* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Immune System - Clark Pleasant Community School Corp
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
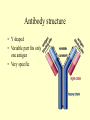
The Immune System Anatomy and Physiology Immune System • Your body’s protection against pathogens (disease causing agents) • Two major categories of defense: • Non-specific and specific Immune System • Non-specific defenses are general, and will work against any pathogen • Species resistance, mechanical barriers, chemical barriers, inflammation, phagocytosis Immune System • Specific defenses fight off only one particular pathogen • Lymphocytes specialize and become T cells and B cells • T cells activate B cells B-cell Activation B cells produce antibodies; the single most effective protection Antibody structure • Y shaped • Variable part fits only one antigen • Very specific Antibodies on B cells Immune System • Antibodies are made in response to a specific antigen • Takes a while to figure out the exact shape to fit the antigen • Once made, memory cells will be kept for future exposures Immune System • Memory cells explain why you don’t get the same disease twice • Some common illnesses, such as cold and flu, are really different mutated forms of the virus. Each time takes a different antibody Immune System • Vaccines: are killed or weakened antigens • They cause you to make the antibodies and memory cells without you getting sick • They are ready if you are ever exposed Type of Immunity • Active: You make the antibodies in response to an antigen • Passive: Already made antibodies are given to you—mother to baby; some injections for illness Type of Immunity • Naturally acquired: you came across the pathogen naturally (got sick) • Artificially acquired: a vaccine; you stimulate the exposure on purpose Type of Immunity • • • • Naturally acquired active immunity Naturally acquired passive immunity Artificially acquired active immunity Artificially acquired passive immunity (does not last long) • Primary: first exposure (get sick, takes time to make antibodies) • Secondary: 2nd or more exposure (quick response from memory cells) What vaccines have you had? • • • • • • Hepatitis B DPT Polio MMR Hib Pneumococcal