* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Week 2
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
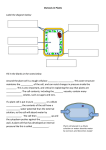
Turbo TAKS Week 2 Lesson 1- Cells Lesson 2- Taxonomy Lesson 3- DNA Lesson 4- Protein Synthesis Lesson 1: Cells 2 Types of Cells Prokaryote- “pro”= before; “kary”- nucleus CELL DOES NOT CONTAIN A NUCLEUS OR MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES Example: Bacteria Study Trick: Remember that pro rhymes with no nucleus Eukaryote- “eu”= true; “kary”- nucleu CELL CONTAINS A NUCLEUS CELL CONTAINS MEMBRANE-BOUND ORGANELLES Examples: Plant, Animal, Protist, Fungus MAJOR ORGANELLES CELL PROCESSES OVERVIEW • Permeability – Diffusion – Osmosis • Cell Division – Mitosis – Meiosis • Energy Conversion – Photosynthesis – Respiration • Storage & Transport Permeability (all cells): Cells contain a semi-permeable membrane that allows certain things in and out of the cell Diffusion (all cells): •Movement of substances from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, •Disposes of wastes and brings in nutrients Osmosis (all cells): Movement of water across a membrane from an area of more water to less water (high to low concentration) Membrane Osmosis (all cells): Movement of water across a membrane from an area of more water to less water (high to low concentration) Membrane Osmosis (all cells): Movement of water across a membrane from an area of more water to less water (high to low concentration) Membrane Osmosis (all cells): Movement of water across a membrane from an area of more water to less water (high to low concentration) Membrane Osmosis (all cells): Movement of water across a membrane from an area of more water to less water (high to low concentration) Membrane Osmosis (all cells): Movement of water across a membrane from an area of more water to less water (high to low concentration) Membrane Osmosis (all cells): Movement of water across a membrane from an area of more water to less water (high to low concentration) Membrane Osmosis (all cells): Movement of water across a membrane from an area of more water to less water (high to low concentration) Membrane Photosynthesis (happens in plant cells): •Converts light energy (radiant energy) to chemical energy (glucose) •Light energy is used to convert CO2 to glucose in plants •Happens in the chloroplast Respiration (happens in all cells): Converts glucose into cell energy (ATP) in the mitochondria ATP Process: Photosynthesis Organism: Plant Place Occurs: Chloroplast ATP CO2 and H2O Glucose and O2 Process: Respiration Organism: ALL Place occurs: Mitochondria The products of Photosynthesis are the reactants of Respiration Mitosis (happens in all cells): Cell reproduction for growth, repair, and maintenance of somatic cells. Somatic cells are body cells (ex: liver, skin, kidney, etc.) Meiosis: Cell reproduction for the production of gametes (sex cells) Storage: •Vacuoles store water, food, and minerals (all cells) •Central vacuole in plant cells •Becomes flaccid if cell loses water •Becomes turgid if cell gains water Transport (all cells): •Endoplasmic reticulum transports proteins to the Golgi bodies to be packaged and processed Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Body Lesson 2: Taxonomy Classification The largest and least specific category is a Kingdom There are 6 kingdoms: 2 prokaryotic and 4 eukaryotic Organisms are then placed into more specific groups in a particular order (KPCOFGS – see diagram) Organisms are called by their Genus and species name Ex: Homo sapiens Classification Animals most closely related will be in the same levels of classification Test tip: Most closely related organisms will have the same genus Group Domestic Cat Leopard Deer Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia Phylum Chordata Chordata Chordata Class Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Order Carnivora Carnivora Artiodactyla Family Felidae Felidae Cervidae Genus Felis Panthera Odocoileus Species Felis cattus Panthera pardus Odocoileus virginianus Which 2 are most closely related? How do you know? Kingdoms of Life Prokaryotic Kingdoms • Archaebacteria – Live in harsh conditions (without oxygen, extreme temperatures, in different chemical environments) • Eubacteria – Bacteria found on and around us – There are good and bad bacteria Eukaryotic Kingdoms: • Fungi – Decomposers/ heterotrophic – Mushrooms • Protista – – – – Heterotrophs & Autotrophs Mostly single-celled Live in water Amoebas, paramecium, euglenas – Has pseudopodia, cilia and/or flagella for movement • Plantae – Multicellular – Autotrophic – True roots, stems, and leaves • Animalia – Motile (can move) – Multicellular – Heterotrophic Lesson 3: DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid Structure D C G D P DNA is made of Nucleotides P P Phosphat e group P P T D D Nucleotide C G Deoxyribose D D Nitrogen Base P P D There are four kinds of nitrogen bases, so there are four kinds of nucleotides... T D P P D P C G D Adenine,Cytosine, Guanine, and Thymine P Cytosine pairs with Guanine D C D T G D DNA is shaped like a Double Helix (twisted ladder) P P D P Adenine pairs with Thymine NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE The order of the nucleotides forms the unique genetic code for the organism The more closely related two organisms are, the more alike the order of their nucleotides will be DNA replication – DNA makes an exact copy of its self – Happens before mitosis and meiosis Mutation – A change in the sequence of nucleotides – Can happen in any cell, but can be passed on to offspring only if it occurs in a gamete cell Lesson 4: Protein Synthesis DNA RNA Protein Transcription (DNA DNA codes for proteins The order of the nucleotides is the code for which a protein will be made TRANSCRIPTION is making o copy of DNA into mRNA (A = U; C=G) Occurs in the nucleus mRNA) Translation (mRNA Protein) The message on the mRNA is read by a ribosome The message is translated into a protein Occurs in the cytoplasm on ribosomes Video: http://vcell.ndsu.nodak.edu/animations/translation/movie.htm Genetic Code • Every three letters on mRNA is a codon • A codon codes for an amino acid • Ex: CCC codes for Proline