* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 07Learning
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
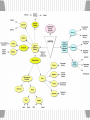
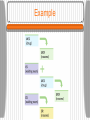
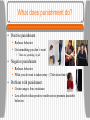
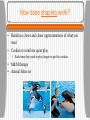
Learning How do we learn? What is Classical conditioning? • Ivan Pavlov (Respondent Behavior) Classical Conditioning • • • • Unconditioned Stimulus(UCS) = Meat Unconditioned Response (UCR)=Salivation Neutral Stimulus = Tone Conditioned Stimulus (CS) = Tone When paired with the unconditioned stimulus • Conditioned response (CR) = Salivation to tone Example Example Example • Father spanks son for swearing. • Son develops a strong fear of his father. Father is a(n) _____________? Conditioned stimulus Classical Conditioning • Acquisition • Extinction Patient riding elevators to extinguish fear of elevators What is generalization? Do you remember? • Who developed classical conditioning? • How can you condition a cat to come when it is time to eat? • What is the UCS, UCR, CS, and CR • What is generalization? What is Operant Conditioning? • B.F. Skinner (Operant behavior) • Associating behavior with its consequences • E.g. Seals in an aquarium doing a trick to receive a fish. What does reinforcement do? • Positive reinforcement Increases behavior Give something a person wants • E.g. Vending machine • Negative reinforcement Increases behavior Remove an unwanted stimulus • E.g. Bill cleans up his room to stop Mother nagging Pos. & Neg. Reinforcement What are primary & secondary reinforcers? • Primary = Innately reinforcing Food Food & Sex Want • Secondary reinforcers (Conditioned reinforcer) Associated with a primary reinforcer E.g. Money Want Food Do you want immediate or delayed Reinforcement? • Immediate reinforcement is more motivating • A smaller check now is immediate reinforcement. • As opposed to delayed reinforcement A larger paycheck at the end of the month. Lottery payout Saving for retirement Social Security at age 62 or 70 What are reinforcement schedules? • Continuous Every time • Partial (Intermittent) Fixed ratio • $15 for every 3 pages you write Fixed Interval What reinforcement schedule does a slot machine use? What reinforcement schedule does your employer use? • $15 for every hour you work Variable ratio • $15 after varying # of pages • (You do not know how many pages you will need to do before you get paid again) Variable interval • $15 given at various times during the day What does punishment do? • Positive punishment Reduces behavior Get something you don’t want • Time out, spanking, or jail • Negative punishment Reduces behavior What you do want is taken away ( Television time) • Problem with punishment Creates anger, fear, resistance Less effective than positive reinforcers to promote desirable behavior. How does shaping work? • Reinforce closer and closer approximations of what you want • Cookies to reinforce quiet play Each time they need to play longer to get the cookies • M&M therapy • Animal behavior Do you remember? • Who developed operant conditioning? • How does operant conditioning differ from classical conditioning? • What is an example of positive and negative reinforcement? • What is an an example of five reinforcement schedules? • What is an example of shaping? What kinds of motivation do you have? • Internal (intrinsic) Motivation Hobby - You like doing it • External (outside) motivation Job - You get money for doing it How does thinking effect your behavior? • Behavior is not automatically produced by a reward. • We think about it, and ask: How much of the reward do I get? What are the chances of getting the reward? Is the reward worth it? What is observational Learning? • Albert Bandura • Modeling - Bobo doll experiment • E.g. Child turning the key to start the car (without explicit training) • Matt using the ATM machine after watching Dad Do you remember? • What do you do because of internal motivation? • What do you do because of external motivation? • How does cognitive processes (thinking) effect rewarded behavior? • What did you learn with observational behavior?