* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immunology & Disease
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination policy wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmune encephalitis wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
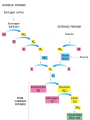
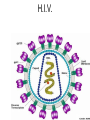
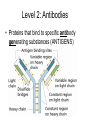
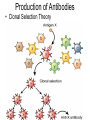
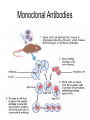
Immunology & Disease Immunity - defense against pathogenic organisms and non-self entities • Non-specific Immunity • • • • • • Skin (very effective if unbroken) Mucous membranes Tears (lysozyme) Stomach acid Phagocytes Inflammatory response Specific Immunity • Natural: • The result of infection with a natural pathogen • Artificial: • The result of inoculation with a vaccine • Ex. You become immune to a particular variant of the common cold virus • Ex. Immunity developed following the vaccination of the chicken pox virus • (most vaccines are either heat killed viruses or synthetic antigen replicates) Specific Immunity Cont’d • Active: • Due to antibodies and memory cells produced by the body itself • Passive: • Due to antibodies received from another organism • Ex. Rabies shot; mother to fetus through the placenta and mother to newborn via colostrum AIDS: Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome • Cause: Human Immunodeficiency Virus • Transmission: bodily fluids – Oral, vaginal, anal sex – Intravenous drug use (shared hypodermic needles) – Crossing placental barrier from Mother to fetus – Breast feeding – Blood transfusions H.I.V. Immune Response to Infection • Barriers to Infection: – Skin: tough, physical barrier; sebaceous glands secrete fatty and lactic acid that lower skin surface pH – Mucous membranes: nose, trachea, urethra, vagina….not a strong physical barrier….do – Possess LYSOZYME in their secretions – Flushing – Capture Level 2: Antibodies • Proteins that bind to specific antibody generating substances (ANTIGENS) Production of Antibodies • Clonal Selection Theory Monoclonal Antibodies Specific Immunity • Categorized by the presence and increased production of B and TLymphocytes Vaccination (+ and -) • Be able to discuss 3 benefits and 3 dangers of vaccination