* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Acquired immunity
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
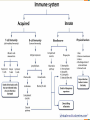
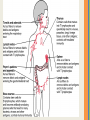
Basics of Immune System Everyone has two types of immunity – innate and acquired. Innate immunity takes advantage of physical barriers your body has to foreign invaders (skin, mucous membranes, stomach acid and circulating white blood cells) to prevent entrance by an antigen or microbe. Acquired immunity mounts a response after an invader has entered the body by producing specialized cells. Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. Humoral immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on production of antibodies to attack pathogens. A small number of “memory” cells continually patrol the blood and produce antibodies in case of later infection. Cell-mediated immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on macrophages that kill cells that become infected. Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. The complement system is another piece of the immune system. It is made up of about 25 specialized proteins that help antibodies destroy pathogens. It also helps clear antibody-antigen complexes that formed during pathogen destruction. As part of the action of the complement system, the inflammatory response is triggered.