* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download System_Structure
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
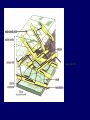
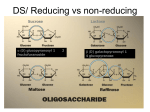
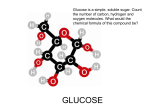
System Structure Somerville et al. 2004 Figure 1 shows an electron microscope picture of the outer cell walls of pea (Pisum sativum). Cell walls are composed of compounds called polysaccharides which create a network of stable fibers within the wall. What is a Polysaccharide? www.lsbu.ac.uk www.sciences.fundp.ac.be A polysaccharide is a chain, created by simple sugars called monosaccharides. Common monosaccharides are glucose and fructose, found in most sweets. They join together by glycosidic bonds, created by dehydration reactions between the -OH group of one monosaccharide to the –H of another. These form the three most important aspects to the cell wall. Cellulose www.chemsoc.org Cellulose is a polymer of the monosaccharide glucose. It forms 180 degree bond angles of the glycosidic bonds, making it a very sturdy, aiding in the structure of the leaf itself. Chains of cellulose form together to create a microfibril, a collection of chains of cellulose combined to form an even more sturdy structure. Collections of these microfibrils form macrofibrils which then form the cellulose fibers. www.abcbodybuilding.com Hemicellulose www.rpi.edu Hemicelluloses are polysaccharides made from these monomers, which hydrogen bond to the surface of the cellulose fibrils. www.scielo.br Pectins Pectins are the acidic polysaccharides found in the parts of fruits and vegetables such as peels and apple pommace. (www.lsbu.ac.uk/water/hypec.html) It is marketed for making jam and jelly, as well as different types of jelly beans! Pectins are hydrophobic polysaccharides that attract water to the cell. This makes the cell more pliable, which is necessary for wall expansion. Pectins primarily form the middle lamella in the cell wall, which join adjacent cells. (Raven, Everett, and Eichhorn 2005) www.ccrc.uga.edu Homogalacturonan (HG) is the most simple of pectins, as discussed in the Somerville paper. But How Do They All Fit In The Cell Wall? A diagram of a plant cell wall, as shown in the Somerville et. al. article. Somerville et. al. According to Somerville et.al, the main force for the structure of the cell wall is from the hydrogen bonding of the hemicellulose to the cellulose microfibrils. www.ippa.info