* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Glycogen Synthesis Glycogen
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
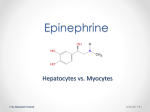
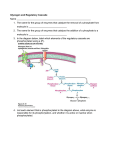
11/11/2015 Glycogen Synthesis Chapter 25, Stryer Short Course Glucose Metabolism Overview Energy Production ATP Pentose Phosphate Pathway Ribose, NADPH Pyruvate • Gluconeogenesis • Glycogen metabolism • Pentose Phosphate Pathway Glycogen Synthesis DHAP Glycogen OH O HO HO OH OH (P) Glycerol (Triacylglycerides) DHAP Glycogen Lactate Glycogen Degradation Pyruvate Amino Acids Gluconeogenesis Glycogen • Storage molecule • Multiple ends allow for quick synthesis and degradation • Glucose must be activated 1 11/11/2015 Chemistry of Synthesis • Step 1 • Near equilibrium • The link to glucose‐6‐phophate, our central molecule Chemistry of Synthesis • Step 2 • Count high energy bonds • Pyrophosphatase – Common motif • UDP‐glucose: activated for incorporation Chemistry of Synthesis • Step 3 • Glycogen synthase • Growing end is non‐reducing • Must be added to core • UDP released 2 11/11/2015 Energetics of Synthesis • Total cost: one ATP equivalent from G‐6‐p Step 4: Branching Overall Energetics OH O HO Glucose-6-P HO OH 2 Pi O P-P-Uridine UDP UTP OH OH O HO OH O HO HO OH O HO P O HO O OH O O O Pi OH O Glucose glycogen costs 2 ATP per stored glucose 3 11/11/2015 Key Regulation Enzymes OH O Glycogen Synthase HO Glucose-6-P HO OH 2 Pi O P-P-Uridine UDP UTP OH OH O HO OH O HO HO OH O HO P O HO O OH O O O Pi Glycogen Phosphorylase OH O Compare/Contrast • a = “usually active” – Favors R‐state • But in the synthase, a is dephosphorylated Liver: Phosphorylated State • Liver phosphorylase a “usually active” • Turned off by [glucose] • Liver glycogen synthase b “usually inactive” • Turned on by [glucose‐ 6‐P] 4 11/11/2015 Reciprocal Regulation • Epinephrine turns on phosphorylase – PKA phosphorylation • Epinephrine turns off glycogen synthase – PKA phosphorylation Protein Phosphatase 1 • Opposite of PKA – Deactivates phosphorylase – Activates glycogen synthase • Active in cell unless epinephrine signals PKA – PKA activates its inhibitors Insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis • Insulin blocks the “turn off” switch for glycogen synthase • Allows PP1 to “turn on” glycogen synthase 5 11/11/2015 Glucose stimulates glycogen synthesis • Insulin is main stimulating signal • Blood glucose level also controls glycogen – First, phosphorylase turned off – Then synthase turned on – No wasted overlap – Mechanism? Phosphorylase a is Glucose Sensor • Phosphorylase a (R state) binds and inactivates PP1 • When [glucose] up, PP1 is released and deactivates phosphorylase • Only when all phosphorylase a has been inactivated is PP1 available to activate glycogen synthase Glycogen Storage Diseases Many disrupt glycogen breakdown in muscle and/or liver (hypoglycemia, enlarged liver, muscle cramps...) 6