* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Principle in Plant Physiology
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
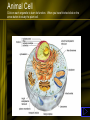
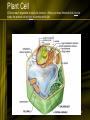
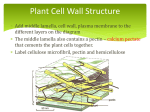
Lectures on Plant Physiology Prepared by Prof Mohammed Naguib Abdel-Ghany Haseneen Professor of Plant physiology For Pre-Dental Students 1 Contents • Plant Cell – Plant Cell structure and function • Different Bio-Physico-Chemical Phenomena – – – – Colloids Diffusion Osmosis Imbibitions • The Enzymes – – – – Structure Mode of action Inhibitors Factors affecting enzymatic activity 2 Cont. • Metabolism • Respiration – Glycolysis, TAC, Fermentation – Factors affecting rate of respiration • • • • Amino acid and protein metabolism Biotechnology -What is biotechnology? Biotechnology benefit 3 1- Plant Cell (Structure and Function) • Cells are the basic unit of life. • Cells carryout all the necessary functions for life such as: reproduction, taking in nutrients and excreting wastes. • Cells are made up of chemicals and molecules. Human cells contain mostly water. 4 The Cell • Cells are classified as prokaryotic and eukaryotic. • Prokaryotic cells lack a well-defined nucleus and many organelles. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells. • Eukaryotic cells include the protists, fungi, plant and animal cells. We will study these cells during this lab. 5 The Cell • Animal Cells • Have centrioles • Store glucose as glycogen • Do not have a cell wall • Contain mitochondria • Plant Cells • Lack centrioles • Store glucose as cellulose or starch • Have a cell wall • Have large vacuoles • Contain chloroplasts as well as mitochondria 6 The Cell • Animal Cell • Click on the cell to study it in more detail • Plant Cell • Click on the cell to study it in more detail 7 Animal Cell Click on each organelle to learn its function. When you have finished click on the arrow button to study the plant cell. 8 Plant Cell Click on each organelle to study its function. When you have finished click here to study the animal cell or here to continue this lab. 9 Cell is a unit or module of plant organization - Supports cells & plant - Controls cell growth & shape 10 Cell Wall • • • • Only found in plant cells Surrounds cell membrane Composed of lignin and cellulose Function to strengthen and protect plant cells. 11 Cell Wall • Structural functions – Provides rigidity to plant – Determines size and shape of cell – Determines size and shape of plant • Other functions – – – – Absorption Transport Secretion Cell-cell communication 12 Structure of cell wall • Cellulose is principal component – Repeated monomers of glucose attached end to end – Bundled into microfibrils – Crystalline properties • Cellulose matrix is embedded in matrix of noncellulosic molecules – Provide cross-links between cellulose microfibrils – Pectins = hydophilic polysaccharides – Glycoproteins- extensins 13 Structure of cell wall continued • Primary wall – Formed first while cells growing and dividing – Enriched in pectins and water (to allow expansion) • Middle lamella – Joins adjacent cells – Mostly pectins 14 Cell wall structure continued • Secondary wall – – – – – – – Not all cells form Deposited after cell has stopped growing Inside primary wall More cellulose Pectins lacking Rigid Formed by cells that provide strength or transport 15 Cell walls (yellow) separated by middle lamella (black) 16 17 Middle lamella (black) separates walls from 2 different cells Cell membrane contacts inner part of wall 18 Cellulose is polymer of glucose that aggregates into threads (microfibrils) 19 Cellulose threads are woven in cell wall 20