* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 20~ DNA Technology & Genomics
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
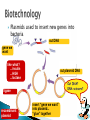
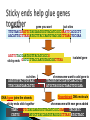
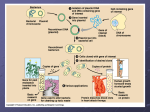
Prepare the calendar with when you are going to do each assignment http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= v2T8Y3-8674 1) Check grades on AP Board. What do you need to do to get an A or B. 2) If black body and red eyes always appears in offspring then genes are linked/not linked. 3) Write the 5 Hardy-Weinberg conditions 4) Give 3 interpretations of this data a) The dominant is______________ b) Sex-linked or autosomal?_________ c) Ratio_______________ Part A—4 pts Part B—4pts Part C—4pts Antonio—Advanced! Calvin, Wendy, Genesis, Jade, Diana, Kendy, Chelsea--Proficient 1. Answer: C 2. Answer: B 3. Answer: B 4. Answer: D 5. Answer: A 6. Answer: C 7. Answer: E 8. Answer: D 9. Answer: E 10. Answer: E 11. Answer: B 12. Answer: C 13. Answer: D 14. Answer: C 15. Answer: B 16. Answer: A 17. Answer: C 18. Answer: C 19. Answer: A 20. Answer: D 21. Answer: C 22. Answer: E 23. Answer: E 24. Answer: E 25. Answer: D 26. Answer: B 27. Answer: A 28. Answer: C 29. Answer: B 30. Answer: D 31. Answer: B 32. Answer: C 33. Answer: D 34. Answer: A 35. Answer: E 36. Answer: B 37. Answer: E 38. Answer: C 39. Answer: E 40. Answer: C 41. Answer: E 42, Answer: B 43. Answer: D 44. Answer: C 45. Answer: D 46. Answer: D 47. Answer: D Part 1: Basic Biotechnology TACGCACATTTACGTACGCGGATGCCGCGACTATGATC ACATAGACATGCTGTCAGCTCTAGTAGACTAGCTGACT human genome CGACTAGCATGATCGATCAGCTACATGCTAGCACACYC GTACATCGATCCTGACATCGACCTGCTCGTACATGCTA 3.2 billion bases CTAGCTACTGACTCATGATCCAGATCACTGAAACCCTA GATCGGGTACCTATTACAGTACGATCATCCGATCAGAT CATGCTAGTACATCGATCGATACTGCTACTGATCTAGC TCAATCAAACTCTTTTTGCATCATGATACTAGACTAGC TGACTGATCATGACTCTGATCCCGTAGATCGGGTACCT ATTACAGTACGATCATCCGATCAGATCATGCTAGTACA TCGATCGATACTGCTACTGATCTAGCTCAATCAAACTC TTTTTGCATCATGATACTAGACTAGCTGACTGATCATG ACTCTGATCCCGTAGATCGGGTACCTATTACAGTACGA TCATCCGATCAGATCATGCTAGTACATCGATCGATACT Genetic Engineering ◦ manipulation of DNA ◦ if you are going to engineer DNA & genes & organisms, then you need a set of tools to work with ◦ this unit is a survey of those tools… Our tool kit… PCR Bacteria review ◦ one-celled prokaryotes ◦ reproduce by mitosis binary fission ◦ rapid growth generation every ~20 minutes 108 (100 million) colony overnight! ◦ dominant form of life on Earth ◦ incredibly diverse Single circular chromosome ◦ haploid ◦ naked DNA no histone proteins ◦ ~4 million base pairs ~4300 genes 1/1000 DNA in eukaryote How have these little guys gotten to be so diverse?? Single circular chromosome ◦ haploid ◦ naked DNA no histone proteins ◦ ~4 million base pairs ~4300 genes 1/1000 DNA in eukaryote How have these little guys gotten to be so diverse?? Small supplemental circles of DNA 5000 - 20,000 base pairs self-replicating ◦ carry extra genes 2-30 genes genes for antibiotic resistance ◦ can be exchanged between bacteria bacterial sex!! rapid evolution ◦ can be imported from environment A way to get genes into bacteria easily ◦ insert new gene into plasmid ◦ insert plasmid into bacteria = vector ◦ bacteria now expresses new gene bacteria make new protein gene from other organism cut DNA plasmid recombinant plasmid + vector glue DNA transformed bacteria Plasmids used to insert new genes into bacteria cut DNA gene we want like what? …insulin …HGH …lactase cut plasmid DNA Cut DNA? DNA scissors? ligase recombinant plasmid insert “gene we want” into plasmid... “glue” together Restriction enzymes ◦ restriction endonucleases ◦ discovered in 1960s ◦ evolved in bacteria to cut up foreign DNA “restrict” the action of the attacking organism protection against viruses & other bacteria bacteria protect their own DNA by methylation & by not using the base sequences recognized by the enzymes in their own DNA Madam I’m Adam Action of enzyme restriction site CTGAATTCCG GACTTAAGGC ◦ symmetrical “palindrome” ◦ produces protruding ends ◦ cut DNA at specific sequences sticky ends CTG|AATTCCG will bind to any complementary DNA GACTTAA|GGC Many different enzymes ◦ named after organism they are found in EcoRI, HindIII, BamHI, SmaI 1960s | 1978 Werner Arber Daniel Nathans Restriction enzymes are named for the organism they come from: EcoRI = 1st restriction enzyme found in E. coli Hamilton O. Smith Cut DNA at specific sites ◦ leave “sticky ends” restriction enzyme cut site GTAACGAATTCACGCTT CATTGCTTAAGTGCGAA restriction enzyme cut site GTAACG AATTCACGCTT CATTGCTTAA GTGCGAA Cut other DNA with same enzymes ◦ leave “sticky ends” on both ◦ can glue DNA together at “sticky ends” GTAACG AATTCACGCTT CATTGCTTAA GTGCGAA gene you want GGACCTG AATTCCGGATA CCTGGACTTAA GGCCTAT chromosome want to add gene to GGACCTG AATTCACGCTT CCTGGACTTAA GTGCGAA combined DNA cut sites gene you want cut sites TTGTAACGAATTCTACGAATGGTTACATCGCCGAATTCACGCTT AACATTGCTTAAGATGCTTACCAATGTAGCGGCTTAAGTGCGAA AATTCTACGAATGGTTACATCGCCG sticky ends GATGCTTACCAATGTAGCGGCTTAA cut sites isolated gene chromosome want to add gene to AATGGTTACTTGTAACG AATTCTACGATCGCCGATTCAACGCTT TTACCAATGAACATTGCTTAA GATGCTAGCGGCTAAGTTGCGAA DNA ligase joins the strands sticky ends stick together Recombinant DNA molecule chromosome with new gene added TAACGAATTCTACGAATGGTTACATCGCCGAATTCTACGATC CATTGCTTAAGATGCTTACCAATGTAGCGGCTTAAGATGCTAGC How can bacteria read human DNA? Gene produces protein in different organism or different individual human insulin gene in bacteria TAACGAATTCTACGAATGGTTACATCGCCGAATTCTACGATC CATTGCTTAAGATGCTTACCAATGTAGCGGCTTAAGATGCTAGC “new” protein from organism ex: human insulin from bacteria aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa bacteria human insulin Since all living organisms… ◦ use the same DNA ◦ use the same code book ◦ read their genes the same way Transformation ◦ insert recombinant plasmid into bacteria ◦ grow recombinant bacteria in agar cultures bacteria make lots of copies of plasmid “cloning” the plasmid ◦ production of many copies of inserted gene ◦ production of “new” protein transformed phenotype DNA RNA protein trait gene from other organism recombinant plasmid + vector plasmid grow bacteria harvest (purify) protein transformed bacteria Genetically modified organisms (GMO) ◦ enabling plants to produce new proteins Protect crops from insects: BT corn corn produces a bacterial toxin that kills corn borer (caterpillar pest of corn) Extend growing season: fishberries strawberries with an anti-freezing gene from flounder Improve quality of food: golden rice rice producing vitamin A improves nutritional value Word processing metaphor… ◦ cut restriction enzymes ◦ paste ligase ◦ copy plasmids bacterial transformation is there an easier way?? ◦ find ????