors Genetics: Senior Exam Review Chapter 1: Introduction to Genetics Know the differences between PROKARYOTES and EUKARYOTES What is the function of DNA? What is a MUTATION? What causes mutations? What 3 categories do mutations fall into and provide an example of each. What is RECOMBINATION? Describe CLONING. What organisms are currently being genetically engineered and for what purposes? Describe the CHROMOSOME THEORY OF INHERITANCE. Who first described inheritance patterns? Vocabulary Review DIPLOID ALLELE HAPLOID GENOTYPE HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES PHENOTYPE What is a NUCLEOTIDE? Know the order of PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis Vocabulary Review CHROMATIN CHROMOSOMES SISTER CHROMATIDS HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Know the ORGANELLE chart from your notes to describe the function of cell organelles Describe the appearance of chromosomes based on centromere location. Describe the cell clock and apply to the type of cell that divides LABILE, STABILE, PERMANENT cells What is the purpose of MITOSIS? What is the order of steps? What is the general description of chromosome action in mitosis? What is the purpose of MEIOSIS? What is the order of steps? What is the general description of chromosome action in meiosis? Vocabulary Review MONAD GENETIC VARIATION DYAD CROSSING OVER TETRAD Know the similarities and differences between SPERMATOGENESIS and OOGENSIS. Understand the impact that certain activities can have on egg and sperm production in HUMANS. Chapter 3: Mendelian Inheritance Be able to CREATE and DESCRIBE a MONOHYBRID cross, including percentages. Be able to INDEPENDENTLY ASSORT alleles for DIHYBRID and TRIHYBRID crosses. Vocabulary Review characteristic/trait phenotype unit factors/alleles genotype gene homozygous segregation heterozygous Know Mendel’s Postulates Unit factors occur in pairs Dominant/Recessive Segregation Independent Assortment – for more than 2 traits Know the COMMONLY used symbols for Pedigree Analysis Be able to construct and analyze an AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT and AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE pedigree. Chapter 4: Modification of Mendelian Ratios Study your Chapter 4 Vocabulary Quiz! Know how to differentiate between different pedigrees Autosomal Dominant/Autosomal Recessive X-linked Dominant/X-linked Recessive Review blood group inheritance ABO MN Rh Factor Describe the issues surrounding sex-linked inheritance in human males Chapter 5: Sex Determination and Sex Chromosomes Vocabulary Review heteromorphic chromosomes Primary sex differentiation Secondary sex differentiation heterogametic sex homogametic sex isogamete heterogamete Bipotential gonads Mullerian ducts Wolffian ducts Testis-determining factor disjunction vs nondisjunction Aneuploidy vs. Euploidy Understand the process of sex differentiation in humans. Describe oogenesis and spermatogenesis in humans. How are they alike? How are they different? Human DIPLOID number is ________; HAPLOID number is ________. Be able to differentiate human chromosome numbers in -ploidy conditions and –somic conditions (Chap 6/Question 1) Remember, chromosomes are only visible during MITOSIS and MEIOSIS. Describe nondisjunction and the impact it CAN have on gamete chromosome numbers. Be able to identify the critical areas AND describe the functions of the Y chromosome and its influence in sex differentiation. PAR MSY SRY Describe/understand fetal sex development in humans. (Chap 5 Quest) What allows the X and Y chromosomes to synapse during conception/What region of each chromosome allows this to occur? What term is used to describe the relationship between the X and Y chromosomes? Can you predict inheritance patterns of X-linked conditions in offspring? (Chap 6/Q 14) Practice Punnett Squares and recognize sex-linked pedigrees! Describe the genotype and phenotype – Be able to ID the karyotype - of the following -somic conditions: Turner Syndrome Klinefelter Syndrome Down Syndrome Viability issues concerning autosomal vs sex chromosome abnormalities/Why are some of these conditions in Chap5 and Chap6 lethal, minor, or detrimental? Why are polyploidy conditions lethal in humans? Why are some polysomy conditions in humans lethal? What is the difference between these two terms? What determines if polysomy conditions result in abnormalities or death? Chapter 9: Evidence Favoring DNA as Genetic Material Understand the sequence of experiments that proved DNA was the mechanism of inheritance. Griffith Avery, McCloud, McCarty Hershey-Chase Know the nucleotide structures, including sugars and phosphate arrangement. Describe the Watson-Crick Model of DNA (page 193-194) Describe electrophoresis Chapter 10: DNA Replication and Recombination Why must DNA replicate? Describe the process of DNA replication as a semiconservative replication process. Understand the difference between conservative and dispersive replication. How did the Messelson-Stahl experiment prove semiconservative replication? Know why E. coli was used as the organism for experimentation. What was significant about the Taylor-Woods-Hughes experiment? List the general steps of DNA replication and the enzymes involved, including their functions. Understand the significance of telomeres and telomerase in relation to cell division and cell aging. Chapter 12: The Genetic Code and Transcription What is the Central Dogma? Describe transcription as a mechanism in the creation of proteins. Know the characteristics of the 3 varieties of RNA, their locations, and their functions. How is mRNA read? What is RNA splicing? What is significant about introns and exons?