* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download introduction and overview
Drosophila melanogaster wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
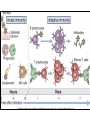
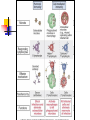
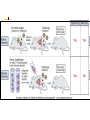
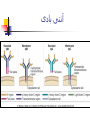
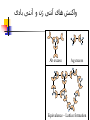
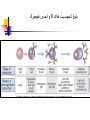
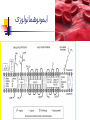
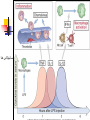
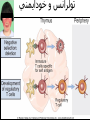
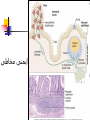
Welcome to Immunology Bahman 1387 Introduction to Immunology A Smallpox Victim Why Should you study immunology? A. It is very exciting B. It will be your partner for your entire professional life Pharmaceuticals drugs can be considered a partner to you— not replacement for-- the immune system OBJECTIVES IN IMMUNOLGY Identify the major principles of the human immune response Introduce the main forms of immune response. What they are and how do they relate to one another ? FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Defense against infections Recognition and protective response to newly introduced substances such as proteins and to tissue grafts Defense against tumors Preservation of genetic integrity of the individual What do you want in an immune response? Defend our body against any foreign Invader This could be done usually by 2 ways Innate Immunity Adaptive Immunity Cooperation! Integration of innate and adaptive immunity to form a more effective defense system The innate and adaptive immune responses work together Overview of key characteristics of innate vs acquired immunity Innate Adaptive specificity No yes Self non-self discrimination No yes Memory Not Yes Specialization Not Specialized Specialized Second response as first more vigorous than first Speed to develop Quick latent Cellular components Humoral components Phagocytic cells NK cells (natural killer) Complement Acute phase proteins Lymphocytes Tcells & B cells Antibodies What are the key characteristics of an effective defense system? Self non-self discrimination Specificity A way of amplifying selectively particular immune responses Diversification: converting one response into multiple types Turning responses off so that they don’t get out of control Memory The ability to respond to a changing environment by inventing new Ag receptors 2- ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY What are the main elements of the Immune system and their characteristics What are, and how do we identify, the key cells of the immune response? Anatomy of primary and secondary lymphoid organs—how do they get around? سلولها و اعضای لنفاوی Antigen: (Ag) something that stimulates an immune response ~ 10 amino acids long. Can be any molecule: Even your own Body structures آنتی ژن Haptenic determinants Native determinants Antibody (Ab): a family of defensive proteins your body makes when it is stimulated by Ag. Ab contains a receptor that specifically binds one Ag and not another. Example : IgG آنتی بادی واکنش های آنتی ژن و آنتی بادی Ab excess Ag excess Equivalence – Lattice formation پاسخ هاي ایمنی ذاتی و التهاب بلوغ لنفوسیت های Bو ایمنی هومورال کمپلمان ایمونوهماتولوژی سیستم سازگاری نسجی )( MHC ایمنی سلولی سایتوکاین ها امتحان میان ترم: 10نمره از 20 ازدیاد حساسیت هاI IIازدیاد حساسیت ها Maybe due to either TH1 or CTL mediated hypersensitivity تولرانس و خودايمني پاسخ هاي ايمني علیه تومورها و سرطان ایمنی مخاطی ایمونولوژی بیماریهای عفونی ایمونوفارماکولوژی واکسن Discovery of small pox vaccine ایمونولوژی پیوند واكسن ها Discovery of small pox vaccine Immunoregulation The ability of the immune system to sense and regulate its own responses is called immunoregulation. IIایمونوفارماکولوژی واکسن Discovery of small pox vaccine توليد فراورده ها در ايمونولوژي در پایان این دوره باید : مفاهیم اساسی در ایمونولوژی را بخوبی تعریف کنید مکانیسم های تولرانس و خودایمنی را توضیح دهید مکانیسم های دفاع بدن در مقابل عوامل عفونی را شرح دهید مکانیسم های دفاع بدن در مقابله با سرطانها را توضیح دهید مکانیسم های رد پیوند را شرح دهید بیماریهای نقص ایمنی را بشناسید بتوانید ارتباط منطقی بین آموخته های این دوره و دانسته های قبلی خود برقرار کنید کاربرد ایمونولوژی را در پیشگیری ،تشخیص و درمان بیماریها بطور کامل بیان کنید قادر باشید در آینده و هرگاه نیاز داشته باشید به منابع این درس مراجعه کرده و مستقال جواب سئواالت خود را بیابید 10+10=20 امتحان آخر ترم 10نمره از 20